Food Chain vs Food Web: What’s the Difference?
@media (min-width: 481px) {
.mobile-top-content {
display: none;
}
}
#mobileTopContentCTACarouselControls { overflow: hidden; text-overflow: ellipsis; white-space: nowrap; }
.mobile-top-content .more { color: #fff; }
.mobile-top-content a { color: #fff; text-decoration: underline; }
.mobile-top-content a:hover { color: #fff; text-decoration: underline; }
@media (max-width: 480px) {
.mobile-top-content {
background-color: #06a10b;
color: #fff;
text-align: center;
/*height: 60px;
padding-top:5px;*/
font-size:80%;
/* display: block; */
margin: 0px -30px;
}
}
When learning about animals, it is important to understand the differences between the food chain vs food web. They are different concepts with different definitions, as this article will endeavor to explain. For example, the food chain refers to what animal eats what animal in a linear, orderly fashion. Food webs are much more complicated compared to food chains.
In this article, we will discuss the key differences between food chains and food webs, including distinct examples and definitions so that you can fully grasp the differences between them. Let’s get started!
Comparing Food Chain vs Food Web
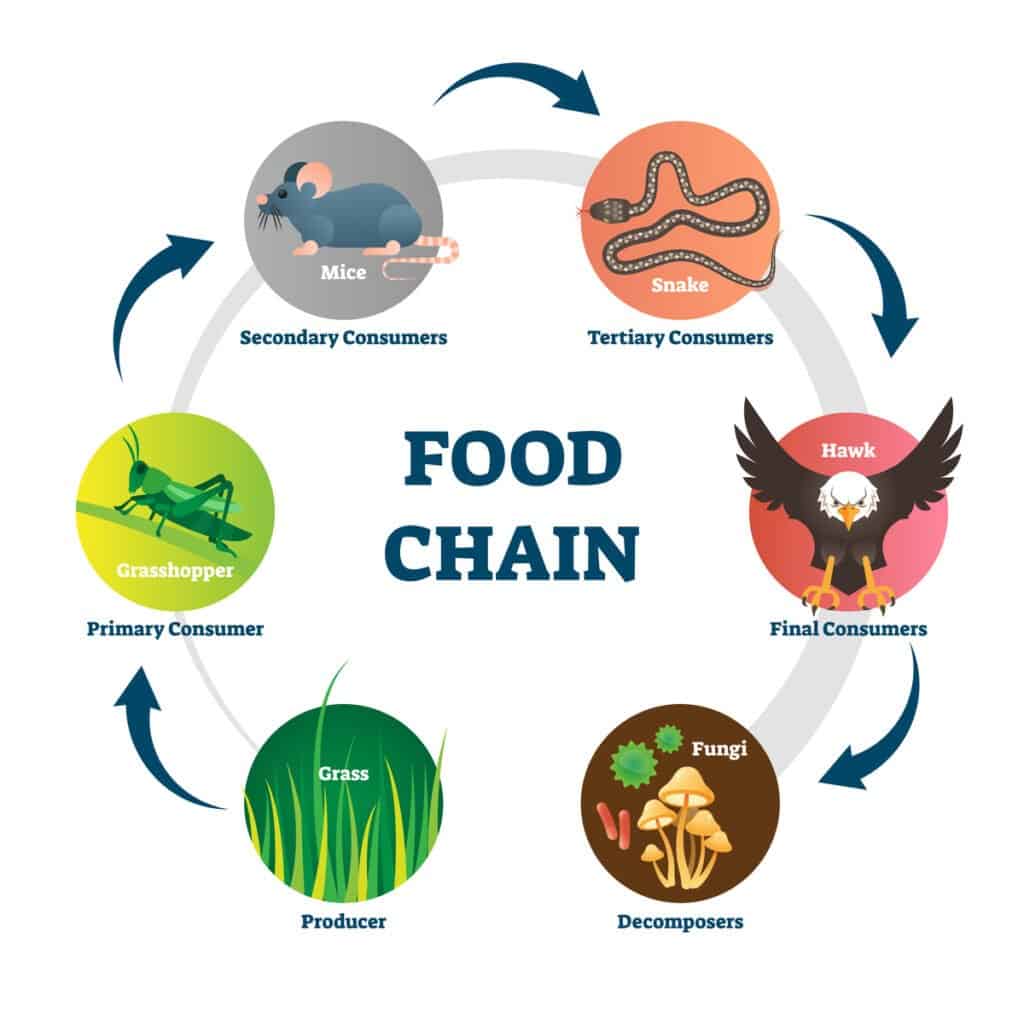
VectorMine/Shutterstock.com
| Food Chain | Food Web |
|---|---|
| Direction: One connected thread | Multiple threads connected |
| Animals Involved: One per category | Multiple organisms per category |
| Decomposers? Sometimes | Always |
| Appearance: One clear line/chain | Multiple lines or interconnections |
The Main Differences Between Food Chain vs Food Web
There are some key differences between a food chain vs food web. Food chains illustrate one clear direction of food from low-level consumers to higher-level consumers, while food webs have many interconnected threads. There are more animals involved in a food web than in a food chain. Plus, food webs often involve decomposers while food chains don’t always illustrate this.
But what else differs between these two concepts, and how can you learn to tell the two apart? Let’s dive in and learn more about the main differences between food chains vs food webs.

Food Chain vs Food Web: Direction
One of the main differences between a food chain vs food web is the direction in which the food and organisms flow. For example, food chains move in one unified direction while food webs have a vast interconnected network. This can be more easily understood with a visual representation, though the concept is easy enough to comprehend.
In both food chains and food webs, animals are connected through their food habits and the way that energy transfers throughout their ecosystems. Food chains show this using a direct order with one linear path, while food webs address the more complicated relationships that many animals have in an ecosystem.
While both food chains and food webs illustrate the relationship between prey and predator in an ecosystem, food chains only give one example for each stage of the food chain, and food webs endeavor to show how each animal or organism interacts with one another on multiple levels.
Food Chain vs Food Web: Amount of Animals Involved
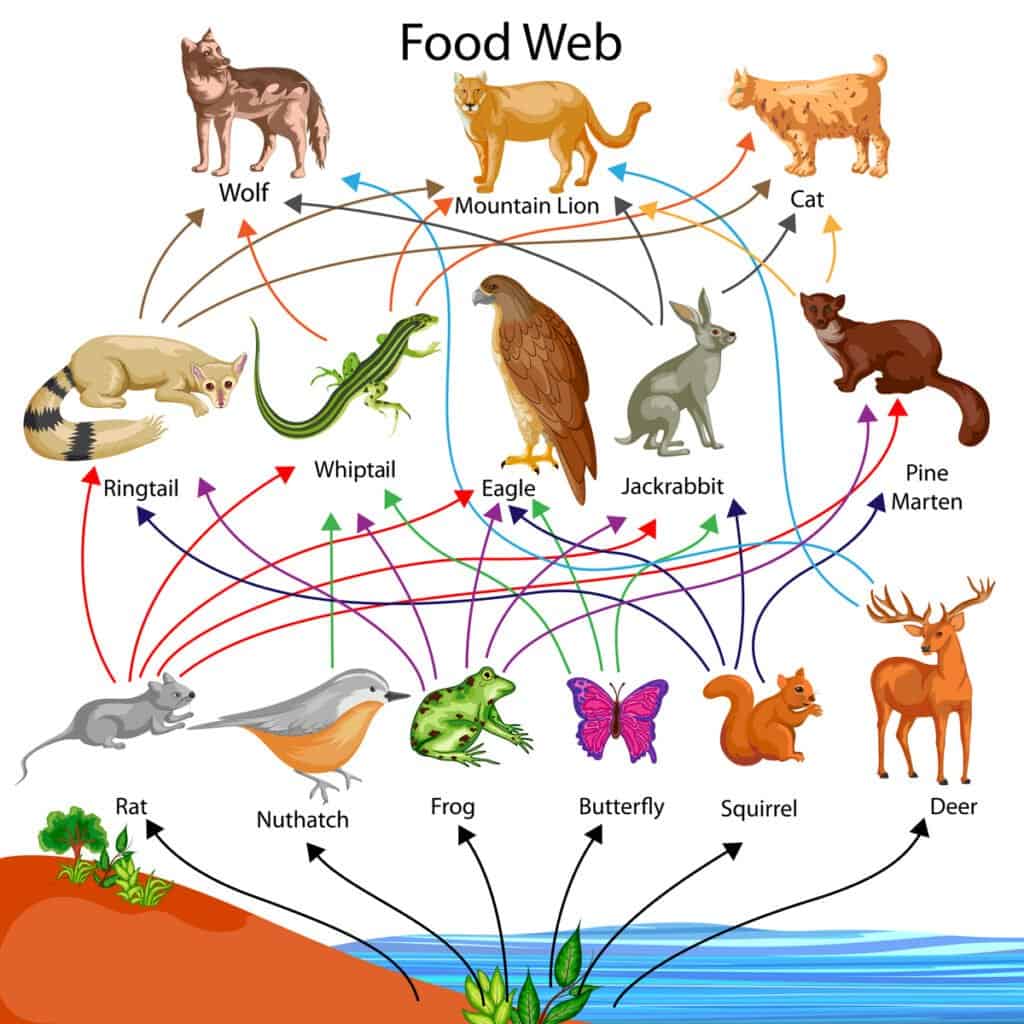
Vecton/Shutterstock.com
Another key difference between food chains and food webs is the amount of animals or organisms involved in the process. A food chain illustrates a simple relationship between producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers, while food webs go far beyond this.
Food webs show the relationship between multiple primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers, while food chains show only one direction or chain at a time. A food web also brings in other elements to the web, while chains remain fairly simplistic in their design. Food webs differ from food chains in the way they illustrate how many different directions energy travels across different consumers.

Galina Savina/Shutterstock.com
Food Chain vs Food Web: Decomposers
Another key difference between a food chain and food web is the presence of decomposers. Food chains tend to err on the side of simplicity, leaving decomposers out of the equation, while food webs usually include these. However, this isn’t always a sure thing, as some food chains are more complicated than others.
Having decomposers included in a food web is necessary to illustrate the totality of an ecosystem, which is why it may not be displayed in a food chain diagram. Some food chains include decomposers when they directly affect the chain of animals, and some food webs may not include decomposers. It just depends on how in-depth the ecosystem, illustration or diagram is!
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is a food chain?
A food chain is a way of representing the way that energy and food passes through an ecosystem. Food chains show a single ordered line of organisms and animals, and they always begin their chains with a producer. You can think of producers as plants or lower animals that fuel many varieties of prey animals. However, a food chain will only show one or two prey animals, and the chain ends with the top predator in a specific ecosystem.
What is a food web?
A food web is a complete and total illustration of how energy and food passes through an ecosystem, from beginning to end, as well as across multiple organisms and consumers. Food webs are much more comprehensive than food chains and they can even include additional ecosystem components, such as decomposers. While food chains illustrate a similar concept, it is always much more simplistic in its design when compared with a food web.
More from A-Z Animals
.more-snake-card-image { max-height:140px !important; }
@media (min-width: 481px) {
.mobile-top-content {
display: none;
}
}
#mobileTopContentCTACarouselControls { overflow: hidden; text-overflow: ellipsis; white-space: nowrap; }
.mobile-top-content .more { color: #fff; }
.mobile-top-content a { color: #fff; text-decoration: underline; }
.mobile-top-content a:hover { color: #fff; text-decoration: underline; }
@media (max-width: 480px) {
.mobile-top-content {
background-color: #06a10b;
color: #fff;
text-align: center;
/*height: 60px;
padding-top:5px;*/
font-size:80%;
/* display: block; */
margin: 0px -30px;
}
}
When learning about animals, it is important to understand the differences between the food chain vs food web. They are different concepts with different definitions, as this article will endeavor to explain. For example, the food chain refers to what animal eats what animal in a linear, orderly fashion. Food webs are much more complicated compared to food chains.
In this article, we will discuss the key differences between food chains and food webs, including distinct examples and definitions so that you can fully grasp the differences between them. Let’s get started!
Comparing Food Chain vs Food Web

VectorMine/Shutterstock.com
| Food Chain | Food Web |
|---|---|
| Direction: One connected thread | Multiple threads connected |
| Animals Involved: One per category | Multiple organisms per category |
| Decomposers? Sometimes | Always |
| Appearance: One clear line/chain | Multiple lines or interconnections |
The Main Differences Between Food Chain vs Food Web
There are some key differences between a food chain vs food web. Food chains illustrate one clear direction of food from low-level consumers to higher-level consumers, while food webs have many interconnected threads. There are more animals involved in a food web than in a food chain. Plus, food webs often involve decomposers while food chains don’t always illustrate this.
But what else differs between these two concepts, and how can you learn to tell the two apart? Let’s dive in and learn more about the main differences between food chains vs food webs.

Food Chain vs Food Web: Direction
One of the main differences between a food chain vs food web is the direction in which the food and organisms flow. For example, food chains move in one unified direction while food webs have a vast interconnected network. This can be more easily understood with a visual representation, though the concept is easy enough to comprehend.
In both food chains and food webs, animals are connected through their food habits and the way that energy transfers throughout their ecosystems. Food chains show this using a direct order with one linear path, while food webs address the more complicated relationships that many animals have in an ecosystem.
While both food chains and food webs illustrate the relationship between prey and predator in an ecosystem, food chains only give one example for each stage of the food chain, and food webs endeavor to show how each animal or organism interacts with one another on multiple levels.
Food Chain vs Food Web: Amount of Animals Involved

Vecton/Shutterstock.com
Another key difference between food chains and food webs is the amount of animals or organisms involved in the process. A food chain illustrates a simple relationship between producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers, while food webs go far beyond this.
Food webs show the relationship between multiple primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers, while food chains show only one direction or chain at a time. A food web also brings in other elements to the web, while chains remain fairly simplistic in their design. Food webs differ from food chains in the way they illustrate how many different directions energy travels across different consumers.

Galina Savina/Shutterstock.com
Food Chain vs Food Web: Decomposers
Another key difference between a food chain and food web is the presence of decomposers. Food chains tend to err on the side of simplicity, leaving decomposers out of the equation, while food webs usually include these. However, this isn’t always a sure thing, as some food chains are more complicated than others.
Having decomposers included in a food web is necessary to illustrate the totality of an ecosystem, which is why it may not be displayed in a food chain diagram. Some food chains include decomposers when they directly affect the chain of animals, and some food webs may not include decomposers. It just depends on how in-depth the ecosystem, illustration or diagram is!






