Spider Monkey
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/spider_monkey-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/spider_monkey-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/spider_monkey.jpg”);
}
}
Found in the tropical jungles of South America!
Spider Monkey Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Primates
- Family
- Atelidae
- Genus
- Ateles
- Scientific Name
- Simia Paniscus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Spider Monkey Conservation Status
Spider Monkey Facts
- Main Prey
- Fruit, Nuts, Leaves
- Habitat
- Tropical jungle and rainforest
- Predators
- Human, Eagles, Jaguar
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Average Litter Size
- 1
- Lifestyle
-
- Troop
- Favorite Food
- Fruit
- Type
- Mammal
- Slogan
- Found in the tropical jungles of South America!
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/spider-monkey-mom-baby-2.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the Spider Monkey images!
“The spider monkey is among the most proficient climbers in the world.“
With its long limbs and tail, this species leaps and bounds from one branch to another in a graceful display of aerial control. It is intelligent, caring, and agile, but also loud and aggressive. Because of hunting and habitat loss, the entire genus is threatened by the specter of extinction. Considerable effort has gone to preserving the last of the spider monkey populations.
3 Spider Monkey Facts
- Although they normally walk on all four legs, spider monkeys have adapted heavily for an arboreal lifestyle. Their movement between trees is a true spectacle. They do not climb carefully up and down trees. Instead, they leap or drop from one tree to another.
- Their prehensile tails have small, hairless tips and grooves that are kind of like fingerprints.
- The spider monkey can breed very well in captivity. Many zoos and conservation organizations have their own breeding programs to keep this animal alive.
Spider Monkey Scientific Name
This primate belongs to a genus of animals that goes by the scientific name Ateles. This word roughly translates to “incomplete” in Greek, referring to the monkey’s reduced or incomplete thumbs. This genus contains seven living species, most of which are named for their color or country of origin. These include the red-faced spider monkey, the white-fronted spider monkey, the Peruvian spider monkey, the brown spider monkey, the white-cheeked spider monkey, the brown-headed spider monkey, and Geoffroy’s spider monkey. The spider monkey genus belongs to the family Atelidae, which also includes howler monkeys and woolly monkeys. This is the only family of primates in the world with full prehensile tails.
Woolly, howler, and spider monkeys are just a few animals that make up the group known as the New World monkeys. As the name implies, these monkeys evolved and flourished in the New World of the Americas. Compared to the Old World monkeys of Asia and Africa, they tend to have a smaller size, flatter nose, and different skeletal structure. The New World and Old World monkey last shared a common ancestor some 40 million years ago, when their evolutionary lineages split apart, going their separate ways.
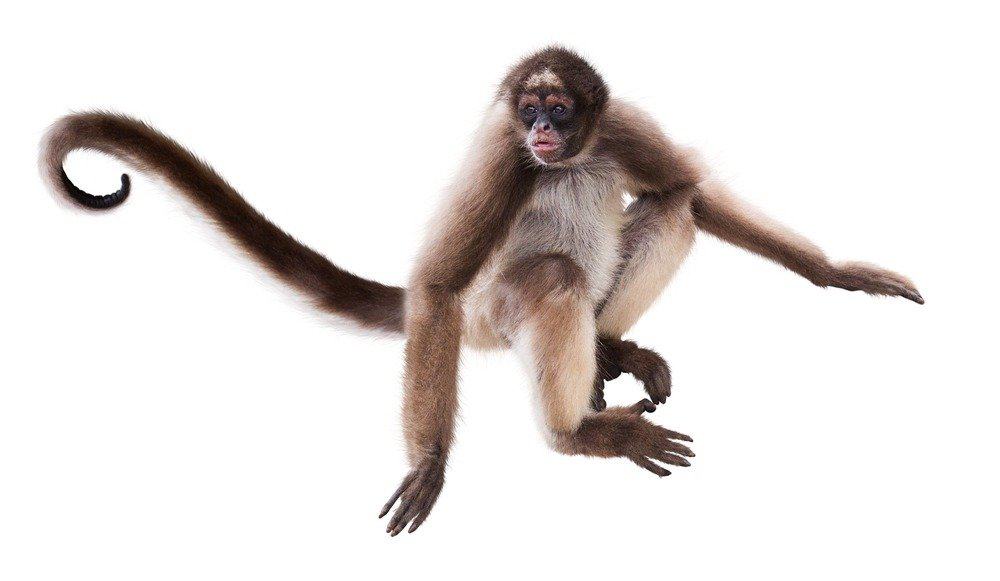
Spider Monkey Appearance
These animals are among the largest of the otherwise small New World monkeys with a weight anywhere between 13 and 24 pounds. This is about the weight of a small domesticated dog but with a much longer tail. Males tend to be slightly larger the females overall.
Other important features of the spider monkey include the incredibly long arms, the flat nose, eye rings, and the rough hair, which is usually a combination of black, white, brown, or tan.
Spider Monkey Prehensile Tail
One of the most prominent and important characteristics of this primate is the massive prehensile tail. Despite (or even because of) the nearly non-existent thumbs, the tail provides the main means through which it can cling to branches and grab objects. The tail itself is much larger than the body, reaching between 20 and 40 inches. By comparison, the body stretches about 14 to 26 inches from head to rump.

BearFotos/Shutterstock.com
Spider Monkey Behavior
These creatures are highly social animals that gather together into large troops of somewhat related individuals. These troops tend to be small, but gatherings of around 50 monkeys have been observed. These troops break up into smaller groups throughout the day to forage and sleep, especially if it’s the case that food is scarce, but they are usually close enough within reach to aid each other against threats. Feeding typically starts in the morning hours and continues throughout the day, while they sleep in trees during the night. The troop doesn’t appear to have a definitive structure, but it is believed that a single female plans out the group feeding activities for the day.
Males tend to stay with one group their entire lives, while females leave the group to find fortune elsewhere. Since many of these male monkeys are related to each other, the bond between them is particularly strong, while the bond between females is comparatively weaker. This is actually the opposite behavior of many monkey species in which the female is usually the one to stay with the group permanently.
To communicate with each other, these primates have a massive range of vocalizations, including barks, howls, screams, and a kind of whinnying noise that resembles a horse. This is combined with all manner of different postures and facial features. For example, spider monkeys make a fierce display of aggression that’s designed to scare off threats and intruders. They do this by shaking the branches with their legs and emitting a screeching sound. A lot of this is just bluster, however, because it’s not backed up by real force. If this gambit doesn’t work, then the troop may split up and run away to divert the attention of the predator. Grooming, usually an important aspect of primate social behavior, is less critical to spider monkey behavior, possibly due to the reduced thumbs. Instead, they scratch themselves with their hands and feet to remove dirt and parasites.
It is believed that these creatures are among the most intelligent of the New World monkeys. Their brains are larger than the closely related howler monkey, at least among monkeys of a similar size. This intelligence may help them with social interactions and foraging behavior. By remembering the exact location of the many different fruits they regularly consume, it greatly improves their survival odds in the wild.
Spider Monkey Habitat
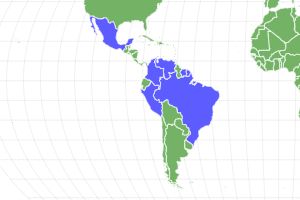
This primate species occupies a large stretch of land between the Amazon rainforest, Central America, and parts of Mexico. Most of the seven species of spider monkeys are largely concentrated in Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, and bits of Peru. Geoffroy’s spider monkey is the northern-most species, appearing all the way up the coast of central Mexico. Each species generally prefers to reside in the middle layers of rainforests and other woodlands, often near rivers and streams.
Spider Monkey Diet
The diet of these creatures consists primarily of fruits, nuts, and flowers. This is supplemented with the meat of spiders and insects. The spider monkey will spend a great deal of the day foraging in small groups. It will pick through the trees, looking for hidden morsels. Some monkeys may eat fruits from more than 100 different species of plants over their lives.
For a complete analysis of the spider monkey’s diet, make sure to read ‘What Do Spider Monkeys Eat?‘
Spider Monkey Predators and Threats
The main predators are pumas, jaguars, snakes, and the occasional eagle. The arboreal lifestyle offers a degree of protection against predators, but some of these animals are adept at climbing trees, and birds of prey can sometimes catch an unaware spider monkey from above. If it wanders down to the forest floor, then the spider monkey is far more vulnerable to predation. It has few natural defenses except for its climbing ability.
These creatures have traditionally been hunted as a source of food. Their raucous and noisy behavior often makes them easy to find in the dense forests. But habitat loss from logging and agriculture is the main threat endangering what remains of the spider monkey populations. This has wiped out much of the natural forests on which it relies, fragmenting the remaining populations. The spider monkey is also vulnerable to several diseases. The rate at which the spider monkey is susceptible to malaria has made it a valuable subject of study by human researchers.
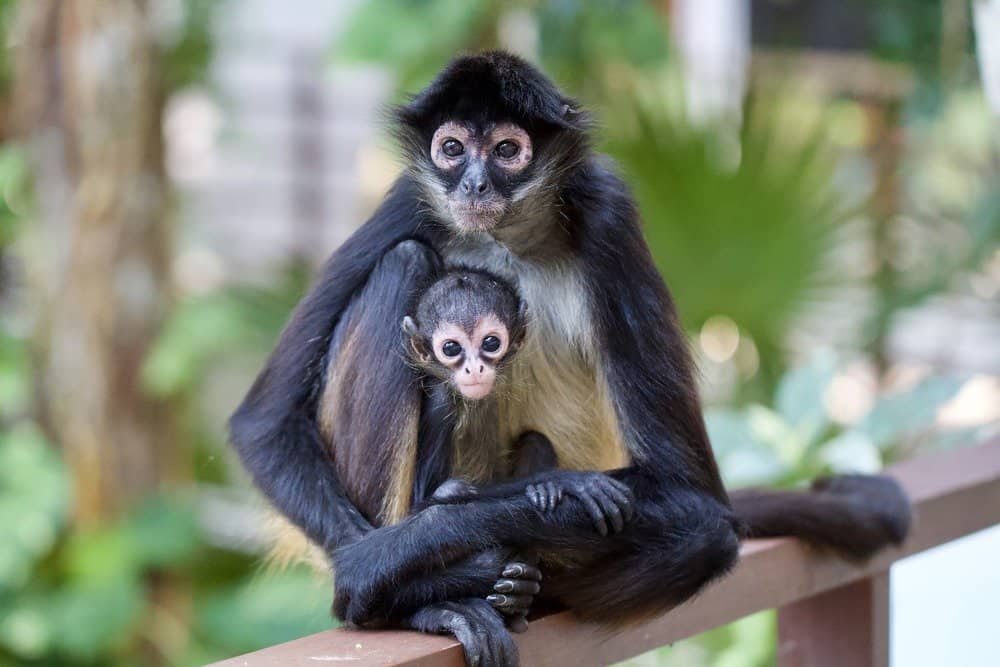
Spider Monkey Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
This animal has a breeding season that lasts all year round. The female monkey has wide latitude to choose which male she wants to mate with. However, males can be quite aggressive, sometimes killing the unrelated child of a female it is currently mating with.
The mother will carry the unborn baby for a gestation period of up to 232 days. Upon giving birth, she will often isolate herself from the rest of the troop. Because this birth and development process is quite taxing on the mother, she will produce only a single child about every two to five years. Rarely will she produce twins. The baby monkey will rely on the mother for nursing and protection for about a year after birth. She alone is responsible for the care of her offspring and does not receive any help from the other males and females of the troop. The child will cling to her back and wrap its tail around her own tail or body for protection while she is foraging.
Because of the extra development time needed to learn social cues and other valuable information, this animal has a relatively long maturity time. It will only start breeding after about five years of age. The typical lifespan of the spider monkey is 20 to 27 years. In captivity, where they are largely free from the pressure of predators, disease, and hunting, they can live up to 40 years.

StanBullett/Shutterstock.com
Spider Monkey Population
This primate species is among the most endangered and precarious groups of primates in the world. According to the IUCN Red List, which is perhaps the most comprehensive source for the conservation status of animals in the world, five of the seven species are endangered, while the brown spider monkey is critically endangered. The red-faced spider monkey is in relatively better health compared to the other species. It is only listed as vulnerable to extinction. It is not entirely clear how many mature individuals are left in the wild, but numbers appear to be in decline across the board. Protection of existing forests and reclamation of old habitats will be critical for their continued survival.
Spider Monkeys in Zoos
Because of their loud behavior and playful, energetic nature, these creatures are a popular exhibit in many zoos across the United States. Geoffroy’s black-handed spider monkey is a prime sight at the Los Angeles Zoo and the St. Louis Zoo. Other species of spider monkeys can be found at the Alexandria Zoo in Louisiana, Connecticut’s Beardsley Zoo, the Central Florida Zoo and Botanical Gardens, Zoo Boise, the Nashville Zoo, the Little Rock Zoo in Arkansas, the Potter Park Zoo in Lansing, Michigan, and many others. Most of these zoos work with wildlife conservation organizations to preserve the spider monkey and rehabilitate numbers. This is helped by the fact that they are relatively easy to breed in captivity.
View all 186 animals that start with S
Spider Monkey FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is a spider monkey?
Spider monkey describes any New World monkey species that belongs to the genus Ateles. It is characterized by the long limbs, dexterous prehensile tail, male-centered social structure, and high intelligence.
What do spider monkeys look like?
The spider monkey has a long, spindly appearance with a mixture of white, black, and brown fur. For obvious reasons, this resemblance to a spider has inspired people to give it the current moniker. Compared to many other New World monkey species, it is relatively large in size.
Where do spider monkeys live?
Spider monkeys spend most of their time living in the trees of dense rainforests. They are highly adapted for this arboreal lifestyle, so their habitat doesn’t change much from region to region. This also makes them vulnerable to habitat loss.
What do spider monkeys eat?
Spider monkeys are omnivorous animals that split their diet between plant matter (such as fruits and nuts) and meat (such as insects and spiders).
Are spider monkeys endangered?
Six of the seven species are either endangered or critically endangered. The other species is just vulnerable to extinction.
What Kingdom do Spider Monkeys belong to?
Spider Monkeys belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum do Spider Monkeys belong to?
Spider Monkeys belong to the phylum Chordata.
What class do Spider Monkeys belong to?
Spider Monkeys belong to the class Mammalia.
What family do Spider Monkeys belong to?
Spider Monkeys belong to the family Atelidae.
What order do Spider Monkeys belong to?
Spider Monkeys belong to the order Primates.
What genus do Spider Monkeys belong to?
Spider Monkeys belong to the genus Ateles.
What type of covering do Spider Monkeys have?
Spider Monkeys are covered in Hair.
What are some predators of Spider Monkeys?
Predators of Spider Monkeys include humans, eagles, and jaguars.
How many babies do Spider Monkeys have?
The average number of babies a Spider Monkey has is 1.
What is an interesting fact about Spider Monkeys?
Spider Monkeys are found in the tropical jungles of South America!
What is the scientific name for the Spider Monkey?
The scientific name for the Spider Monkey is Simia Paniscus.
What is the lifespan of a Spider Monkey?
Spider Monkeys can live for 15 to 27 years.
How fast is a Spider Monkey?
A Spider Monkey can travel at speeds of up to 35 miles per hour.
What are the differences between spider monkeys and howler monkeys?
The main differences between spider monkeys and howler monkeys are their size, intelligence, and vocalization.
Sources
- Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/spider-monkey
- National Geographic, Available here: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/mammals/group/spider-monkeys/
- Thought Co., Available here: https://www.thoughtco.com/spider-monkey-4693644