Common House Spider
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/09/Common-House-SPider-Crawling-on-a-Living-Room-Floor-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/09/Common-House-SPider-Crawling-on-a-Living-Room-Floor-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/09/Common-House-SPider-Crawling-on-a-Living-Room-Floor.jpg”);
}
}
Common House Spider
Parasteatoda tepidariorum
House spiders have the ability to eat most insects in a home.
Common House Spider Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Arthropoda
- Class
- Arachnida
- Order
- aranae
- Family
- Theridiidae
- Genus
- Parasteatoda
- Scientific Name
- Parasteatoda tepidariorum
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Common House Spider Conservation Status
Common House Spider Locations
Common House Spider Facts
- Prey
- Mosquitoes, flies, ants
- Name Of Young
- Spiderling
- Group Behavior
-
- Solitary
- Fun Fact
- House spiders have the ability to eat most insects in a home.
- Biggest Threat
- Loss of habitat, pesticides
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Eight spindly legs
- Other Name(s)
- House spider
- Gestation Period
- 30-50 days
- Litter Size
- 400+ eggs
- Habitat
- The corners of a room
- Predators
- Birds, cats, dogs, wasps
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Type
- Insect
- Common Name
- House spider
- Location
- Worldwide
- Group
- Solitary
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/09/Close-Up-of-Common-House-Spider-1024×535.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the Common House Spider images!
A single common house spider egg sac may contain 400 eggs or more
Common house spiders make their webs in the corners and nooks of a home. They are very small creatures measuring less than one-quarter of an inch in length. They live on a diet of flies, mosquitoes, fleas, and ants. Though these spiders have venom, their bite is considered harmless to people and pets.
4 Incredible Common House Spider Facts!
- Some of these spiders eat four times each day
- If it’s not capturing enough insects, this spider will move to another location
- Though they are solitary, these spiders sometimes build webs near each other
- Their dark colors help to camouflage them in a home
Common House Spider Species, Types and Scientific Name
Parasteatoda tepidariorum is the scientific name of the common house spider, which is also sometimes called the American house spider. The word Parasteatoda refers to the genus of the spider and the Latin word tepidariorum relates to a warm environment. These spiders take shelter inside warm homes or other structures.
They belong to the Theridiidae family and the order Araneae. There is one subspecies of the common house spider known as the common gray house spider.
There are 10 other types of spiders that fall into the general category of house spiders. These include:
- Black house spider- Badumna Insignis
- Brown house spider- Steatoda grossa
- Common cellar spider- Pholcus phalangioides
- Domestic house spider- Tegenaria domestica
- Giant house spider- Eratigena atrica
- Hobo spider- Eratigena agrestis
- Geometric house spider- Latrodectus Geometricus
- Tiny house spider- Oonops domesticush
- Yellow sac spider– Chiracanthium inclusum
- Southern house spider- Kukulcania hibernalis
Appearance: How to Identify a Common House Spider
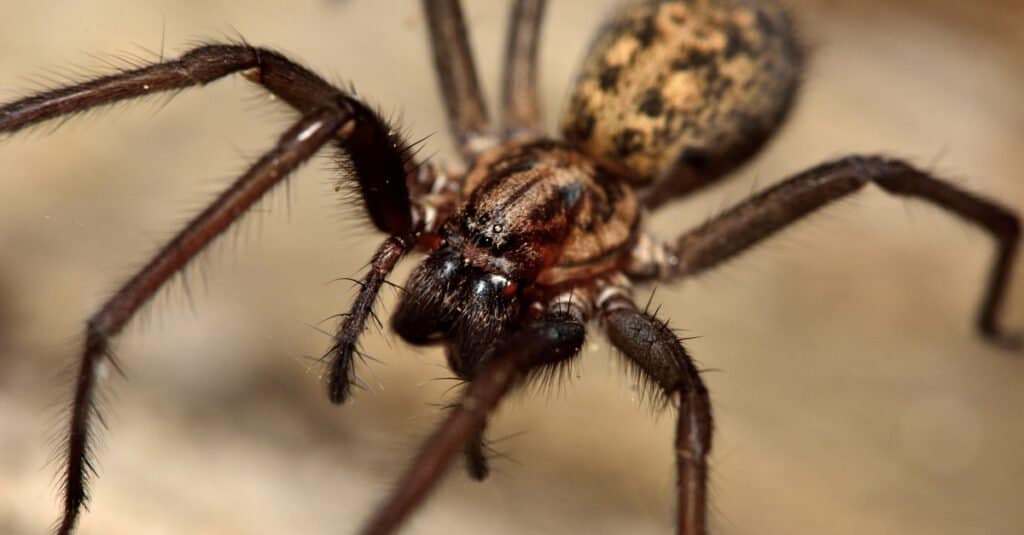
The common house spider is found in colors ranging from light tan to black. Females are 0.19 to 0.24 inches in length. Males are smaller in size measuring 0.15 to 0.19 inches long. These spiders weigh less than one ounce.
One of the features setting male common house spiders apart from females is the orangish-brown coloration on their legs.
These spiders have eight spindly legs and eight eyes. Surprisingly, even with so many eyes, they can’t see more than three or four inches in front of them.
One of the most interesting things about the common house spider is its body is similar in shape to the black widow spider. They both have bulb-shaped abdomen. But, despite a similar shape, the venom of a black widow spider is far more dangerous.
The Giant house spider is the largest type of house spider. The body of a female giant house spider can grow to almost three-quarters of an inch. Furthermore, they have a leg span of 1.8 inches.
Their dark colors help common house spiders disappear into the corner of an attic, garage, basement, or spare room in a home. In addition, their coloration can keep them hidden from cats, birds, and dogs that could consume them in one gulp. Though their venom kills small insects, it’s not powerful enough to harm a larger animal.
Common house spiders are mostly solitary with one exception. Scientists have observed males and females occupying the same web while they go through the mating process.
It’s not unusual to find the webs of two or three common house spiders in the same general space without being right next to one another. This is probably because there is an ample food source in the area.

IanRedding/Shutterstock.com
Habitat: Where to Find the Common House Spider
Common house spiders populate every area in the world except for Antarctica. True to their name they live in corners of homes, attics, garages, and garden sheds. When looking for a place to build a web, these spiders choose an area where the air is flowing. A corner of a window where air is leaking in from outside is a common place to find this spider. A corner in a drafty room or near a pipe that is coming in through an exterior house wall of are both favorable places to find this spider’s web. The flow of air increases the chances that a fly, mosquito, flea, or other insects will move through the area.
Diet What Do Common House Spiders Eat?
Spiders are carnivores. They are nocturnal so they eat and make repairs to the web at night.
What eats common house spiders?
Common house spiders are eaten by birds, spider wasps, centipedes, and sometimes domesticated dogs and cats.
What does a common house spider eat?
A common house spider captures flies, mosquitoes, ants, fleas, and other small insects in the sticky strands of its web. When an insect is caught, the spider puts additional silk threads on top of it. This spider bites its prey and injects it with venom to liquefy its organs. It drinks the insides of its prey and consumes any parts that are not too hard to ingest.
If you observe a common house spider in your home, look at the area beneath its web. The tiny pieces of debris are the discarded parts of its prey.
Prevention: How to Get Rid of Common House Spiders
One common house spider can get rid of a lot of insects in a home. Getting rid of these spiders can mean an increase in pesky flies, mosquitoes, and ants in a home.
However, some homeowners object to the webs and the debris beneath the webs left behind by these spiders. There are ways to get rid of common house spiders or discourage them from making webs in your home.
One way to discourage these spiders from entering your home is to make it less appealing. Check the insulation around your windows and doors.
When you vacuum your carpet, be sure to clean the baseboards too. Use your vacuum cleaner’s extension wand to clean all the corners of the room.
A natural repellent is another option. Spray it in various corners to discourage common house spiders from constructing their webs and laying eggs.
View all 157 animals that start with C
Common House Spider FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
How many legs does a common spider have?
Common house spiders have eight legs. This is one of those features along with enjoying a diet of insects shared by many types of spiders.
How do you identify a common house spider?
The colors of common house spiders range from tan to black. Males have a combination of orange and brown on their legs. The size of this spider’s body is less than one-quarter of an inch long.
If you see a large common house spider, it’s probably a female because they are bigger than males.
A female’s eggs are contained in a sac that looks like it’s made of very thin, brown paper. This is a common sight in this spider’s web.
One of the most notable features of this spider is its messy web. Other types of spiders spend hours building intricate webs complete with spirals and radials. But, a common house spider builds a web of uneven silken threads attached to a wall and whatever objects are around it. But, despite being a little messy, it serves its purpose!
Are common house spiders dangerous?
No, they are harmless. These spiders do have venom that they use on their regular diet of small insects. But this venom is not powerful enough to harm a human or even a pet.
What is the most common house spider to find in your house?
The American house spider is most often found in houses.
What does a common house spider bite look like?
The bite of this spider looks a lot like a small blister with a ring of red around it. Though it’s harmless to a human, it may itch a little bit as it heals.
Sources
- University of Wyoming, Available here: http://www.uwyo.edu/cesinsects/spider/eight-legged%20facts.htm
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Giant_house_spider
- Treehugger, Available here: https://www.treehugger.com/facts-about-misunderstood-house-spider-4868827
- ZME Science, Available here: https://www.zmescience.com/other/did-you-know/common-spiders-living-house/
- Galveston County Master Gardeners, Available here: https://aggie-horticulture.tamu.edu/galveston/beneficials/beneficial-22_spiders-overview.htm















