Red-Footed Tortoise
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2022/06/Red-Footed-Tortoise-header-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2022/06/Red-Footed-Tortoise-header-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2022/06/Red-Footed-Tortoise-header.jpg”);
}
}
Red-Footed Tortoise
Chelonoidis carbonarius
Male and female Red-Footed Tortoises move their heads to communicate.
Red-Footed Tortoise Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Reptilia
- Order
- Testudines
- Family
- Testudinidae
- Genus
- Chelonoidis
- Scientific Name
- Chelonoidis carbonarius
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Red-Footed Tortoise Conservation Status
Red-Footed Tortoise Facts
- Fun Fact
- Male and female Red-Footed Tortoises move their heads to communicate.
- Biggest Threat
- The pet trade
- Diet
- Herbivore
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2022/06/Red-Footed-Tortoise-header-1024×614.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the Red-Footed Tortoise images!
Want a fun pet that is low maintenance and fascinating? The Red-Footed Tortoise has been a popular pet for years that can keep you company for a lifetime.
These tortoises are named for their shells and body coloring. They have actual red feet, which makes them particularly fun to watch walk and climb. These tortoises can live up to 50 years, making them lifelong pets. They are native to South America. While their conservation status is Not Evaluated according to the Smithsonian, it is always a good idea to work with a reputable company when adopting a pet.
Red-Footed Tortoise Facts
- Red-Footed Tortoise males compete with each other to find a mate.
- These tortoises can live up to 30 years or more.
- Male and female Red-Footed Tortoises move their heads to communicate.
- Tortoises are reptiles, just like turtles and crocodiles.
- Like other tortoises, the Red-Footed Tortoise spends the majority of its time on land.
Red-Footed Tortoise Scientific Name
The Red-Footed Tortoise is known by its scientific name, Chelonoidis carbonarius. It is part of the Chelonoidis genus, which includes other South American tortoises such as the Chaco Tortoise and the closely-related Yellow-Footed Tortoise. The Red-Footed Tortoise belongs to the Testudinidae family and the Testudinoidea superfamily. All tortoises belong to this family and are classified based on the presence of their shell as well as their tendency to live primarily on land.
They belong to the order Testudines. This includes tortoises as well as turtles, which live primarily in water. In plain language, scientists use the term turtle to refer to all members of this order. When discussing animals in more detail, they differentiate between water-loving turtles and land-loving tortoises.
The Red-Footed Tortoise is part of the Class Reptilia, Phylum Chordata, and Kingdom Animalia. There are over 11,000 species of reptiles, including crocodiles, turtles and tortoises, lizards, and snakes. Birds are not generally considered part of the Reptile class, although they are closely related to many of the species.
Red-Footed Tortoise Appearance
It should come as no surprise that the Red-Footed Tortoise has red feet. The brilliant color is one of the easiest and fastest ways to recognize this animal. They also have red markings on their face that contrast with their otherwise drab coloring. Both males and females have red markings on their bodies. These markings are scales that are present on the feet, legs, and head.
Their shells, called carapaces, are mostly black. They have sections with a white or light-colored marking in the center of each one. These sections are called scutes. These tortoises do not have a nuchal scute, which is a scute that covers the neck common in many other tortoises and turtles.
The shells of these tortoises are usually oval and they have an elongated body. They have four legs and a tail, although no toes and no spurs or claws.
While many tortoises can get over 100 pounds, the Red-Footed Tortoise is not one of them. They are still large, with males typically being larger and heavier than females. Adult male Red-Footed Tortoises can get up to 18-20 inches long and over 50 pounds. Females are smaller and have slightly fewer red markings on their bodies.

SimplyAdrienne/Shutterstock.com
Red-Footed Tortoise Behavior
Like other tortoises, the Red-Footed Tortoise tends to walk slowly. They can even appear to be moving in slow motion. They are not very active, especially after they have eaten a large meal. These tortoises spend a lot of their day resting. They do not hibernate or go dormant, but they can rest for multiple days without moving or eating.
These turtles need to be able to regulate their temperature using their environment. They are cold-blooded and need heat from the surrounding air to stay safe and healthy. In the wild, Red-Footed Tortoises do this by burrowing or using tree cover to stay warm. This can also protect them from potential predators since it is harder for them to be found. For those keeping these tortoises as pets, make sure to provide heat to keep their environment around 90 degrees. They also need basking spots to soak up even more heat from lamps.
Red-Footed Tortoise Habitat
These tortoises are native to South America and need a hot, humid climate to survive. They are often found in the rain forest where they can find food, shelter, and an environment that keeps their body temperatures in the right range.
There are a few variations of these tortoises based on where they live in their native South America. They are not considered distinct species, however. Scientists categorize all variations as Chelonoidis carbonarius. Variations are mostly seen in their coloring and the design on their shells. The carapaces, the upper part of the shell, range in color from dark brown or black to lighter grey. They all have lighter colors within the center of their scutes, although these can vary as well.
Some Red-Footed Tortoises live in the wild on the Caribbean Islands. Scientists think that they were brought there by settlers and explorers and have thrived in the tropical climate that is much like their native South America.
Red-Footed Tortoises are also kept as pets. They are popular due to their interesting coloring and designs, as well as their low-maintenance lifestyle. As long as you set up the right tortoise environment, maintain a safe temperature, and provide food, these tortoises can live for a long time in captivity.
Red-Footed Tortoise Diet
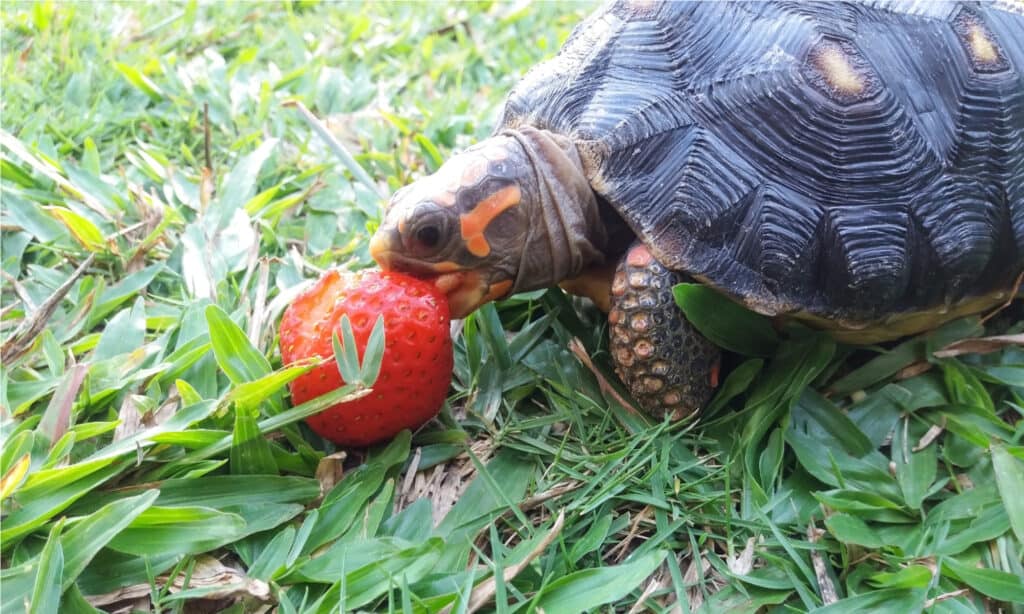
The exact diet of the Red-Footed Tortoise varies based on what is available in its environment. Like many other tortoises, the Red-Footed Tortoise is an omnivore. They eat fruits and seeds that are easy to get, often those that have fallen onto the ground. They eat the entire fruit, including the seeds. These pass through their digestive tract and can be dispersed to result in new plants.
Red-Footed Tortoises also eat bugs, such as ants and beetles. They can eat grasses, flowers, and roots as well. Tortoises can even be found feasting on carrion and other animals. Because they are slow and low to the ground, they aren’t adept predators. Instead, they eat plants, insects, and some small animals that are easy to catch.
Red-Footed Tortoises Predators and Threats
The tortoise’s shell does a great job of protecting it from potential predators. The dark brown or black coloring as helps them blend into their environment. Red-Footed Tortoises can spend a lot of time at rest, not moving. When they are covered with leaves, it can be very difficult to spot them at all.
Jaguars are not always deterred by these natural defense mechanisms, however. They like to eat Red-Footed Tortoises and Yellow-Footed Tortoises. Their strong jaws and teeth allow them to bite into the shell and pry it apart. Some tortoises survive these attacks, although many become lunch for a hungry jaguar.
Red-Footed Tortoises are the most vulnerable when they are still eggs or young, newly hatched tortoises. Their shells have not hardened to the same durability as adult tortoises. They are also smaller and easier for hungry predators to eat. Lizards, coatimundis, and mongooses like to eat Red-Footed Tortoise eggs.
Red-Footed Tortoise Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
Red-Footed Tortoise mothers lay eggs, usually 2 to 7 at a time. They use a nest to keep them safe and sheltered as they develop. Their nests are usually buried in the soil. This helps provide protection from predators like the coatimundi who like to snatch and eat tortoise eggs. It also regulates the temperature to make sure that the babies develop properly. It takes around 150 days for the baby tortoises to grow inside their eggs and become ready to hatch.
Once they hatch, the baby tortoises usually stay in the nest for a few days as they stretch out and get ready to live in the dangerous world. When they reach around 8 inches long, the tortoises are considered adults and ready to mate.
Red-Footed Tortoises can live up to 30 years in captivity. Predators and the natural risks of the environment make it harder for wild tortoises to live as long. Scientists do not know exactly what the average life expectancy of the wild Red-Footed Tortoise is, but they estimate that it is less than 30 years.
Red-Footed Tortoise Population
There are no specific known numbers of the wild Red-Footed Tortoise population and they are not on the endangered animals list. However, the export of these animals out of their home environments is monitored and requires a permit according to the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES).
The biggest threats to the wild population are changing habitat and capture to be sold as pets. While the increased interest in these animals from pet owners can help them live in captivity, it is important to know where these animals came from and that they were bred in a safe manner. Capturing Red-Footed Tortoises from the wild to be sold as pets is not a good practice.
Red-Footed Tortoises in the Zoo
Because they have such interesting coloring and long lifespans, Red-Footed Tortoises make interesting and educational additions to zoos. For example, the Red-Footed Tortoise is an animal ambassador at the Maryland Zoo. They teach zoo patrons about their behavior, habitat, and diets at the zoo. They also make appearances outside of the zoo with their trained handlers to bring increased awareness to the species.
The National Zoo in Washington, DC also has Red-Footed Tortoises on display as part of their Amazonia exhibit. They are housed alongside other animals that live in the same habitat and environments to show how they all live together. Many zoos keep Red-Footed Tortoises along with other types of tortoises.
View all 74 animals that start with R
Red-Footed Tortoise FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Is a Red-Footed Tortoise a good pet?
These animals make great pets, although you should consider a few factors before committing to owning one. It is important to be prepared to care for a pet that can live a long time, up to 30 years in captivity. They also have specific habitat requirements, especially for adequate heat and moisture. Finally, work with a reputable source to make sure that conservation efforts are honored.
How big do Red-Footed Tortoises get?
In captivity, these tortoises can get up to 20 inches long and around 50 pounds. The males are generally larger than females. Red-Footed Tortoises in the wild are usually smaller than their counterparts taken care of in captivity.
Do Red-Footed Tortoises bite?
These tortoises do not usually bite. They are safe to handle, especially if they are used to their handler and have been kept as a pet for a long time. When they feel threatened, they may bite, however. Red-Footed Tortoises do not have teeth but their beaks can still hurt and cause minor injuries.
Sources
- National Geographic, Available here: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/reptiles
- The Spruce Pets, Available here: https://www.thesprucepets.com/red-footed-tortoises-1237265#:~:text=A%20popular%20pet%20with%20striking,be%20a%2050%2Dyear%20commitment.
- National Zoo, Available here: https://nationalzoo.si.edu/animals/red-footed-tortoise#:~:text=Red%2Dfooted%20tortoises%20live%20throughout,signals%20to%20identify%20each%20other.
- Maryland Zoo, Available here: https://www.marylandzoo.org/animal/red-footed-tortoise/