Western Gorilla
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2019/11/shutterstock_1519533602-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2019/11/shutterstock_1519533602-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2019/11/shutterstock_1519533602.jpg”);
}
}
Western Gorilla
Gorilla Gorilla
There are two sub-species!
Western Gorilla Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Primates
- Family
- Hominidae
- Genus
- Gorilla
- Scientific Name
- Gorilla Gorilla
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Western Gorilla Conservation Status
Western Gorilla Facts
- Main Prey
- Leaves, Fruit, Flowers
- Habitat
- Rainforest and dense jungle
- Predators
- Human, Leopard, Crocodile
- Diet
- Herbivore
- Average Litter Size
- 1
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/western_gorilla3.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the Western Gorilla images!
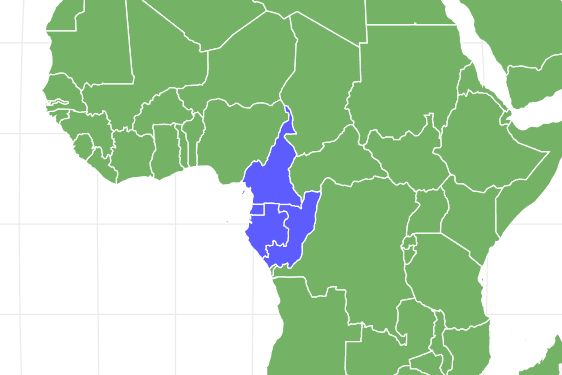
The western gorilla is one of two gorilla sub-groups found on the African continent (the other being the eastern gorilla). The western gorilla is the most numerous species gorilla and also the larger out of the two.
The western gorilla is found inhabiting the tropical jungles and forests of western and central Africa, along with lowland swamps and secondary forests. All western gorillas are now considered to be critically endangered as much of their natural habitat has now been deforested or taken over by humans.
There are two separate sub-species of western gorilla which are the western lowland gorilla and the cross river gorilla. Although only slightly different in appearance, the two western gorilla species are distinguished by there differing skull and tooth sizes.
The western gorilla is one of the great apes, a group that includes orang-utans, gorillas, humans and chimpanzees. As with the other great apes, the western gorilla has a number of features which makes living in the jungle a bit easier, including having opposable thumbs which come in handy when the western gorilla is peeling fruit.
The western gorilla is an omnivorous animal, but the majority of its diet is made up of eating fruit which the western gorilla is known to travel vast distances through the forests to find. The western gorilla also eats leaves, nuts and berries, along with insects and occasionally small animals such as lizards and rodents. The western gorilla has also been observed using basic tools in the wild in order to more effectively gather food.
Due to it’s large size, the western gorilla has few real predators in its native African forests, with large cats such as leopards and the odd crocodile being the only real natural threat to the western gorilla. The biggest threat to the western gorilla is habitat loss caused by deforestation and also being hunted by humans. Parts of the western gorilla’s territory has also been taken over by civil unrest in recent years, which, along with poaching, has had a truly devastating effect on wild populations.
The western gorilla tends to live in groups which are led and protected by the alpha male. The alpha male western gorilla also mates with the females in his group, producing generally single offspring, known as babies. The western gorilla babies remain with their mother until they are a few years old and become independent.
Today, all western gorillas are critically endangered species but there are thought to be 95,000 western lowland gorillas remaining in the wild, significantly more than their cross river gorilla cousins, whose numbers in the wild are thought to be as low as 300 individuals.
View all 74 animals that start with W
Western Gorilla FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Western Gorillas herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Western Gorillas are Herbivores, meaning they eat plants.
What Kingdom do Western Gorillas belong to?
Western Gorillas belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
How fast is a Western Gorilla?
A Western Gorilla can travel at speeds of up to 25 miles per hour.
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World’s Wildlife
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David W. Macdonald, Oxford University Press (2010) The Encyclopedia Of Mammals