Fennec Fox
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/fennec_fox-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/fennec_fox-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/fennec_fox.jpg”);
}
}
Can get all their water from their food!
Fennec Fox Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Carnivora
- Family
- Canidae
- Genus
- Vulpes
- Scientific Name
- Vulpes zerda
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Fennec Fox Conservation Status
Fennec Fox Facts
- Prey
- Berries, Fruit, Rodents, Reptiles
- Name Of Young
- Kit
- Group Behavior
-
- Sociable
- Fun Fact
- Can get all their water from their food!
- Estimated Population Size
- Unknown
- Biggest Threat
- Habitat loss and hunting
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Large, over-sized ears
- Gestation Period
- 52 days
- Habitat
- Sandy and semi-arid desert
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Average Litter Size
- 3
- Lifestyle
-
- Nocturnal
- Common Name
- Fennec Fox
- Number Of Species
- 1
- Location
- North Africa
- Slogan
- Found in the African Sahara Desert!
- Group
- Mammal
Fennec Fox Physical Characteristics
- Color
-
- White
- Cream
- Sandy
- Skin Type
- Fur
- Top Speed
- 25 mph
- Lifespan
- 10 – 14 years
- Weight
- 1kg – 1.5kg (2.2lbs – 3.3lbs)
- Length
- 24cm -41cm (9in – 16in)
- Age of Sexual Maturity
- 9 months
- Age of Weaning
- 5 weeks
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/fennec_fox3.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the Fennec Fox images!
Fennec Fox Classification and Evolution
The fennec fox is a small species of fox found in the deserts of North Africa. They are the smallest canine species but have the largest ears relative to their body size which are used to both aid their hearing and to help them to control their body temperature in the hostile environments in which they live. Fennec foxes are largely nocturnal animals as this both helps protect them from the scorching African heat and keeps them safe from predators during the day. Their adorable appearance has lead to them being kept as pets throughout much of their natural range and also overseas. Male fennec foxes are known as reynards and females are called vixens.
Fennec Fox Anatomy and Appearance
Fennec foxes are the smallest species of fox found anywhere in the world growing up to 41cm in length and weighing just 1.5kg. They have long and bushy black-tipped tails that help to steer them when changing direction when running and also keep their nose and feet warm while they are curled up sleeping in their dens. Fennec foxes are animals with light, sandy coloured fur that helps to ensure they are well camouflaged when they are out on the sand. Their fur is long and thick which helps to keep them warm when the desert temperatures plummet at night but also keeps them cooler during the hot daytime hours as the colour also reflects the sun away from their bodies. The most distinctive feature of the fennec fox is their pointed oval, over-sized ears which can grow up to 15cm in length. Their large ears give the fennec fox incredibly sensitive hearing so they are able to find prey and also act as a temperature regulator to prevent them from getting too hot. Fennec foxes have long and sharp, curved claws that enable them to effectively dig their burrows with great speed.
See all of our expert product reviews.
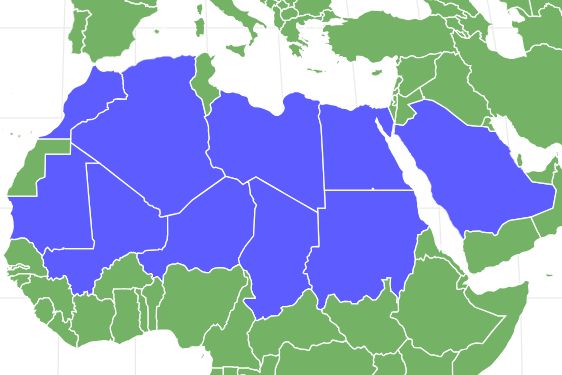
Fennec Fox Distribution and Habitat
Fennec foxes are animals that are found inhabiting both sandy and semi-arid desert regions across northern Africa and the northern Sinai peninsula. They have a relatively wide range from Morocco across to Egypt, south to north Niger and Sudan and east to Kuwait. Fennec foxes are found in both the Sahara and Nubian deserts, where they dig extensive underground burrows with sandy dunes thought to be the optimum habitat for them. Although little is really known about the exact distribution of wild fennec fox populations, they are not thought to be too threatened in their natural environments at this time as they are able to successfully survive in a range of desert environments from coastal regions to more sparse areas of the inland deserts.
Fennec Fox Behaviour and Lifestyle
Fennec foxes are largely nocturnal animals that tend to be most active during the cooler nights. The sandy colour of their thick fur means that they can more easily go unseen on the sand but they tend to avoid too much activity during the day due to the searing heat. Fennec foxes are unique amongst foxes as they are actually relatively sociable animals (other fox species are highly solitary only coming together to mate). They inhabit elaborate, inter-connecting burrows in small communities of up to 10 individuals with each individual or mating pair having their own territory within their underground community. Like other canines, male fennec foxes mark their territory with urine and become incredibly aggressive towards one another, particularly when competing for females during the mating season.
Fennec Fox Reproduction and Life Cycles
Fennec foxes mate between January and March. Once they have found a mate, the mate for life with couples inhabiting the same part of the den for the whole year round. After a nearly two month long gestation period, the female fennec fox (vixen) gives birth to between 2 and 5 offspring that are known as kits. Born with grey skin and weighing just 50grams at birth, fennec fox kits suckle on their mother’s milk until they are about 5 weeks old when they start to be weaned onto more solid foods. Young fennec foxes remain in their maternal den protected by the female for their first two months with the adult male being temporarily evicted until the kits are older. Fennec foxes are fully mature by the time they are 11 months old and can live for up to 12 years in the wild.
Fennec Fox Diet and Prey
Fennec foxes are omnivorous animals that primarily hunt for food during the cooler nights. They eat a wide range of desert vegetation including grasses, roots, berries and fruit as well as hunting for insects, small reptiles and rodents in and on the sand. Using their incredibly sensitive hearing, they can hear their prey walking around on the soft sand or burrowing into it. Like many other desert dwelling creatures, fennec foxes are well adapted to living in such a dry environment and get almost all of the water that they need through the vegetation they eat. Their kidneys are specially developed to ensure that there is minimal water loss in their day to day lives.
Fennec Fox Predators and Threats
Due to their agile nature and the fact that they spend most of the daytime hours sleeping safely in their underground burrows, fennec foxes have very few common predators in their natural environment. Eagle owls are considered to be the main predator of the fennec fox but they are also thought to be preyed about by larger mammals too including hyenas, caracals, jackals and domestic dogs. Fennec foxes are often trapped and captured by people to be sold into the pet trade as well as being hunted by locals for their beautiful fur. In some regions, fennec foxes are also threatened by habitat loss from expanding human settlements.
Health and Entertainment for your Fennec Fox
See all of our expert product reviews.
Fennec Fox Interesting Facts and Features
Fennec foxes have many adaptations to help them to successfully survive in their desert environment and one of their most notable features is their furry feet. Their thick fur continues onto the soles of their feet to allow them to walk around on the scorching hot sand without a problem. Highly unusual amongst canines, the sociable nature of the fennec fox is quite a remarkable behavioural trait. These small communities are often referred to as either a skulk or a leash. Their extensive underground burrows provide each individual or mating pair with their own small territory within their community, where fennec fox individuals dig their own burrows which they line with soft materials including feathers and fur to ensure that they are warm and comfortable when they are sleeping during the day.
Fennec Fox Relationship with Humans
The wide range of the fennec fox means that they only really come into contact with people in certain regions as they are able to successfully survive in the more remote and hostile regions of the desert. In areas where local human populations are expanding, fennec foxes are starting to be increasingly threatened by habitat loss as human settlements develop. Fennec foxes have long since been hunted by local people for their beautiful fur and are commonly captured and sold into the exotic pet trade all around the world.
Fennec Fox Conservation Status and Life Today
The fennec fox has been classified by the IUCN as an animal that is of Least Concern from becoming extinct in the wild in the near future. Despite the fact that certain fennec fox populations are becoming increasingly threatened from habitat loss and hunting, there is currently no known range-wide threats resulting in population decline that would warrant them being placed into a threatened listing category.
View all 62 animals that start with F
Fennec Fox FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Fennec Foxes herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Fennec Foxes are Omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and other animals.
What Kingdom do Fennec Foxes belong to?
Fennec Foxes belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do Fennec Foxes belong to?
Fennec Foxes belong to the class Mammalia.
What phylum to Fennec Foxes belong to?
Fennec Foxes belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do Fennec Foxes belong to?
Fennec Foxes belong to the family Canidae.
What order do Fennec Foxes belong to?
Fennec Foxes belong to the order Carnivora.
What type of covering do Fennec Foxes have?
Fennec Foxes are covered in Fur.
What genus do Fennec Foxes belong to?
Fennec Foxes belong to the genus Vulpes.
Where do Fennec Foxes live?
Fennec Foxes live in North Africa.
In what type of habitat do Fennec Foxes live?
Fennec Foxes live in sandy and semi-arid deserts.
What are some predators of Fennec Foxes?
Predators of Fennec Foxes include eagles, owls, hyenas, and jackals.
How many babies do Fennec Foxes have?
The average number of babies a Fennec Fox has is 3.
What is an interesting fact about Fennec Foxes?
Fennec Foxes are found in the African Sahara Desert!
What is the scientific name for the Fennec Fox?
The scientific name for the Fennec Fox is Vulpes zerda.
What is the lifespan of a Fennec Fox?
Fennec Foxes can live for 10 to 14 years.
How many species of Fennec Fox are there?
There is 1 species of Fennec Fox.
What is the biggest threat to the Fennec Fox?
The biggest threats to the Fennec Fox are habitat loss and hunting.
How many Fennec Foxes are left in the world?
The population size of the Fennec Fox is unknown.
How fast is a Fennec Fox?
A Fennec Fox can travel at speeds of up to 25 miles per hour.
How to say Fennec Fox in …
fennec fox
fennec
Fennek
фенек
Vulpes zerda
Fennec
Fenek
Fennek
Feneko
Fennecus zerda
Fennekrebane
Aavikkokettu
Vulpes zerda
פנק
Pustinjska lisica
Sivatagi róka
Vulpes zerda
フェネック
Vulpes zerda
Rubah fennec
fennek
Fenek pustynny
Feneco
Fenec
Fenek
Fennek
Çöl tilkisi
Cáo tai to châu Phi
耳廓狐
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World’s Wildlife
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David W. Macdonald, Oxford University Press (2010) The Encyclopedia Of Mammals
- National Geographic, Available here: http://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/mammals/f/fennec-fox/
- IUCN Red List, Available here: http://www.iucnredlist.org/details/41588/0