Narwhal Skull: How Its Massive Tusk Connects

Dotted Yeti/Shutterstock.com
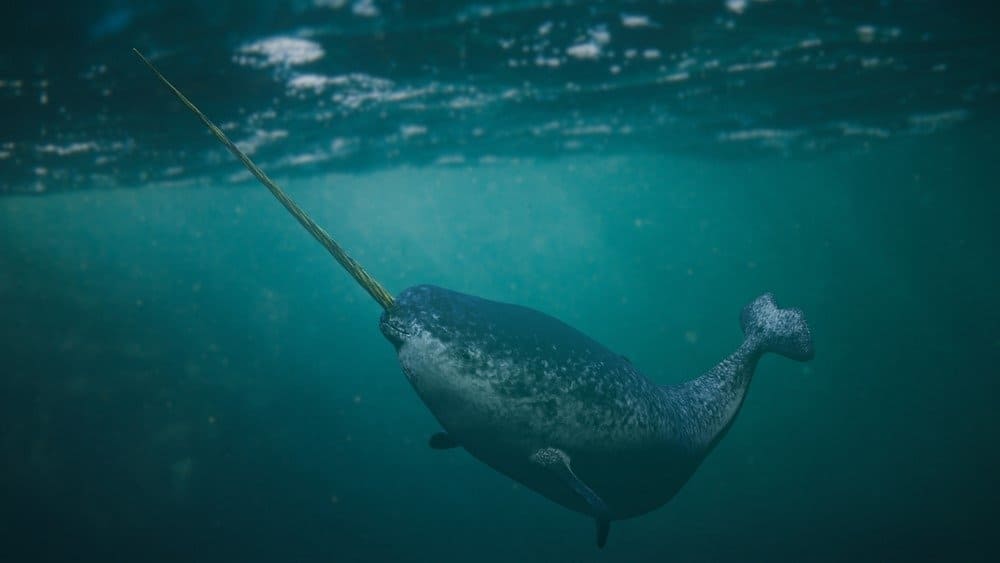
Monodon monoceros, or the narwhal, has always fascinated marine explorers, scientists, and animal lovers. Unlike other arctic whales, older males have a single spiraling tusk that extends six to nine feet from the upper jaw, on the left front side. There is an approximately one foot long right tooth buried in the cranium that does not protrude. There have also been reports of males having two tusks. Keep reading to learn more about the narwhal tusk and how it connects!
The Narwhal Skull
Morphart Creation/Shutterstock.com
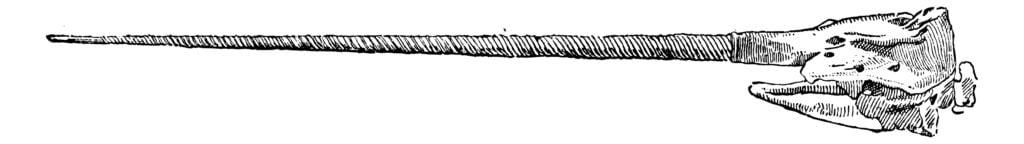
The baby narwhal or calf has six maxillary (upper) and two mandibular (lower) teeth. Only one pair develops in the maxillary jaw, and the others are vestigial, meaning they serve no purpose. Tusk size, girth, morphology, wear, and coloring vary widely.
Male tusks are usually longer and have a more variable ridge shape, often resembling a gentle wave when viewed horizontally. Female tusks are shorter, straighter, and have a more regular morphology, appearing whiter. All narwhal tusks, or canine teeth, have a unique left-hand spiral, encased in cementum, and tissue seen exclusively around the base of a tooth stuck in bone.
Scientists from the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History, Harvard University, and other institutions have examined over 130 museum skulls. Twenty-one narwhal skulls were from deaths by native hunters in Canada. The diversity in position, shape, and tissue structure indicates that these teeth are “following a pattern compatible with evolutionary obsolescence,” experts write.
How Narwhal Tusks Connect to their Skull

Obs70/Shutterstock.com
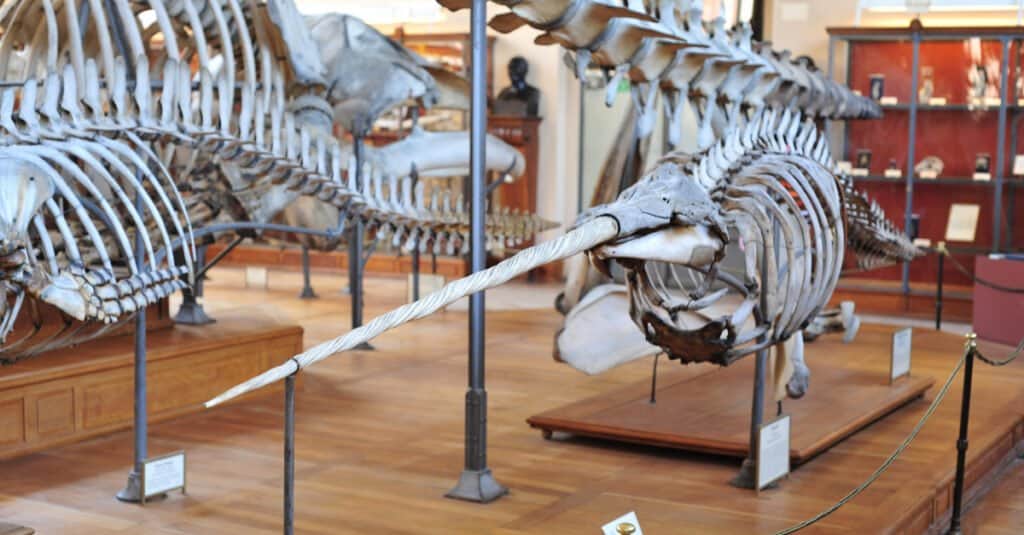
The narwhal tusk is connected to the rest of the body by the blood. A new layer of the narwhal’s tusks is added each year, much like the rings on a tree trunk. Each new layer of the tusk preserves elements of the animal’s physiology.
Narwhals have the most unusual tooth expressions. To open its mouth, the strap-toothed whale possesses two teeth that wrap over its upper jaw. Tusks exhibit significant dental asymmetry. They have unusual dimorphic or sexual expressions since females do not erupt tusks as frequently as males. The tusk also has a spiraling shape.
How Does The Narwhal Tusk Grow?

Vovantarakan/Shutterstock.com
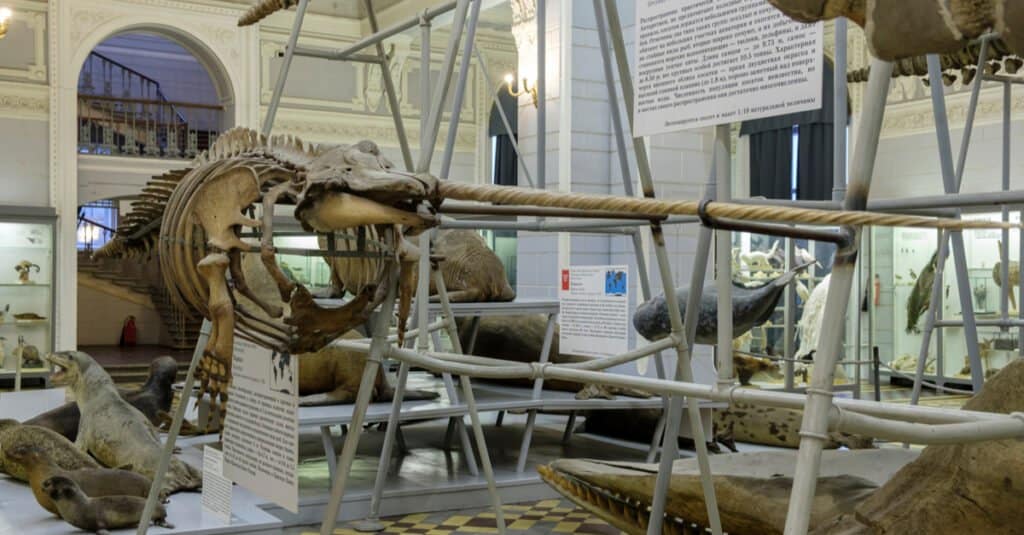
The narwhal’s tusk, like all teeth, grows from its root. However, unless the rate of new material addition is entirely even, one side of the tooth will develop quicker. A tusk growing in such a way would be bent. That’s what happens to walruses and elephants with tusks. A large, curved tusk would hinder a narwhal’s ability to swim.
With the narwhal, the tusk twists as it grows, each point passing over varying growth rates in the socket. This results in a twisted tusk with a straight axis.
Why Does The Narwhal Have Such A Massive Tusk?

Dotted Yeti/Shutterstock.com
With the energy used to make one tusk, the narwhal could easily generate 30 to 40 teeth. However, there is no evidence that this animal used to have more vertical teeth in its mouth. Evolution has instructed the narwhal to create an enormous tusk instead.
Until recently, no scientific theory proposed the tusk as a sensory organ. Recent research shows the huge, modified narwhal tusk has up to ten million small nerves running from its surface to the whale’s brain.
An electron microscope scan of two narwhal tusks revealed small tubes extending from the pulp at the tooth’s center to the outside environment. This animal chose to be exposed to the Arctic’s harsh conditions. No other animal has been known to do that. This is strong proof that it’s processing vital information.
A Tusk That Stores Valuable Ecological Information
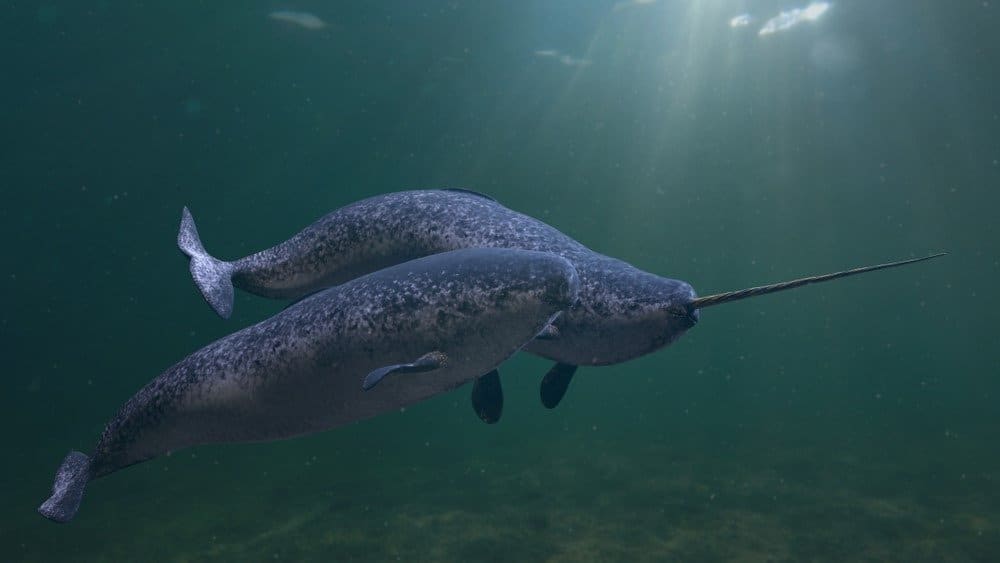

It is now believed that narwhals may detect changes in pressure, temperature, and most importantly, the relative concentration of various particles at different depths using their tusks.
Predators such as narwhals face significant threats from climate change and pollution in the Arctic. It is possible to learn a lot about an animal’s diet and environmental exposure from its tusk, which carries information on what and where they ate during the year. Mercury levels in male narwhal teeth may be traced back as far as the 1960s because of natural development layers in the tusks.
The animals’ tusks reveal that their diets and exposure to pollution have changed over the past half-century in response to the disappearance of sea ice. According to an international team of specialists, human emissions have also contributed significantly to a rise in the level of mercury in recent years.
In Conclusion
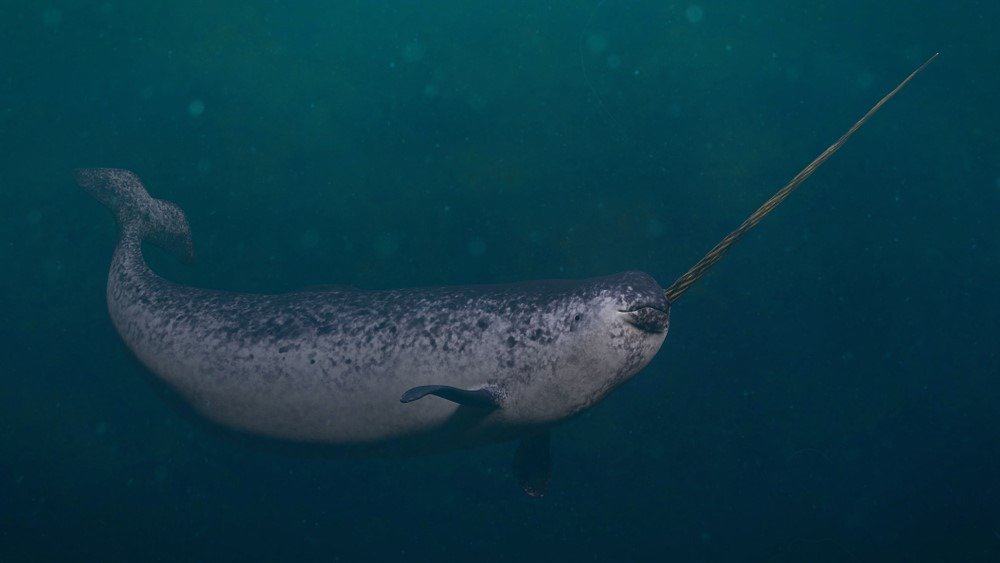

Dotted Yeti/Shutterstock.com
Until now, the solitary spiral tusk of the narwhal has been a mystery to biologists. More recent research, on the other hand, has allowed us to learn more than ever before about this magnificent creature. The tusk, for example, is no longer thought to be utilized for male jousting, according to field observations and conversations with Inuit hunters who have tracked the whale for millennia. Instead, when male narwhals rub tusks, it may be more of a sensory experience at play. One thing is for certain, the narwhal and its tusk sure are beautiful to look at!
More from A-Z Animals

Dotted Yeti/Shutterstock.com
Monodon monoceros, or the narwhal, has always fascinated marine explorers, scientists, and animal lovers. Unlike other arctic whales, older males have a single spiraling tusk that extends six to nine feet from the upper jaw, on the left front side. There is an approximately one foot long right tooth buried in the cranium that does not protrude. There have also been reports of males having two tusks. Keep reading to learn more about the narwhal tusk and how it connects!
The Narwhal Skull

Morphart Creation/Shutterstock.com
The baby narwhal or calf has six maxillary (upper) and two mandibular (lower) teeth. Only one pair develops in the maxillary jaw, and the others are vestigial, meaning they serve no purpose. Tusk size, girth, morphology, wear, and coloring vary widely.
Male tusks are usually longer and have a more variable ridge shape, often resembling a gentle wave when viewed horizontally. Female tusks are shorter, straighter, and have a more regular morphology, appearing whiter. All narwhal tusks, or canine teeth, have a unique left-hand spiral, encased in cementum, and tissue seen exclusively around the base of a tooth stuck in bone.
Scientists from the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History, Harvard University, and other institutions have examined over 130 museum skulls. Twenty-one narwhal skulls were from deaths by native hunters in Canada. The diversity in position, shape, and tissue structure indicates that these teeth are “following a pattern compatible with evolutionary obsolescence,” experts write.
How Narwhal Tusks Connect to their Skull

Obs70/Shutterstock.com
The narwhal tusk is connected to the rest of the body by the blood. A new layer of the narwhal’s tusks is added each year, much like the rings on a tree trunk. Each new layer of the tusk preserves elements of the animal’s physiology.
Narwhals have the most unusual tooth expressions. To open its mouth, the strap-toothed whale possesses two teeth that wrap over its upper jaw. Tusks exhibit significant dental asymmetry. They have unusual dimorphic or sexual expressions since females do not erupt tusks as frequently as males. The tusk also has a spiraling shape.
How Does The Narwhal Tusk Grow?

Vovantarakan/Shutterstock.com
The narwhal’s tusk, like all teeth, grows from its root. However, unless the rate of new material addition is entirely even, one side of the tooth will develop quicker. A tusk growing in such a way would be bent. That’s what happens to walruses and elephants with tusks. A large, curved tusk would hinder a narwhal’s ability to swim.
With the narwhal, the tusk twists as it grows, each point passing over varying growth rates in the socket. This results in a twisted tusk with a straight axis.
Why Does The Narwhal Have Such A Massive Tusk?

Dotted Yeti/Shutterstock.com
With the energy used to make one tusk, the narwhal could easily generate 30 to 40 teeth. However, there is no evidence that this animal used to have more vertical teeth in its mouth. Evolution has instructed the narwhal to create an enormous tusk instead.
Until recently, no scientific theory proposed the tusk as a sensory organ. Recent research shows the huge, modified narwhal tusk has up to ten million small nerves running from its surface to the whale’s brain.
An electron microscope scan of two narwhal tusks revealed small tubes extending from the pulp at the tooth’s center to the outside environment. This animal chose to be exposed to the Arctic’s harsh conditions. No other animal has been known to do that. This is strong proof that it’s processing vital information.
A Tusk That Stores Valuable Ecological Information

It is now believed that narwhals may detect changes in pressure, temperature, and most importantly, the relative concentration of various particles at different depths using their tusks.
Predators such as narwhals face significant threats from climate change and pollution in the Arctic. It is possible to learn a lot about an animal’s diet and environmental exposure from its tusk, which carries information on what and where they ate during the year. Mercury levels in male narwhal teeth may be traced back as far as the 1960s because of natural development layers in the tusks.
The animals’ tusks reveal that their diets and exposure to pollution have changed over the past half-century in response to the disappearance of sea ice. According to an international team of specialists, human emissions have also contributed significantly to a rise in the level of mercury in recent years.
In Conclusion

Dotted Yeti/Shutterstock.com
Until now, the solitary spiral tusk of the narwhal has been a mystery to biologists. More recent research, on the other hand, has allowed us to learn more than ever before about this magnificent creature. The tusk, for example, is no longer thought to be utilized for male jousting, according to field observations and conversations with Inuit hunters who have tracked the whale for millennia. Instead, when male narwhals rub tusks, it may be more of a sensory experience at play. One thing is for certain, the narwhal and its tusk sure are beautiful to look at!





