Pipe Snake
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2022/04/Coral-Cylinder-Snake-Anilius-scytale-scytale-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2022/04/Coral-Cylinder-Snake-Anilius-scytale-scytale-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2022/04/Coral-Cylinder-Snake-Anilius-scytale-scytale.jpg”);
}
}
Pipe Snake
Some of these snakes flatten their neck and raise their heads to imitate cobras if they’re threatened.
Pipe Snake Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Pipe Snake Conservation Status
Pipe Snake Facts
- Fun Fact
- Some of these snakes flatten their neck and raise their heads to imitate cobras if they’re threatened.
- Estimated Population Size
- Unknown
- Diet
- Omnivore
Pipe Snake Physical Characteristics
- Skin Type
- Scales
- Venomous
- No
- Aggression
- Low
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Discover alligator-eating snakes, spiders larger than your phone, and 1000 more incredible animals in our daily FREE email.
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2022/04/Red-tailed-Pipe-Snake-Cylindrophis-ruffus-crossing-path-1024×614.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the Pipe Snake images!
Pipe Snakes are ancient and primitive
Lizards appeared on earth well before snakes, and some snake families are so old that they retain the pelvic girdles and even something of the hind limbs of their lizard ancestors, even though these are vestigial. They also may have lizard-like heads, though they no longer have ears or eyelids. This is true of the pipe snakes. These are smallish, burrowing snakes that can be found in the forests of South America and southeast Asian countries such as Borneo and Sumatra.
Four Amazing Facts About Pipe Snakes
Here are four amazing facts about the pipe snake.
button.pulse {
transform: scale(1); animation: pulse 2s infinite;
box-shadow: 0 0 0 0 rgba(11, 247, 25, 1);
}
@keyframes pulse {
0% { transform: scale(0.90); box-shadow: 0 0 0 0 rgba(11, 247, 25, 0.5); }
60% { transform: scale(1); box-shadow: 0 0 0 15px rgba(11, 247, 25, 0); }
100% { transform: scale(0.90); box-shadow: 0 0 0 0 rgba(11, 247, 25, 0); }
}
- Snakes in the Cylindrophiidae family can’t open their mouths very wide, so they eat animals as long and slender as they are such as caecilians and other snakes.
- Some of these snakes flatten their neck and raise their heads to imitate cobras if they’re threatened. Others raise their tails instead of their necks.
- Uropeltidae snakes also startle attackers by rolling over and flashing their brilliantly colored abdomens. The red and yellow colors are not only startling but mimic the colors of dangerous snakes.
- The Anomochilus snakes were once classified as Anomolochilus until the naturalist Carlos Berg noticed the name was already taken by a genus of beetles.
Where To Find Pipe Snakes
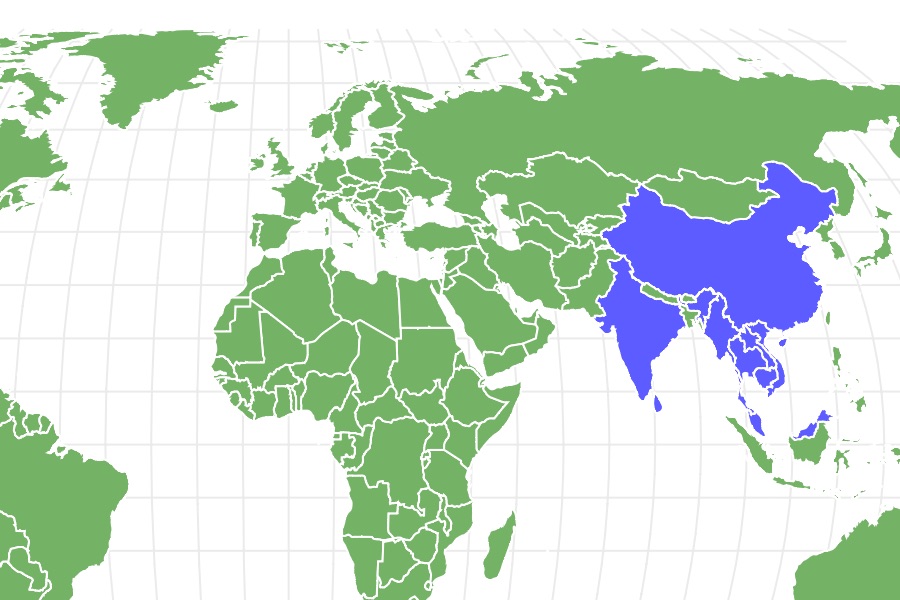
Anilius pipe snakes are found in Trinidad and Tobago and South America, especially in the Amazon rainforest. Anomochilus snakes are found in Sumatra, Malaysia and Borneo, while Cylindrophiidae snakes are also found in Borneo and Sumatra as well as Sri Lanka, south India, southern China, Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam, Myanmar and Laos. Uropeltidae are found in India. Pipe snakes live in forest habitats and most are fossorial, or animals that like to dig into the ground.
Pipe Snake Scientific Name
The scientific names of pipe snake genera are Anomochilus, Uropeltidae,
Anilius and Cylindrophis. Anomochilus, Anilius and Cylindrophis are the only genera in their respective families. Cylindrophis means “cylinder shaped serpent” in Greek, while Uropeltidae is Greek for “shield tail” and refers to the shield at the end of this burrowing snake’s tail.
There are three species in Anomochilus. They are:
- A. leonardi
- A. weberi
- A. monticola
There are no subspecies.
There is only one species in Anilius, A. scytale. It has two subspecies:
- A. s. phelpsorum
- A. s. scytale
There are 14 species in Cylindrophis. They are:
- C. aruensis
- C. boulengeri
- C. burmanus
- C. engkariensis
- C. isolepis
- C. jodiae
- C. lineatus
- C. maculatus
- C. melanotus
- C. opisthorhodus
- C. osheai
- C. ruffus
- C. subocularis
- C. yamdena
There are seven genera in Uropeltidae, and 60 species. Genera are:
Melanophidium
Platyplectrurus
Pseudoplectrurus
Plectrurus
Rhinophis
Teretrurus
Uropeltis
Appearance and Description
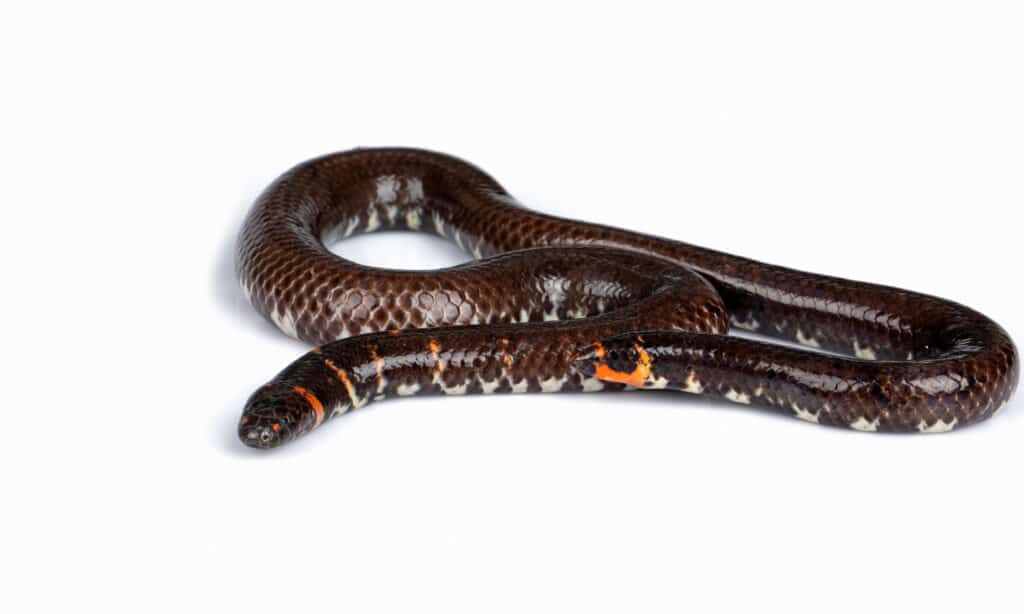
First, these snakes have bodies that are cylinder shaped, which gives them the look of pipes. They are not large and few grow to a length very much past three feet. They do come in a variety of colors and patterns, with the most spectacular being Anilius scytale, a brilliantly red snake with black bands down the length of its body.
Types of Pipe Snakes
Some types of pipe snakes include the dwarf pipe snakes, or anomochilids. These snakes are fossorial and grow up to 20 inches in length. The dwarf pipe snake has tiny eyes and lacks a tracheal lung but still has something of a vestigial pelvic girdle. If you turn the snake over, the pelvis is indicated by tiny spurs around the cloaca.
The cylinder-shaped Cylindrophis snakes, also found in Asia, are also fossorial. The head is blunt and can be hard to tell from the tail, which is short. These snakes also have a pelvic girdle which manifests as spurs. They have smooth scales along their back, but the ventral scales are small. When it’s threatened the snake coils up, tucks its head in the coils, and raises its tail to flash the colors of the ventral scales. It can’t open its mouth wide and has to rotate its skull and its jaws to swallow its prey. Eating can take as long as half an hour.
The red-tailed pipe snake is the genus’ type species and can grow as long as 39 inches. It has a dark ground color with red bands.
Uropeltidae are noted for the shields at the end of their tails, which gives them their generic name. They are found in Sri Lanka and India, and like the other pipe snakes they are fossorial and have a cylindrical shape. Unlike the other snakes they’ve lost their pelvic girdle, and their eyes are tiny. They react to threats much like the Cylindrophis snakes, and their diet is largely made up of earthworms found in the earth they burrow through.

Lauren Suryanata/Shutterstock.com
How Dangerous Are They?
All genera of pipe snakes are nonvenomous.
Pipe Snake Behavior and Humans
These snakes rarely have interactions with humans because they often burrow beneath the ground. Preferring habitats with rich, loose soil, they create tunnels that are wide enough for them to turn around in. This allows them to move backward and forwards with ease. A heavy rainstorm may wash them up and sometimes subject them to being roadkill. Many of these snakes have not been extensively studied, and the conservation status of some is unknown. The status of Cuvier’s shield-tail, for example, is data deficient, though the conservation status for the red-tailed pipe snake is least concern as is the status of the coral cylinder snake. Their diet is made up mostly of slender animals like themselves, since they can’t open their mouths widely. They are constrictors and sometimes squeeze their prey into unconsciousness or death before swallowing it whole.
These snakes are also ovoviviparous, which means the mother snake holds the eggs in her body, and they hatch just before the babies are born or immediately thereafter. In at least one species the baby snakes are surprisingly long at birth. They can be half the length of the mother. Perhaps because of this pipe snakes do not give birth to many young at once. The usual number seems to be between two and five. Scientists do not know the lifespan of these snakes, but if their lifespan is like other snakes they live around 10 years.
View all 117 animals that start with P
Pipe Snake FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are pipe snakes poisonous?
Though there are many kinds of pipe snakes, none are poisonous.
How many types of pipe snakes are there?
There are at least 76 types of pipe snake that belong to four families.
How long is a pipe snake?
Pipe snakes are not large snakes and do not grow longer than 39 inches.
What color are pipe snakes?
Pipe snakes come in a variety of colors. Anilius scytale is a bright red with black stripes. The Kerala burrowing snake has golden scales with violet edges and dark violet bands, while the purple red earth snake is purple-red on top and bright red spotted with black on the bottom.
Where do pipe snakes live?
These snakes are found in South America, Trinidad and Tobago and southeast Asia. The preferred habitat appears to be forests, rice paddies and places near a source of fresh water.
Sources
- Wikipedia , Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anomochilus
- IUCN Red List, Available here: https://www.iucnredlist.org/search?query=Anilius%20scytale&searchType=species
- Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/pipe-snake
- Encylopedia.com , Available here: https://www.encyclopedia.com/science/encyclopedias-almanacs-transcripts-and-maps/pipe-snakes-cylindrophiidae