Tortoise
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2019/11/Tortoise-header-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2019/11/Tortoise-header-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2019/11/Tortoise-header.jpg”);
}
}
Tortoise
Can live until they are more than 150 years old!
Tortoise Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Tortoise Conservation Status
Tortoise Facts
- Main Prey
- Grass, Weeds, Leafy greens
- Fun Fact
- Can live until they are more than 150 years old!
- Habitat
- Sandy soil close to water
- Diet
- Herbivore
- Average Litter Size
- 5
- Lifestyle
-
- Solitary
- Favorite Food
- Grass
- Type
- Reptile
- Slogan
- Can live until they are more than 150 years old!
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2019/11/Tortoise-Aldabra-1024×535.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the Tortoise images!
The tortoise, any member of the family Testudinidae, is a reptilian vertebrate that lives exclusively on land.
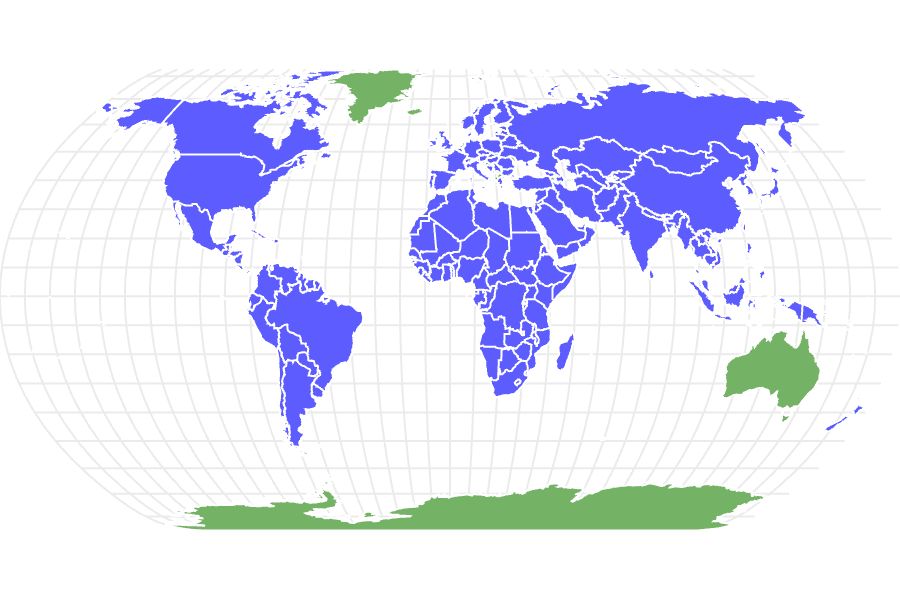
Also known as land turtles, tortoises are found on all continents except for Antarctica and Australia. With nearly 50 species spread across more than 15 genera, tortoises vary widely in terms of size, color, and other features. Many exist only in the wild, but some are kept as pets. Several species are considered endangered to some degree, but conservation efforts have helped increase populations in some cases. With an average lifespan of 80 to 150 years, tortoises are the longest living land animals on the planet.
5 Incredible Tortoise Facts!
- Survivors: Tortoises can survive for extended periods of time without consuming any water or food. On whaling ships, they were often kept on their backs and used as a source of fresh meat on long voyages.
- Persistent: Like all turtles, tortoises move very slowly. On arid islands, tortoises lick dew off of boulders, leaving half-sphere depressions in the rock.
- Long Living: Adwaita, an Aldabra giant tortoise, purportedly lived to the age of 255 years. There are several other examples of tortoises living well past the age of 150 years.
- Widespread: Tortoises are widely distributed and can be found from southern North America to southern South America; across Eurasia to southeast Asia; across the Mediterranean basin; through sub-Saharan Africa; on Madagascar and on some Pacific Islands.
- Ancient: Turtles and tortoises are believed to have first appeared around 220 million years ago.
Want more tortoise facts? Make sure to read ‘10 Incredible Tortoise Facts.‘
Tortoise Scientific Name
In some parts of the world, the term “tortoise” is used interchangeably with the term “turtle.” However, the consensus generally is that tortoise refers to a turtle that lives exclusively on land. These animals are reptiles; therefore, they belong to the class Reptilia. They are furthered classified into the order Testudines and the family Testudinidae. From there, there are approximately 49 species spanning more than 15 genera. The term Testudines is derived from the Latin word for tortoise. The pronunciation of tortoise is confusing. The proper pronunciation is “tore” followed by “tuss.”
Tortoise species vary considerably in terms of size, color, and other features. The smallest, padlopers – members of the genus Homopus – grow up to 4 to 6 inches in length and are found in southern Africa. The largest, the giant tortoise – members of the genus Geochelone — can have shells measuring more than 3.3 feet long.
Top Tortoise Species
- Galapagos Tortoise – Members of the genus Chelonoidis, Galapagos tortoises are found in the Galapagos Islands off the coast of Venezuela and on Aldabra, an island in the Indian Ocean approximately 430 miles east of Tanzania. During the 16th century, their population size was estimated at more than 250,000; by the 1970s, it had dwindled to just around 3,000 individuals. Since they have no natural predators, it is believed that human activity is almost exclusively to blame. Through conservation efforts, thousands of captive-bred juvenile tortoises have been released back into the wild. By the year 2000, their population had grown to around 19,000 individuals.
- Indian Star Tortoise – Known by the scientific name Geochelone elegans, the Indian star tortoise is found in India, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. This species grows to an average size of about 10 inches long, and it features a very convex shell. The Indian star tortoise is listed as endangered by the IUCN, and its primary threat is the exotic pet trade.
- Leopard Tortoise – This tortoise, known by the scientific name Stigmochelys pardalis, is found across the savannas of east and south Africa – roughly from the southern Cape to Sudan. The only member of its genus, the leopard turtle thrives in grassland habitats, including in arid and savanna regions. The fourth-largest tortoise species, this animal grows to an average length of 16 inches and an average weight of 29 pounds and is mostly yellow in color. Unlike many other large tortoises, the leopard tortoise is not endangered.
Other common tortoise species include the gopher tortoise, the African spurred tortoise, the Madagascar tortoise, the spider tortoise, and the desert tortoise.
Tortoise Appearance
Tortoises are cold-blooded, or ectothermic, animals with high-domed shells, or carapaces. The only species with a flat shell is the pancake tortoise, Malachochersus tornieri. Like most turtles, they can retract their heads and necks into their shells for protection. They hold the distinction of being the only vertebrates whose pectoral and pelvic girdles are located within their ribcages, and they are the only vertebrates with shells.
Their shells consist of 59 to 61 bones that are covered by plates called scutes. The pronunciation of “scute” is the same as “scoot.” Scutes also form segments, creating distinct patterns on tortoises’ shells. The shell’s underside is called the plastron, and the two halves are connected by a bridge. Tortoiseshells are made up mostly of keratin, and tortoises can sense pain through their shells just as people can sense pain through their fingernails.
The tortoise has a toothless jaw. Although this animal lacks teeth, it possesses a horny beak that it can use to break up food and other matter. All tortoises share specialized hind-limb anatomy consisting of elephantine, or cylindrical, hind limbs, and hind feet. Each digit of the animal’s forefeet and hind feet features two or fewer phalanges.
Many species of tortoise have sexual dimorphism, meaning that females and males have distinct features. The easiest way to determine the gender of a tortoise is by examining its tail. Females’ tails tend to be smaller, and they drop straight down. Males typically have much longer tails, which they usually keep pulled up and to the side at the back of the shell.

Tortoise versus Turtle
All shelled vertebrates, including tortoises and terrapins, are considered to be turtles. This includes all 200 or so species of the Testudines group, which feature a compressed anatomical structure with the shell fused to the ribs and vertebrae and the pelvic girdle within the rib cage. Turtles can be aquatic, semi-aquatic, or mostly terrestrial, but tortoises are exclusively terrestrial. Tortoise feet look like tiny elephant feet while other turtles have webbed feet. Finally, most tortoises have very convex or rounded, carapaces while turtles’ shells are usually more streamlined. Exceptions include the box turtle and the Sonoran mud turtle, which have more rounded shells.
Tortoise Behavior
Tortoises are primarily diurnal animals, meaning that they are awake by day and sleep by night. However, many species tend to be crepuscular, meaning that they are most active during the twilight hours. All tortoises are reclusive creatures with placid behavior. They are known for moving very slowly; the average speed of a tortoise is estimated at about 0.2 to 0.5 kilometers per hour. Since they lack ears, tortoises rely less on hearing and more on vision and smell.
As cold-blooded animals, tortoises typically bask for one to two hours after dawn to absorb heat for the day. They then spend several hours foraging for food. They tend to travel early in the morning and late in the afternoon, and they take dust baths to keep pests at bay. Tortoises rarely make any sound except during copulation or in aggressive situations.
Tortoise Habitat
The tortoise is found on all continents except for Australia and Antarctica. Species are distributed across southern North America through southern South America and are also found on some Pacific Islands, across Eurasia to southeast Asia, in sub-Saharan Africa, across the Mediterranean basin and on Madagascar. They generally prefer semi-arid climates but are found everywhere from deserts to tropical rainforests, and they can thrive at sea level or in more mountainous terrain.
Tortoise Diet
Most tortoise species are herbivores, subsisting primarily off of foliage, flowers, and some fruits. Some species located in moist forest environments are more opportunistic and will consume limited amounts of animal matter as needed.
For more on the diet of tortoises, make sure to read our complete guide ‘What Do Tortoises Eat? 20+ That They Eat.”
Tortoise Predators and Threats
Human activity poses the greatest threat to tortoises around the world. In particular, tortoises are hunted for their oil and meat. Their habitats are often cleared for agriculture and other developments. In many parts of the world where they live, the introduction of non-native animals, including rats, pigs, and goats, negatively impacts their populations. Tortoises have no natural predators, so the introduction of non-native species can be very detrimental.
Tortoise Reproduction, Babies and Lifespan
Most tortoise species mate throughout the year. To initiate the mating process, the male tortoise rams the female tortoise’s shell with his shell and may nip at her legs. Copulation is tricky because of the convex shells at play, but the male balances himself precariously to make it happen.
Female tortoises use their hind limbs to dig nests. They lay their eggs at night and cover the clutch with soil, sand, and organic material. Incubation averages 100 to 160 days and the eggs are left unattended. Fully formed hatchlings use egg teeth to break out of the ping-pong-ball-sized eggs and then dig their way to the surface. They are hatched with an embryonic egg sac that provides nutrition for the first three to seven days. Baby tortoises make their way to their mother’s burrow, where she protects them for about 80 days before they are on their own.
Tortoises are the longest living land animals on earth. Their lifespan averages between 80 and 150 years. Several examples of long-living tortoises are found in the historical record. One of the best known, Tui Malila, was gifted to the Tongan people by explorer James Cook in 1777 and died in 1965 at 188 years of age.
Tortoise Population
Tortoise populations vary by species and region. Several species are listed as Critically Endangered by the IUCN, including the radiated tortoise, the Madagascar tortoise, and the spider tortoise. Some, including the geometric tortoise, are classified as Endangered. Several more are classified as Vulnerable, including the Galapagos giant tortoise, the Aldabra giant tortoise, and the desert tortoise.
Tortoises in the Zoo
Major zoos around the world have examples of many tortoise species. The San Diego Zoo, for example, received its first Galapagos tortoises in 1928 and now has a total of 16, including nine original members. Many zoos have Aldabra giant tortoises, including Zoo Atlanta. You can find examples of the African spurred tortoise at Zoo New England, and the Australia Zoo once housed Harriet, a giant tortoise that was brought to England by Darwin and lived to the age of 176 years.
View all 74 animals that start with T
Tortoise FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Tortoises herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Tortoises are mostly herbivores, but some species may consume small amounts of animal matter.
What Kingdom do Tortoises belong to?
Tortoises belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do Tortoises belong to?
Tortoises belong to the class Reptilia.
What phylum to Tortoises belong to?
Tortoises belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do Tortoises belong to?
Tortoises belong to the family Testudinidae.
What order do Tortoises belong to?
Tortoises belong to the order Testudines.
What type of covering do Tortoises have?
Tortoises are covered in scales.
In what type of habitat do Tortoises live?
Tortoises live in sandy soil close to water.
What is the main prey for Tortoises?
Tortoises eat grass, weeds, and leafy greens.
What are some predators of Tortoises?
Predators of Tortoises include foxes, badgers, and coyotes.
How many babies do Tortoises have?
The average number of babies a Tortoise has is 5.
What is an interesting fact about Tortoises?
Tortoises can live until they are more than 150 years old!
How long does a tortoise live?
On average, tortoises can live for 80 to 150 years.
What is the difference between a turtle and a tortoise?
All tortoises are turtles, but all turtles are not tortoises. Tortoises live only on land, and their limbs look like tiny elephant legs or clubs while other turtles have webbing at the extremities. Their carapaces, or upper shells, are usually very convex, or rounded, while other turtles have more streamlined shells.
Where does a tortoise live?
Tortoises primarily live in semi-arid regions, but they are found everywhere from the desert to the tropical rainforest. They are found on all continents except for Antarctica and Australia.
How big does a tortoise get?
The largest species of tortoise, the giant tortoise, boast shells that grow as long as 3.3 feet. The Galapagos giant tortoise can attain a weight of up to 920 pounds. Many other tortoise species are much smaller. The smallest, the padloper tortoise, has an average shell length of just 4 to 6 inches.
Do tortoises recognize their owners?
Tortoises are keenly intelligent animals and are often kept as pets. Over time, they can become familiar with their owners’ behaviors, sounds, and scents. They are capable of learning that the person who owns them is a source of food and safety, so they can become more trusting of particular people over time.
How fast is a Tortoise?
A Tortoise can travel at speeds of up to 0.3 miles per hour.
How do Tortoises have babies?
Tortoises lay eggs.
What are the differences between sea turtles and tortoises?
The main differences between sea turtles and tortoises are that sea turtles are aquatic, have streamlined shells, and have physical adaptions for life in the water. Tortoises are terrestrial, have domed shells, and are suited to life on land.
Read about other differences here!
What are the differences between a snapping turtle and a tortoise?
The main differences between a snapping turtle and a tortoise are that snapping turtles are aquatic, omnivorous, and only live in the Americas. Tortoises are terrestrial, herbivorous, and live across the world.
Sources
- San Diego Zoo, Available here: https://animals.sandiegozoo.org/animals/turtle-and-tortoise
- New World Encyclopedia, Available here: https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Tortoise
- National Geographic, Available here: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/news/2017/12/shell-game–how-to-tell-a-turtle-from-a-tortoise/
- Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/tortoise
- Rainforests, Available here: https://rainforests.mongabay.com/endangered/charts/reptiles-turtles.html