Immortal Jellyfish
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/immortal-jellyfish-1-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/immortal-jellyfish-1-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/immortal-jellyfish-1.jpg”);
}
}
Immortal Jellyfish
Turritopsis dohrnii
Excellent hitchhiker on long-trip cargo ships
Immortal Jellyfish Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Cnidaria
- Class
- Hydrozoa
- Order
- Anthoathecata
- Family
- Oceaniidae
- Genus
- Turritopsis
- Scientific Name
- Turritopsis dohrnii
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Immortal Jellyfish Conservation Status
Immortal Jellyfish Facts
- Prey
- Tiny sea creatures
- Group Behavior
-
- Colony
- Fun Fact
- Excellent hitchhiker on long-trip cargo ships
- Estimated Population Size
- Unknown
- Biggest Threat
- Predation
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Regeneration ability
- Other Name(s)
- The Benjamin Button jellyfish
- Gestation Period
- 2-3 days
- Habitat
- Temperate to tropical saltwater worldwide
- Predators
- Larger jellyfish, sea anemones, tuna, sharks, swordfish, sea turtles, penguins
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Favorite Food
- Plankton, fish eggs, larvae, brine shrimp
- Type
- Medusuzoa
- Common Name
- Immortal jellyfish, Benjamin Button jellyfish
- Number Of Species
- 1
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/immortal-jellyfish-1.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the Immortal Jellyfish images!
The immortal jellyfish can regenerate and live forever.
The immortal jellyfish, also known as the Benjamin Button jellyfish, is one of few known animals that can regenerate and live forever, and the only jellyfish species that has an indefinite lifespan. It was discovered in 1883 in the Mediterranean Sea. However, researchers and scientists did not know the facts about their transformation ability until the mid-1990s. It regularly resets to a sexually immature stage after it has reproduced as well as when it is injured, starving or dying. The only way it can die is by being eaten, being removed from the water, or acquiring a disease.
5 Incredible Immortal Jellyfish Facts!
- It is unknown how old the oldest immortal jellyfish is.
- It is the only jellyfish species that does not remain in the last stage, called the Medusa stage, until death.
- The regeneration process is called “transdifferentiation” and it occurs when the jellyfish’s cells convert to an immature polyp state.
- The species has also been found on the Atlantic Ocean side of Panama, Spain and Japan. It has spread throughout the world after getting caught in the ballast waters of long-distance ocean cargo ships.
- If it starves or gets sick in its immature state when it’s called a polyp, it cannot regenerate and will die.
Immortal Jellyfish Classification and Scientific name
The scientific name of the immortal jellyfish is Turritopsis dohrnii. Although it is in the Cnidaria family, it is not a true jellyfish, which is in the class Scyphozoa, not Hydrozoa. The species was formerly classified as Turritopsis nutricula along with other jellyfish species. It was named by German marine biology student August Friedrich Leopold Weismann in 1883. Due to its cell transformation ability which reverts it to an immature state, it is also called the Benjamin Button jellyfish. Closely related species are Turritopsis rubra and Nemopsis bachei.
Immortal Jellyfish Species
There is only one species of immortal jellyfish. However, over 2,000 species of jellyfish exist.
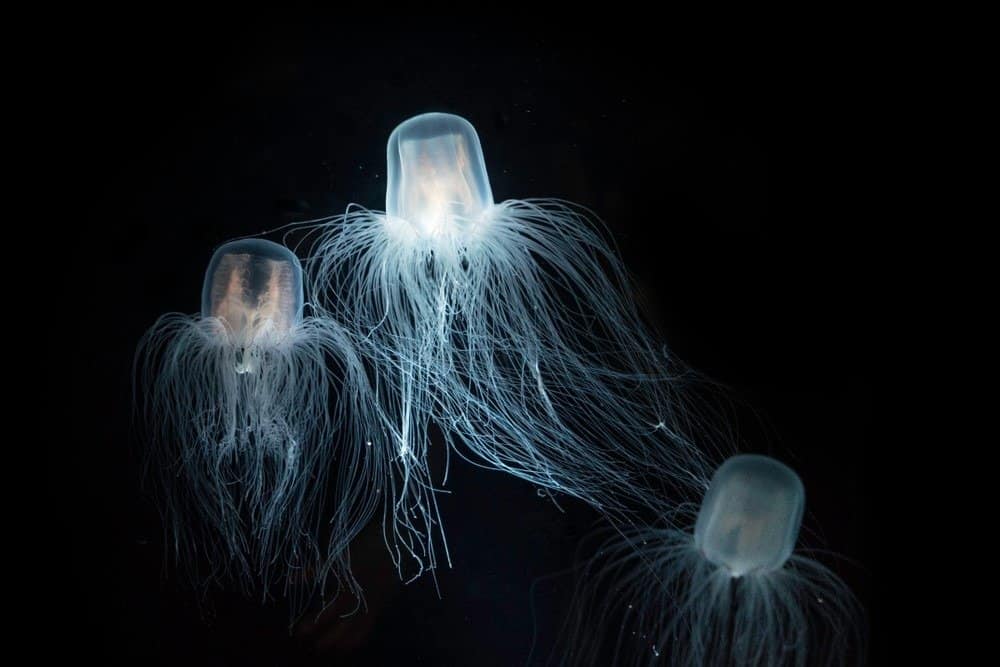
Immortal Jellyfish Appearance
The immortal jellyfish is almost invisible and resembles a tiny ice cube. Its body is bell-shaped and transparent with a height of 0.18 inches and a diameter from 0.18 up to 0.4 inches, making it smaller than a pinky nail. It has a large stomach which is bright red and has a cruciform shape in cross section. Internally, like other jellyfish, it has a hydrostatic skeleton called a mesoglea which has a jellylike substance mostly consisting of water, and it is consistently thin except for the apex. The epidermis (skin) in the cap has dense nerve cells which form a large ring-like structure above the radical canal, a common feature of cnidarians. Younger immortal jellyfish are 0.04 inches in size and have 8 tentacles, while adult ones can have 80-90 tentacles. The tentacles are white in color.
In its immature polyp state, it is made up of stolons (stems) and upright branches with feeding polyps capable of forming medusa buds. Its polyp form lives on the ocean floor and is also known as a hydroid. Polyps live in the parent hydroid colony for a few days and develop into tiny 0.039-inch medusae which then go free and are solitary. The hydroid with several polyps is not a common feature of most jellyfish.
On the other hand, there are physical differences depending on the waters they live in, although they are all the same species. For example, those living in tropical waters have 8 tentacles, while those in more temperate waters have 24 or more tentacles.

Fon Duangkamon/Shutterstock.com
Immortal Jellyfish Distribution, Population, and Habitat
Few facts exist about the population size of the immortal jellyfish. The habitat it was initially discovered in was the Mediterranean Sea. However, it actually lives in worldwide coastal areas featuring tropical and temperature waters as it has spread by hitchhiking in the ballast water of long-distance cargo ships. Its preferred habitat is warm water and like other jellyfish, has been found on both the bottom of the ocean as well as near the surface.
Immortal Jellyfish Predators and Prey
The typical diet of the immortal jellyfish contains any smaller creatures it can consume in one of two ways: Passively while immature as a hydroid on the ocean floor with any passing prey, or actively hunting and using its stinging tentacles as it drifts through the water. Its diet consists mainly of plankton, fish eggs, larvae, and brine shrimp, while its predators are larger jellyfish, sea anemones, tuna, sharks, swordfish, sea turtles, and penguins.
Immortal Jellyfish Reproduction and Lifespan
Immortal jellyfish reproduce both sexually and asexually, but it is not hermaphroditic. The sexually mature medusa stage which reproduces by the spawning and fertilization of eggs with sperm, while the sexually immature polyps reproduce by budding. It is the unique life cycle with transformation back into the polyp state that can result in so many genetically identical offspring and no limit on lifespan. Learn about the longest living animals here.
In sexual reproduction, the sperm fertilize the eggs, after which the egg develops. The jellyfish hatch as larvae, called planula, and swim out on their own. Helping to propel them through the water are small hairs called cilia which are on their tiny, oval-shaped bodies. After a few days, it is time for the next stage of the life cycle and the planula larvae drop down to the ocean floor and attach themselves to a rock. They then undergo transformation into a cylindrical colony of polyps, which become a parent hydroid colony of genetically identical, free-swimming medusae through spawning. The offspring grow into adults in a matter of weeks.
Scientists and researchers have only been able to observe the transformation of the immortal jellyfish in captivity, not in the ocean. At the same time, however, it is difficult to keep in captivity. Only one scientist so far, Shin Kubota from Kyoto University, has managed to keep a group for a long period of time.
The immortal jellyfish’s regeneration ability involves the transformation of its cells to a sexually immature state. Due to its unique life cycle, it does not have a fixed lifespan like other jellyfish species. The gene in mitochondrial DNA (mRNA) discovered to be responsible for its transformation is medusae stage-specific and expresses itself tenfold more than in other stages of the life cycle.
Immortal Jellyfish in Fishing and Cooking
The immortal jellyfish is not considered a pet and due to its small size, it is not used in cooking, although jellyfish are edible and larger species are consumed, particularly in Asian countries.
Immortal Jellyfish Population
The immortal jellyfish have massive populations that are genetically identical, and like other jellyfish species, they go through dramatic population booms. Predation reduces their population to smaller levels.
View all 29 animals that start with I
Immortal Jellyfish FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
How long do immortal jellyfish live?
They can theoretically live forever, given no harm in the polyp stage and no disease or loss of food and habitat in the medusa stage.
What do immortal jellyfish eat?
Immortal jellyfish eat tiny sea creatures including plankton, fish eggs, larvae, and brine shrimp.
How many immortal jellyfish are there?
It is unknown how many immortal jellyfish there are, but they exist worldwide.
Are immortal jellyfish dangerous?
Immortal jellyfish can sting, but they are not poisonous, unlike the box jellyfish which is also tiny at just 0.98 inches.
What species are similar to the immortal jellyfish?
Turritopsis rubra and Nemopsis bachei.
Are there other immortal cnidarians?
The Hydra is another immortal cnidarian.
What Kingdom do Immortal Jellyfish belong to?
Immortal Jellyfish belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
How do Immortal Jellyfish have babies?
Immortal Jellyfish lay eggs.
Sources
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Turritopsis_dohrnii#Diet
- NatGeoKids, Available here: https://www.natgeokids.com/nz/discover/animals/sea-life/jellyfish-facts/
- World Atlas, Available here: https://www.worldatlas.com/what-do-immortal-jellyfish-eat.html
- American Museum of Natural History, Available here: https://www.amnh.org/explore/news-blogs/on-exhibit-posts/the-immortal-jellyfish
- Ten Random Facts, Available here: http://tenrandomfacts.com/immortal-jellyfish/
- Savage Facts, Available here: https://savagefacts.com/immortal-jellyfish-facts-the-secret-of-its-immortality/
- National Geographic, Available here: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/2009/01/immortal-jellyfish-swarm-oceans-animals/
- Immortal Jellyfish, Available here: https://immortal-jellyfish.com/immortal-jellyfish-facts/
- Pet Jellyfish, Available here: https://www.petjellyfish.co.uk/help-advice/water-parameters-for-jellyfish-tanks/
- Famous Scientists, Available here: https://www.famousscientists.org/facts-about-the-immortal-jellyfish/