Eel
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/eel-1-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/eel-1-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/eel-1.jpg”);
}
}
Eel
Eels can be a mere few inches long to 13 feet!
Eel Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Eel Conservation Status
Eel Facts
- Prey
- Smaller fish, invertebrates, crustaceans, shrimp, crabs, sea urchins
- Group Behavior
-
- Solitary/Group
- Fun Fact
- Eels can be a mere few inches long to 13 feet!
- Estimated Population Size
- Unknown
- Biggest Threat
- Human consumption of freshwater eels
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Snakelike appearance
- Gestation Period
- Unknown
- Habitat
- Ocean, river, freshwater
- Predators
- Larger eels, larger fish, fish-eating birds, and (for freshwater eels) humans
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Type
- Anguilliform, Actinopterygii, Teleost
- Common Name
- Eel
- Number Of Species
- 800
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/08/fangtooth-moray-1024×535.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
The body of an eel has a slimy coating, hence the phrase, “Slippery as an eel.”
The most dangerous eel species is the conger. Although these fish are very snakelike in appearance, they are actually fish. They are ray-finned fishes of the order Anguilliformes, with the term “eel” referring to snake-like fish such as electric, ribbon, wolf eels, lampreys, and morays along with true eels for a total of 800 species. The eel fish can be anywhere from a few inches to 13 feet or more in length. A few freshwater species have become endangered due to human over-consumption.
5 Incredible Eel Facts!
- Eel fish can swim backwards.
- The slender giant moray is the longest species at 13 feet.
- The largest eel ever recorded was a European conger that reportedly reached 350 pounds!
- The gulper (pelican) has an incredibly large mouth resembling a pelican’s pouch.
- Onejaws have no upper jaw but unusually large mouths, and none of the 15 species exceed 7 inches in length.
Eel Classification and Scientific Name
Anguilliforms include freshwater as well as saltwater fish such as marine morays. There are 19 families, 111 genera, and approximately 800 species. They are further classed from the Phylum Chordata into the Actinopterygii Class. They are also Teleosts, or members of the infraclass Teleostei, which contains 96% of all currently existing fish species.
Conger or true eels (Conger conger) are members of the family Congridae which includes both congers and garden eels. Only members of the order Anguilliformes are true eels. The electric eel is not a true eel but a knifefish, related to carp and catfish, and a member of the order Gymnotiformes and the genus Electrophorus. It is also an air-breather and, unlike true species, lives in freshwater. The wolf eel‘s scientific name is Anarrhichthys ocellatus. The scientific name of the ribbon eel, also known as the leaf-nosed moray or bernis, is Rhinomuraena quaesita. Morays are of the family Muraenidae; however, the ribbon eel is sometimes classed in its own family Rhinomuraenidae. Lampreys are jawless fish of the class Hyperoartia, order Petromyzontiformes, and superclass Cyclostomata.
Eel Species
There are over 800 species, including snake-like fish and true eels. Conger, electric, fire, and muraena are the most dangerous species. The conger and muraena have powerful jaws with sharp teeth strong enough to drag people, while several shocks from an electric eel can cause respiratory or heart failure in people with underlying heart issues. The fire eel has toxic skin.
Eel Appearance
Different species vary in appearance by their length, color, mouth, and fins. For example, wolf eels are a species of wolffish that differs from true species with their paired gill slits and pectoral fins, while the lamprey has a toothed, funnel-shaped mouth. However, all have long snakelike or wormlike bodies that end in a modified tail fin that is really the fusion of the dorsal and anal fins. They are also characterized by strong jaws and small, sharp teeth. These fish have no pelvic fins and many lack pectoral fins. The larvae are called glass eels, so named due to their transparency. The term does not refer to a fish species but the larval stage referring to the fish’s life stage after hatching up to adulthood
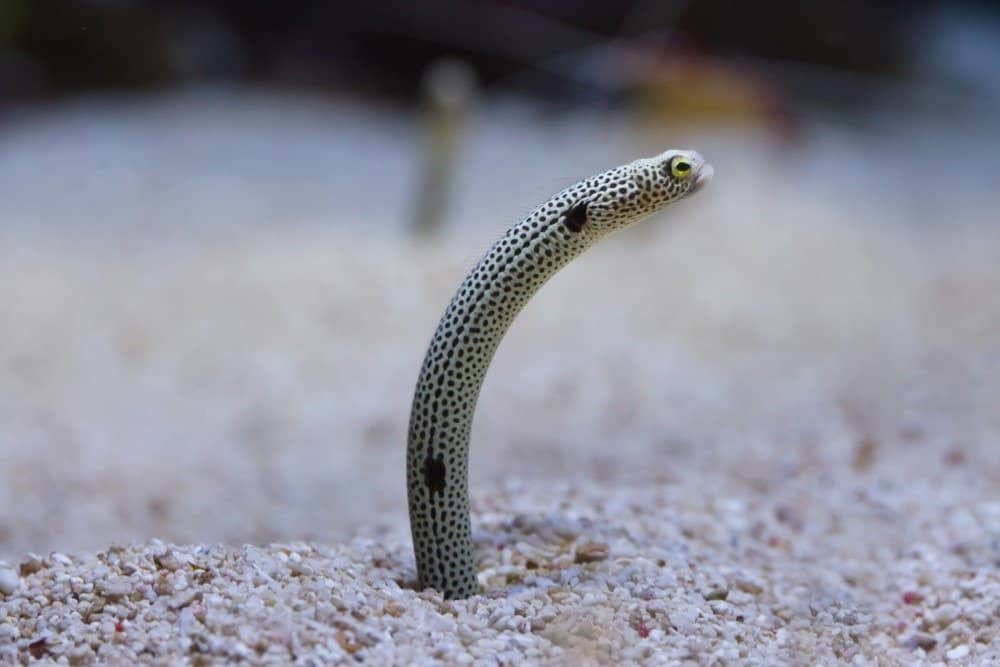

Vladimir Wrangel/Shutterstock.com
Eel Distribution, Population, and Habitat
The population of all 800 species worldwide is unknown. It is possible for them to inhabit a small or large range because each species has its own unique distribution. Eel fish can inhabit many types of habitat including oceans, rivers, lakes, and smaller bodies of water. They live deep underwater so as to burrow into the floor or find shelter in coral reefs, rock fissures, muddy or pebbly water. Fish of the family Anguillidae typically inhabit freshwater.
Eel Predators and Prey
American and European species are threatened by habitat destruction and climate change. Overconsumption by humans is responsible for endangering American and Japanese species and critically endangering the European species.
What eats eels?
There are several types of predators depending on the species and its size. Generally, larger fish, seabirds (including herons and storks), and mammals (including raccoons and humans), eat these fish.
What do eels eat?
These are primarily predatory fish with carnivorous diets, sometimes cannibalistic. They eat smaller fish, invertebrates, crustaceans, shrimp, crabs, sea urchins. Those in freshwater habitats also consume insect larvae, including that of mosquitos, and worms. Freshwater species eat carrion in addition to live prey.
Eel Reproduction and Lifespan
These fish reproduce with a large mating group in which they dance around each other to spawn, after which the eggs hatch into larvae, called glass eels. After the adults spawn, they die. Freshwater species will go to marine waters to mate. However, not much else is known about their reproduction.
The lifespan of these fish generally ranges from 32-88 years depending on the species. On the low end, the short-finned species lives 32 years. The American species lives 43 years and the European species is the longest living at 88 years.
Eel in Fishing and Cooking
The main commercial types and the scientific names of each species are the American (Anguilla rostrata), European (Anguilla anguilla), Japanese (Anguilla japonica), and the short-finned eel (Anguilla australis). All of them are freshwater fish (family Anguillidae). A popular saltwater species in Japanese cuisine is the white-spotted conger (Conger myriaster).
Eel Population
Determining this fish’s population is dependent on each species, as a worldwide assessment of all 800 species has not been done. The IUCN status of the American and Japanese species are both Endangered, while the European species is Critically Endangered. The short-finned species has not yet been assessed.
View all 68 animals that start with E
Eel FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
How do eels reproduce?
Eels reproduce by spawning.
Where do eels live?
It depends on the species, but they live in either salt or freshwater habitats of various sizes.
Is it safe to eat eel?
Yes, as long as it is properly prepared. Eel blood is toxic to humans and so needs proper cooking for the heat to destroy the protein compounds. The skin is also toxic in some species and so needs removal.
Is an eel a snake or a fish?
All eels are fish in spite of their snakelike bodies.
Do eels bite?
Yes, some eel species bite. Congers and muraena have small, sharp teeth with strong jaws that can be powerful enough to drag people.
Are Eels herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Eels are Carnivores, meaning they eat other animals.
What Kingdom do Eels belong to?
Eels belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What is an interesting fact about Eels?
Eels can be a mere few inches long to 13 feet!
Sources
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eel
- Ocean Conservancy, Available here: https://oceanconservancy.org/blog/2019/07/09/difference-between-electric-eels/
- Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/eel/Annotated-classification
- New Scientist, Available here: https://www.newscientist.com/article/2081008-how-are-baby-eels-made-we-still-dont-know/
- Animals, Available here: https://animals.net/eel/
- Study, Available here: https://study.com/academy/lesson/eel-predators-lesson-for-kids.html
- Tankarium, Available here: https://www.tankarium.com/freshwater-eels/
- Fact File, Available here: https://factfile.org/10-facts-about-eels
- What De What, Available here: https://whatdewhat.com/vicious-fish-most-dangerous-eels-world/
- Cuteness, Available here: https://www.cuteness.com/article/do-eels-eat
- What Eats?, Available here: http://www.whateats.com/what-eats-an-eel
- eHow, Available here: https://www.ehow.co.uk/info_8586270_do-eels-eat.html
- Independent, Available here: https://www.independent.co.uk/environment/eels-climate-change-extinction-endangered-species-fish-global-warming-a8753166.html
- US Department of Agriculture, Available here: https://pubag.nal.usda.gov/catalog/6277911