Brachiosaurus
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2022/05/Brachiosaurus-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2022/05/Brachiosaurus-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2022/05/Brachiosaurus.jpg”);
}
}
Brachiosaurus
Brachiosaurus
Palentologists originally believed that brachiosaurus lived in the water, but they lived on land.
Brachiosaurus Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Family
- Brachiosauridae
- Genus
- Brachiosaurus
- Scientific Name
- Brachiosaurus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Brachiosaurus Conservation Status
Brachiosaurus Facts
- Fun Fact
- Palentologists originally believed that brachiosaurus lived in the water, but they lived on land.
- Biggest Threat
- Injury, illness, and lack of food and water
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Its long neck
- Distinctive Feature
- Brachiosaurus was roughly the height of a 4-story building!
- Diet
- Herbivore
- Favorite Food
- Plants, including those up to 30 feet off the ground.
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2022/06/two-brachiosaurus-near-a-stream-in-the-nature-this-is-a-3d-render-picture-id1278212077-1024×614.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the Brachiosaurus images!
As one of the most recognizable dinosaurs, the popular Brachiosaurus was a well-known herbivore that liked to munch on leaves with its long, long neck.
Brachiosaurus actually refers to an entire genus of dinosaurs that lived during the Late Jurassic period. These dinosaurs have made appearances in everything from kids’ toys to blockbuster movies.
Brachiosaurus Species, Types, and Scientific Name
Brachiosaurus is a genus of the Brachiosauridae family. The most common species within this genus is B. altithorax. It is part of the Sauropoda clade, also known as Sauropods. This clade includes other long-necked dinosaurs. All of these dinosaurs were herbivores and lived very similar lives. There are Sauropods of all different sizes. Many even lived in the same regions at the same time.
Brachiosaurus was a dinosaur and part of the Chordata phylum. This refers to animals, including modern-day species. They were ultimately part of the Kingdom Animalia, the Animal Kingdom, just like today’s humans.
Brachiosaurus
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Clade | Sauropoda |
| Family | Brachiosauridae |
| Genus | Brachiosaurus |
| Species | Brachiosaurus altithorax |
Description and Size
Brachiosaurus is a genus in the Brachiosauridae family. They are one of the better-known Sauropods. The Sauropoda clade includes other herbivore dinosaurs that walk on four legs and have long tails and necks.
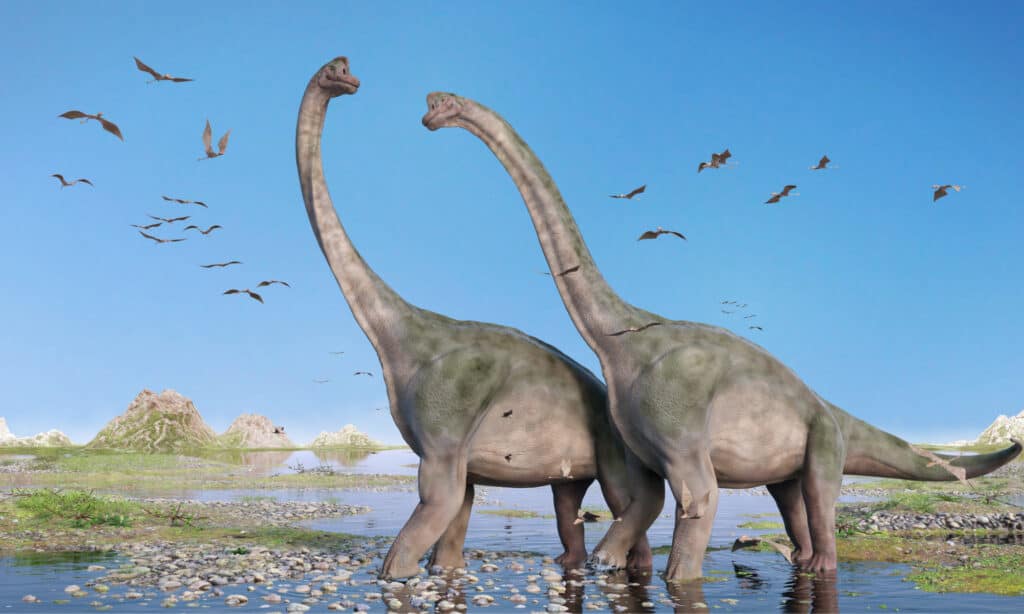
Brachiosaurus is known for its long neck. This is one of its most easily identified features. Based on specimens of the Brachiosaurus altithorax, estimates of its overall length are up to 85 feet. This accounts for length from the top of their head all the way to the tip of their tail. They stood between 30 and 40 feet tall. This helped them reach vegetation that was much higher than other dinosaurs of their day. Brachiosaurus was roughly the height of a modern four-story building!
The Brachiosaurus walked on four legs. Its front legs were longer than the back legs. Brachiosaurus is often referred to as the “arm lizard.” These longer front legs helped support their neck, which was longer and heavier than their tail. Longer front legs also helped Brachiosaurus reach higher into the trees for food. Brachiosaurus’ neck formed an S-shape, with the top curving forward and the base curving back to connect to its body. The middle section was relatively straight.
It had a relatively small head and brain compared to its large size. Brachiosaurus could weigh up to 28 tons. But due to their small legs relative to their long necks and large mid-sections, Brachiosaurus couldn’t actually run very fast.
Brachiosaurus nostrils were on top of their heads. This initially supported the idea that Brachiosaurus lived in water. Now, scientists believe that Brachiosaurus lived on land even though their nostrils were on the top of their bodies.

iStock.com/dottedhippo
Diet – What Did Brachiosaurus Eat?
Despite their giant size, Brachiosaurus subsisted entirely on plants. These herbivores ate leaves and other vegetation, often from high up in the trees. Like other Sauropods, Brachiosaurus ate plants while standing on four legs. Brachiosaurus could reach plants that were as high as 30 feet off the ground. Researchers believe that they favored high vegetation that was 16 feet or higher off the ground.
Brachiosaurus probably had to eat a lot to maintain its size. Some scientists believe that its long neck evolved to let it eat and digest complex plants that were high up in the trees. Other herbivores that lived alongside Brachiosaurus, including other Sauropods, ate from lower trees and branches.
Some of the fiercest competition for Brachiosauruses was likely getting enough food. They had to fight off other Sauropods and other Brachiosauruses to eat enough. Scientists theorize that the various species of Sauropods developed at different heights so that there was enough vegetation for each of them to eat their fill.
Habitat – When and Where It lived
The Brachiosaurus lived during the Late Jurassic period, between 156 and 145 million years ago. Many other Sauropods, including the Apatosaurus and Diplodocus, also lived during this time period. They probably lived through the Cretaceous Period.
Initially, scientists believed that Brachiosaurus lived in the water. They thought that their size was too large to be supported by their legs and bodies on land. However, based on further analysis of their feet as well as their bones, researchers now believe that Brachiosaurus roamed on land.
Based on discoveries of fossils, Brachiosaurus lived in North America. Many were found in the Morrison Formation in the Southwest United States. Scientists believe that this region was lush during the time of the dinosaurs, providing plenty of water from rivers and plant life to eat. Savannahs with ferns and conifer trees provided food for Brachiosaurus and other herbivores.
Threats And Predators
Many dinosaurs, even carnivores, probably left Brachiosaurus alone due to their large size. It would have taken a lot of smaller dinosaurs to take down an enormous Brachiosaurus.
Large carnivores that lived during the Jurassic Period included the Allosaurus and Dilophosaurus. The Tyrannosaurus rex did not actually evolve until after the Jurassic Period after the Brachiosaurus was no longer roaming the earth. Allosaurus was the main predator of the Jurassic Period. These carnivores were smaller than the better-known T. rex, although they were just as formidable of hunters.
Injury, illness, and lack of food and water were always threats to dinosaurs during this time. This included Brachiosaurus. While their environment was rich in natural resources that helped them survive, the young and old dinosaurs were the most vulnerable.
Discoveries and Fossils – Where It was Found
Brachiosaurus was first discovered in 1900. A team of researchers found fossils in Colorado in the Grand River Valley. They eventually classified these fossils as Brachiosaurus in 1903. The dinosaur was named by Paleontologist Elmer Riggs. https://imp.world/s/animals/location/north-america/united-states/colorado/
Other fossils discovered in the late 1800s were later determined to be Brachiosaurus fossils, specifically a skull. It wasn’t until 1998 that the link was made, however. These first discoveries were made in Colorado, although not identified as the first Brachiosaurus discoveries until over 100 years later.
The Morrison Formation in the Southwest United States is a rock formation where many fossils from the Jurassic Period were discovered, including Brachiosaurus. The rock formation stretches from Montana all the way to New Mexico. So many dinosaur fossils have been discovered here that the National Park Service designated it as the Dinosaur National Monument.
Brachiosaurus is one of the rarer finds in the Morrison Formation. However, scientists do know that they lived during the time period and in the same location as many dinosaurs that are plentiful in that rock formation. They have discovered large Brachiosaurus fossils in the rock dating to the Jurassic Period.
In 2019, scientists found a Brachiosaurus humerus fossil in the Morrison Formation. It weighed nearly 1,000 pounds and was over 6 feet long. Because its location was so hard to reach, the team had to use a pair of Clydesdale horses to pull it out of the earth. The horses were barely taller than the bone itself. The fossil was taken to the Utah Field House of Natural History State Park Museum.
Extinction – When Did It Die Out?
The latest fossils found of the Brachiosaurus show that it lived in the late Jurassic Period, probably around 145 million years ago. Most scientists believe that it lived into the Cretaceous Period and went extinct after a massive meteor hit the earth. Called an extinction event, the meteor caused the climate to shift so much that plants and animals were unable to survive the ice age went extinct.
Similar Animals to The Brachiosaurus
Many other Sauropods lived during the Jurassic Period and shared common features with the Brachiosaurus. These include:
- Apatosaurus: These Sauropods were a bit smaller than Brachiosaurus and likely ate vegetation that was lower to the ground. They still had long necks and tails. They also walked on four legs just like the Brachiosaurus.
- Diplodocus: Another Sauropod of the Jurassic Period, Diplodocus was longer and taller than Brachiosaurus. It weighed less, however.
View all 192 animals that start with B
Brachiosaurus FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
When did Brachiosaurus live?
The Brachiosaurus was alive during the Late Jurassic period, between 156 and 145 million years ago. Researchers believe that it lived all the way through the Cretaceous period and went extinct following a specific extinction event that caused an ice age.
How big was a Brachiosaurus?
Brachiosaurus was very long and tall. It measured around 85 feet from its head to the tip of its tail. It stood around 30-40 feet tall. It stood on four legs, although it could reach its neck high up into the trees for food.
Sources
- National Geographic Kids: Brachiosaurus, Available here: https://kids.nationalgeographic.com/animals/prehistoric/facts/brachiosaurus#:~:text=Huge%20herbivore,Why%20so%20big%3F
- National Geographic Kids: Apatosaurus, Available here: https://kids.nationalgeographic.com/animals/prehistoric/facts/apatosaurus
- NPS: Diplodocus, Available here: https://www.nps.gov/dino/learn/nature/diplodocus-longus.htm#:~:text=Diplodocus%20Facts,pair%20of%20processes%20called%20chevrons.
- Smithsonian Mag: Brachiosaurus discovery, Available here: https://www.smithsonianmag.com/smart-news/pair-horses-helped-excavate-hulking-brachiosaurus-fossil-utah-180974223/
- NPS: Morrison Formation, Available here: https://www.nps.gov/dino/learn/nature/morrisonformationutah.htm