Wood Turtle
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/05/Wood-turtle-header-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/05/Wood-turtle-header-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/05/Wood-turtle-header.jpg”);
}
}
Wood Turtle
Temperature determines the sex of turtle eggs
Wood Turtle Facts
- Prey
- Insects, earthworms, small arthropods such as millipedes
- Name Of Young
- Hatchling
- Group Behavior
-
- Solitary/Group
- Fun Fact
- Temperature determines the sex of turtle eggs
- Estimated Population Size
- Several thousand depending on species
- Biggest Threat
- Habitat loss, pet trade, animal predators, humans
- Most Distinctive Feature
- The scutes, which have beautiful growth rings
- Other Name(s)
- Nihonishigameor, ornate wood turtle, Honduran wood turtle, black river turtle, spot-legged turtle, brown land turtle, Splengleri turtle
- Gestation Period
- 8 months
- Litter Size
- 1 to 20
- Habitat
- Deciduous forests, rain forests, marshes, bogs, rivers, streams
- Predators
- Alligators
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Type
- Reptile
- Common Name
- Wood turtle
- Number Of Species
- 9
- Location
- North America, Central America, South America, China, Vietnam, Japan
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/05/Wood-turtle-on-moss-1024×535.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the Wood Turtle images!
“The Wood Turtle is a slow but intelligent reptile.”
A description of a wood turtle is of an attractive, smallish turtle that rarely grows over 10 inches long. There are several species of wood turtle. There is the North American wood turtle found in the eastern part of the continent; the Central American wood turtle, or ornate wood turtle; the Japanese wood turtle and the furrowed wood turtle, which is found from Mexico south to Guatemala and Honduras. There’s also the Central American black wood turtle; South America’s Maracaibo wood turtle; the brown wood turtle; the large-nosed wood turtle and the Colman wood turtle. A few of these make good pets while others, especially those found in the tropical rainforests of Central and South America, should not be kept as pets. Some of these turtles are endangered.
Wood Turtle facts
Some facts about these turtles include:
- A well-cared-for turtle can live as long as 58 years. A person who wants one for a pet should take this into account!
- These turtles have attractive scutes that show growth rings much like the cross-section of a tree.
- They are omnivorous and eat both plant and animal matter.
- They’re sometimes seen deliberately stomping on the ground as they walk. Some scientists believe the noise mimics the sound of rain falling on the ground. This brings earthworms up to the surface where the turtle can easily snap them up and eat them.
Wood Turtle Scientific name
The North American wood turtle’s scientific name is Glyptemys insculpta. Glyptemys means “carved turtle,” and insculpta builds on this, as it means “sculptured” in Latin. This refers to the annular rings on the scutes. It is one of two species in its genus, the other being the bog turtle.
Rhinoclemmys is a genus of several of these turtles. It comes from the Greek for “nose” and “turtle,” and describes the prominent noses on some of these turtles.
With R. pulcherrimus, the painted wood turtle, pulcherrimus means ‘prettiest” in Latin. There are four subspecies of the painted wood turtle:
- R. pulcherrima incisa
- R. pulcherrima pulcherrima
- R. pulcherrima manni
- R. pulcherrima rogerbarbouri
R. areolata also refers to the growth rings on the shell of the furrowed turtle.
R. funerea describes the black shell and skin of the black turtle.
R. annulata also references the annular rings on the scutes of the brown turtle.
The Japanese species scientific name is Mauremys japonica. “Mauremys” refers to Mauritania, from where this genus of turtle allegedly originates, and “emys” is Greek for a freshwater turtle. Japonica means the turtle is from Japan.
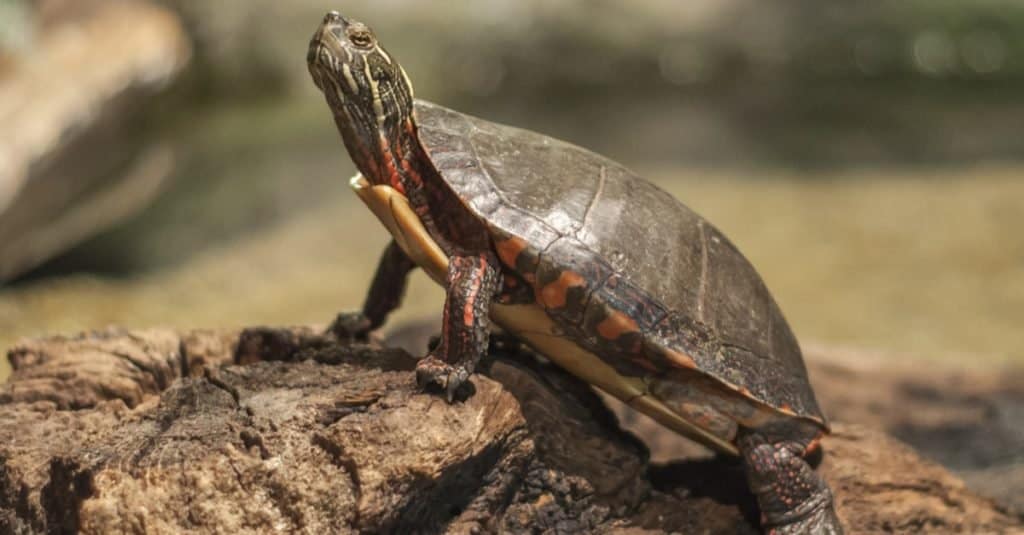
Wood Turtle Appearance
Depending on the species, these turtles can grow from 7 to 9.8 inches long, though the Vietnamese wood turtle or Splengleri turtle is only about 4.5 inches long. They have distinctive scutes, and in the case of the North American turtle, the description of the annular rings compares them to elegant wood carvings in older specimens.
The North American turtle has a black head which may have lighter markings, with yellow, orange, or salmon pink on the throat and the lower legs, depending on where the turtle is found. The heads of adult males are wider than those of the female, and the carapace has more of a dome shape. The plastron, which is the underside of the shell, is depressed in the center, and their tails are longer and thicker than those of the females.
The Central American or painted turtle has a beautiful, multicolored carapace. The colors are believed to mimic those of the coral snake, which is venomous. Females are larger than males.
The furrowed turtle has a boxy carapace with red markings on its face while the Maracaibo turtle has a somewhat pyramidal shell that is the brown and amber color of traditional tortoiseshell. The spot-legged wood turtle is known for its freckled legs.
The Vietnamese turtle or Vietnamese black-breasted leaf turtle is tiny, with a brightly colored head and protuberant eyes. The back of the carapace is serrated. This characteristic, along with its reddish-gold color, gives it the look of a fallen leaf. Males have longer shells and longer tails and can weigh as little as 0.88 of an ounce.
The Japanese turtle or pond turtle is called nihonishigameor in Japanese. That means “the stone turtle”. It is critically endangered, which is ironically making it popular as a pet as breeders are trying to raise its numbers. It is a brown turtle with hints of gold in the shell and does indeed look like a stone when it stands still. There may be black spots or blotches on its head, and its plastron is black. The top of its shell is rounded and bears a black keel. The scutes may have small ridges.

Lmnopg007/Shutterstock.com
Wood Turtle Behavior
These turtles are active during the day and since they’re cold-blooded, they spend much time basking on logs or other surfaces near water. Sometimes they will bask in a hidden area on land. The North American wood turtle, which is found in Canada, has evolved behaviors such as angling its shell toward the sun in a certain way to keep its body warm during cooler months.
These turtles in cooler climates hibernate in the winter. They dig into the bottoms of shallow streams and rivers and may stay there for as long as six months. Turtles may also estivate when the weather becomes too hot.
These animals are generally careful not to roam too far from a source of water, though they can travel a long way in search of food. Even turtles who are moved a long way from their home territory return to it, even if it takes weeks or months. However, the turtles do not seem to be very territorial, even though they can be aggressive to other wood turtles. This is true of both male and female wood turtles. When sold as pets, wood turtles seem to be curious, friendly, and intelligent.
Wood Turtle Habitat
The North American turtle’s habitat is wide-ranging, though it prefers to live near slow streams with sandy or muddy bottoms that are edged by shrubbery. The soft bottoms of these streams are easy for the turtle to dig into when they hibernate, and the shrubbery helps to hide nests. The turtle spends the warmer months in wet meadows, bogs, and fields, then spends the rest of the year in the water.
The Japanese turtle also lives in and near streams, marshes, and ponds on Japan’s Kyushu, Shikoku and Honshu islands. It’s found in the montane forests of northern Vietnam and southeastern China.
Wood Turtle Diet
Since these turtles are omnivores, they eat eggs, insects, snails and slugs, worms, crustaceans, and small, newborn animals. Indeed, they seem amenable to eating any food source that they can catch. Because turtles are slow, many don’t have fish or any other animal that can get away quickly in their diet, though the painted wood turtle has been seen to catch and eat fish. They will consume carrion. They also eat fruit, leaves, flowers, tubers, roots, and fungi. The North American turtle can eat on land and water while the painted wood turtle usually eats on land.
Wood Turtle Predators and Threats
Humans are the biggest threat to these turtles. Humans break up their natural habitat, which makes it difficult for turtles to find mates and nest. Many turtles are run over and killed as they try to cross roads to get to old nesting areas. Other turtles are collected as pets from the wild, which should be discouraged. There are cultures where wood turtles are food. Even if none of this was true, the mortality for turtle eggs and hatchlings has always been high. Just about every carnivore in the forest, whether they be foxes, raccoons, skunks, snakes, snapping turtles, alligators or even domestic cats is fond of eating them.
Wood Turtle Reproduction and Life Cycle
One of the facts that make the existence of these turtles precarious is the age at which they reach sexual maturity. A North American wood turtle isn’t ready to breed until it’s at least 14 years old. When this finally happens, older male turtles dominate younger ones and may push one off of a female even during copulation. Still, the female may mate with more than one male.
Before this can happen, males and female turtles engage in a courtship ritual where they swing their heads or touch noses. Sometimes the male simply chases the female until he catches her. Some turtles mate in shallow water or on land. A description of wood turtle mating emphasizes its singular passion. It most often occurs in spring or fall.
The female will start nesting in late spring to summer. She’ll find a place with soil that’s soft enough for her to dig into. The area is often elevated to protect the eggs from flooding. She may start several nests but discard them as inadequate before she finds a perfect spot. The number of eggs laid depends on the species. The Vietnamese wood turtle lays as few as one egg per clutch, while the North American wood turtle can lay as many as 20.
When the eggs are laid, the female covers them up with care then leaves, never to see them again. Temperature determines the sex of a baby turtle. A female baby is the result of higher temperatures, while a male baby is the result of lower temperatures.
Depending on the species, eggs can hatch in as little as 47 days in the North American turtle or at least 70 days in the Vietnamese turtle.
Wood Turtle Population
The wood turtle population depends on the species of turtle. For example, in 2019 biologists determined there are about 5000 North American turtles left in Massachusetts. Fortunately, the efforts to care for this turtle and other wood turtles are ongoing.
View all 74 animals that start with W
Wood Turtle FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is a wood turtle?
A wood turtle is a kind of turtle found in forests. Despite their name, most are never very far from a body of water.
What do wood turtles eat?
Wood turtles are omnivorous and eat ruts vegetables, fungi, including poison mushrooms, worms and insects.
Are wood turtles good pets?
A few wood turtles do make good pets in that they’re easy to take care of. The painted wood turtle; the North American wood turtle; the Japanese wood turtle and the ornate wood turtle make good pets. However, some of them are expensive. The price of a painted wood turtle can run from $100 to $200. The price of a North American wood turtle can run between $300 and $400, while the price of a Japanese wood turtle can be around $200.
Why is the wood turtle endangered?
Wood turtles are endangered due to habitat destruction or fragmentation, climate change and collection by humans for the pet trade. Turtles are run over as they try to cross roads or shot for fun by miscreants. Also, turtle populations have always been vulnerable because it takes turtles a long time to reach reproductive age, and even the turtle’s natural predators can wipe out an entire season of eggs and hatchlings.
Are wood turtles rare?
The rarity of the wood turtle depends on the species. The Japanese wood turtle is rare even though it is sold as a pet.
Where does a wood turtle live?
Wood turtles live in the eastern and central parts of the United States and the southeastern provinces of Canada. They’re also found in Central America, Mexico, Venezuela, Colombia, Trinidad and Tobago, French Guiana, Brazil, Suriname and Guyana.
Sources
- WBUR, Available here: https://www.wbur.org/earthwhile/2019/08/12/rare-wood-turtles-conservation
- Reptiles Magazine, Available here: https://www.reptilesmagazine.com/wood-turtle-care-sheet/
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wood_turtle
- Animal Diversity Web, Available here: https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Glyptemys_insculpta/
- Fresh Marine, Available here: https://www.freshmarine.com/japanese-wood-turtles.html
- All Turtles, Available here: https://www.allturtles.com/wood-turtle/
- The Reptile Database, Available here: https://reptile-database.reptarium.cz/species?genus=Glyptemys&species=insculpta
- Backyard Nature, Available here: https://www.backyardnature.net/mexnat/woodturt.htm
- Turtle Source, Available here: http://www.theturtlesource.com/i.asp?id=100200358&p=Japanese-Wood-Turtles