Mammoth vs. Elephant: What’s the Difference?
Elephants and mammoths are closely related animals, belonging to the same order. Of the three families in this order, only the elephant family is still alive today. So, what’s the difference that separates elephants vs. mammoths?
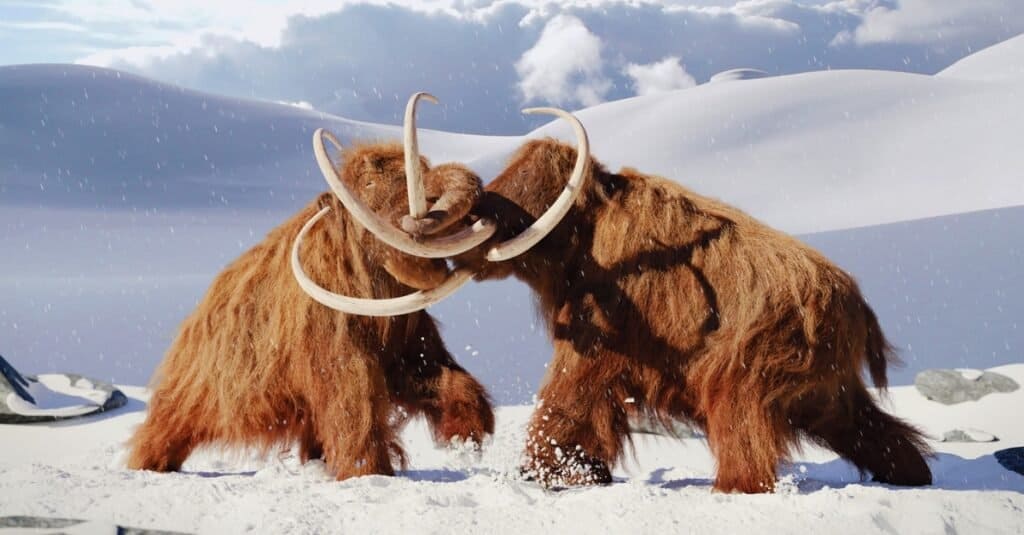
Both animals are gentle herbivores, though mammoths may have sometimes fought using their long tusks. In this article, we’ll discuss all of the differences between elephants and mammoths, including why elephants have survived while mammoths went extinct.
Comparing Elephant vs Mammoth

Dotted Yeti/Shutterstock.com
Elephants and mammoths are very similar creatures, and they even descended from the same ancestor long ago!
However, they do have distinct differences—mainly due to the ways mammoths adapted to cooler environments. Before we dive in, let’s talk about the species of elephant alive today.
African Elephant: African elephants have large ears, two extensions from their trunks used for gripping, and dipped backs. There are two species of African elephants, the African bush elephant which is larger and lives on savannas and the African forest elephant which is smaller and lives in dense forest environments.
Asian Elephant: It’s still debated which elephant species is closest related to mammoths, but many believe it may be the Asian elephant. These elephants have small ears, rounded backs, and just one extension from the trunk. Female Asian elephants do not have tusks. Asian elephants are an endangered species.
There were many mammoth species including the Wooly Mammoth, Pygmy Mammoth, and Steppe Mammoth. All of these species are now extinct.
| Elephant | Mammoth | |
| Status | Endangered | Extinct |
| Habitat | Africa, Asia | North America, Asia, Europe |
| Body | Rounded or dipped back | Humped back |
| Tusks | Shorter tusks with 1-2 extensions; only male Asian elephants have tusks | Long tusks with two extensions; both sexes had tusks |
| Ears | Asian elephant ears are smaller, while African elephant ears are larger | Small ears |
| Fur | Little fur | Thick fur, sometimes with double coat |
The 5 key Differences Between Mammoths and Elephants

iStock.com/leonello
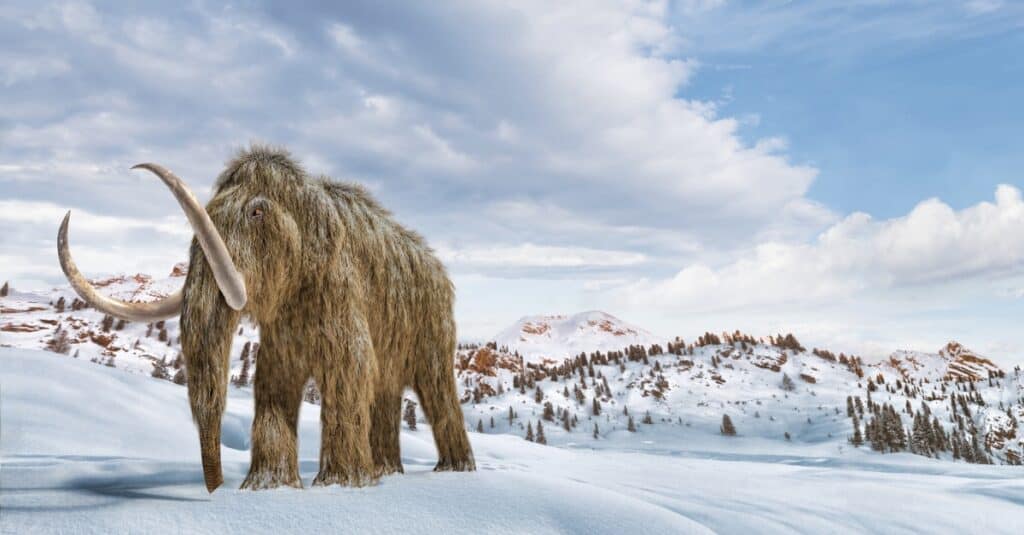
1. Mammoths are Extinct
The major difference between these species is that only one is living. Mammoths went extinct around 4,000 years ago in large part thanks to a rapidly changing climate and hunting from humans spreading across the globe.
Elephants are still alive today, although all species of elephant are threatened. Asian elephants are on the endangered species list while African bush elephants are endangered and African forest elephants are now critically endangered.
It’s so important to keep the elephants left today alive, or this entire order of animals will be gone from our Earth for good.
2. Mammoths had Bigger Tusks
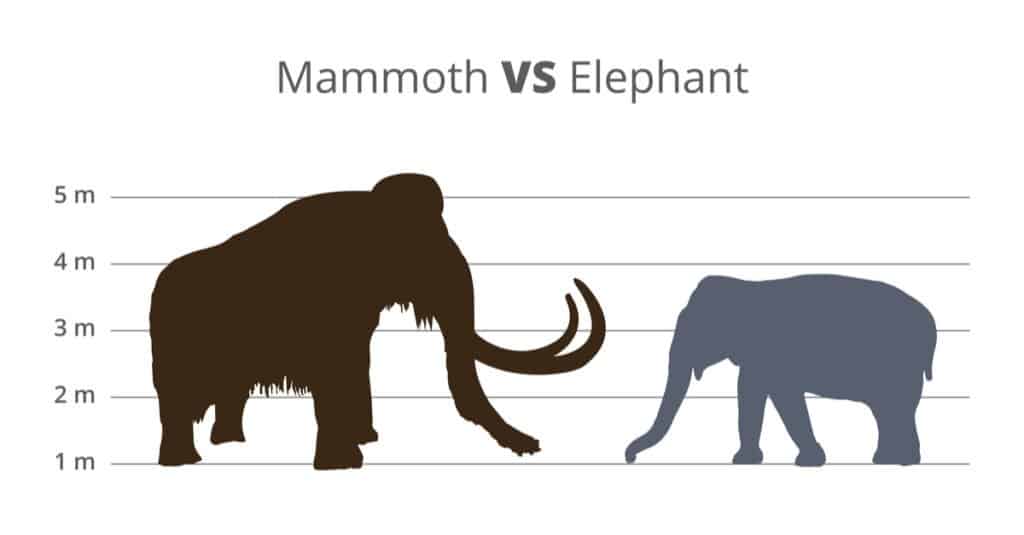
Mammoths were heavier than elephants, with much longer tusks. They were more twisted than elephant tusks, and could grow up to 16 feet long.
In comparison, the longest ever elephant tusks were 11 feet and 7 inches in length.
Another important variation exists only in Asian elephants: the females do not have tusks. Both sexes of mammoths and African elephants have tusks.
And last but not least when it comes to their trunks, both African elephants and mammoths have (or had) two extensions from the tips of their trunk that are (or were) used for gripping. Asian elephants have only one.
3. Mammoths had Thick Coats
If you’ve ever seen an elephant, you know that they have very thin layers of hair—it may even look like they don’t have fur at all.
You couldn’t say this about a mammoth. They had thick fur to adapt to cold environments. Some of them even had double coats to keep them warm through harsh winters.

iStock.com/USO
4. Their Habitats were Different
Mammoths and elephants are the descendants of the same animal. Sometime in history, however, mammoths evolved to travel outside of the warm climates of Africa, Asia, and Europe.
While elephants remained in these environments, mammoths travelled as far as North America!
Over time, they adapted to colder climates and thus were able to survive these further travels.
petrroudny43/Shutterstock.com
5. They have Different Body Shapes
Mammoths had humps on their back near their shoulders, but elephants do not have this. Asian elephants have more rounded backs, while African elephants’ backs slope downward toward the middle.
Mammoths and Asian elephants also have more distinctive foreheads, while African elephant foreheads slope straight downward into the trunk. There is a much less visible dividing structure between the head and trunk.
Mammoths had larger foreheads than either elephant species, and it was kind of rounded in shape.
Lastly, African Elephants have longer ears than either the Asian elephant or mammoths.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Why did Mammoths go Extinct?
Mammoths went extinct around 4,000 years ago. Their numbers dwindled due to human hunters, but they ultimately went extinct due climate change. The earth heated so quickly and drastically that mammoths weren’t able to adapt to the loss of habitat and food sources.
Of course, elephants did not have to adapt to changing arctic conditions during this time, as they remained in their homelands on the African and Asian continents.
Where can I see Elephants?
The best (and easiest!) place to see elephants today is in a local zoo with a focus on conservation of the species.
Never fund the use of elephants for human entertainment, as often elephants in these situations are abused.
For instance, sometimes elephant rides are advertised. Elephants aren’t like horses, however—they aren’t built for carrying a human, and it hurts them to do so. They often suffer from spinal injuries, blisters, and infections.
Although performances involving animals are dying out, it’s important never to go to a show where any animal is performing “tricks” to entertain a crowd. These animals get nothing out of these performances, and are often abused behind the scenes.
How Can we Stop Elephant Extinction?
To stop elephants from becoming extinct we must support conservation efforts, take a stand against poaching, and fight climate change.
Habitat loss and poaching are the biggest threats to elephants currently.
More from A-Z Animals
Elephants and mammoths are closely related animals, belonging to the same order. Of the three families in this order, only the elephant family is still alive today. So, what’s the difference that separates elephants vs. mammoths?
Both animals are gentle herbivores, though mammoths may have sometimes fought using their long tusks. In this article, we’ll discuss all of the differences between elephants and mammoths, including why elephants have survived while mammoths went extinct.
Comparing Elephant vs Mammoth

Dotted Yeti/Shutterstock.com
Elephants and mammoths are very similar creatures, and they even descended from the same ancestor long ago!
However, they do have distinct differences—mainly due to the ways mammoths adapted to cooler environments. Before we dive in, let’s talk about the species of elephant alive today.
African Elephant: African elephants have large ears, two extensions from their trunks used for gripping, and dipped backs. There are two species of African elephants, the African bush elephant which is larger and lives on savannas and the African forest elephant which is smaller and lives in dense forest environments.
Asian Elephant: It’s still debated which elephant species is closest related to mammoths, but many believe it may be the Asian elephant. These elephants have small ears, rounded backs, and just one extension from the trunk. Female Asian elephants do not have tusks. Asian elephants are an endangered species.
There were many mammoth species including the Wooly Mammoth, Pygmy Mammoth, and Steppe Mammoth. All of these species are now extinct.
| Elephant | Mammoth | |
| Status | Endangered | Extinct |
| Habitat | Africa, Asia | North America, Asia, Europe |
| Body | Rounded or dipped back | Humped back |
| Tusks | Shorter tusks with 1-2 extensions; only male Asian elephants have tusks | Long tusks with two extensions; both sexes had tusks |
| Ears | Asian elephant ears are smaller, while African elephant ears are larger | Small ears |
| Fur | Little fur | Thick fur, sometimes with double coat |
The 5 key Differences Between Mammoths and Elephants

iStock.com/leonello
1. Mammoths are Extinct
The major difference between these species is that only one is living. Mammoths went extinct around 4,000 years ago in large part thanks to a rapidly changing climate and hunting from humans spreading across the globe.
Elephants are still alive today, although all species of elephant are threatened. Asian elephants are on the endangered species list while African bush elephants are endangered and African forest elephants are now critically endangered.
It’s so important to keep the elephants left today alive, or this entire order of animals will be gone from our Earth for good.
2. Mammoths had Bigger Tusks
Mammoths were heavier than elephants, with much longer tusks. They were more twisted than elephant tusks, and could grow up to 16 feet long.
In comparison, the longest ever elephant tusks were 11 feet and 7 inches in length.
Another important variation exists only in Asian elephants: the females do not have tusks. Both sexes of mammoths and African elephants have tusks.
And last but not least when it comes to their trunks, both African elephants and mammoths have (or had) two extensions from the tips of their trunk that are (or were) used for gripping. Asian elephants have only one.
3. Mammoths had Thick Coats
If you’ve ever seen an elephant, you know that they have very thin layers of hair—it may even look like they don’t have fur at all.
You couldn’t say this about a mammoth. They had thick fur to adapt to cold environments. Some of them even had double coats to keep them warm through harsh winters.

iStock.com/USO
4. Their Habitats were Different
Mammoths and elephants are the descendants of the same animal. Sometime in history, however, mammoths evolved to travel outside of the warm climates of Africa, Asia, and Europe.
While elephants remained in these environments, mammoths travelled as far as North America!
Over time, they adapted to colder climates and thus were able to survive these further travels.

petrroudny43/Shutterstock.com
5. They have Different Body Shapes
Mammoths had humps on their back near their shoulders, but elephants do not have this. Asian elephants have more rounded backs, while African elephants’ backs slope downward toward the middle.
Mammoths and Asian elephants also have more distinctive foreheads, while African elephant foreheads slope straight downward into the trunk. There is a much less visible dividing structure between the head and trunk.
Mammoths had larger foreheads than either elephant species, and it was kind of rounded in shape.
Lastly, African Elephants have longer ears than either the Asian elephant or mammoths.






