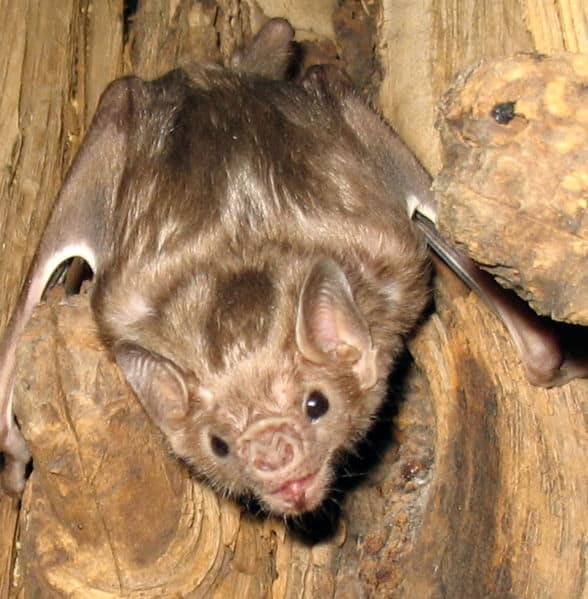
Bat
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/bat2-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/bat2-400×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/bat2.jpg”);
}
}
Detects prey using echolocation!
Bat Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Chiroptera
- Family
- Microchiroptera
- Genus
- Emballonuridae
- Scientific Name
- Chiroptera
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Bat Conservation Status
Bat Facts
- Main Prey
- Mice, Frogs, Fruit
- Distinctive Feature
- Large ears detect prey using echolocation and have strong, flexible wings
- Habitat
- Woodland and caves
- Predators
- Owls, Eagles, Snakes
- Diet
- Omnivore
- Average Litter Size
- 1
- Lifestyle
-
- Pack
- Favorite Food
- Mice
- Type
- Mammal
- Slogan
- Detects prey using echolocation!
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/bat4.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
“A mother bat gives birth to her babies while hanging upside down”
There are 47 species of bats living in the United States. Bats live in many types of environments except in extremely cold places (polar regions) and extremely hot ones (deserts). Bats are important pollinators and help to control the population of insects. These animals are social and live in groups that can number in the hundreds of thousands! Though vampire bats are the most well-known, there are only three species of bats that use another animal’s blood as food.
5 Bat Facts
• Some bats travel up to 2,400 miles each year to spend the winter in a place with a warm climate
• 70% of all bats feed on beetles, moths, flies, mosquitoes, and other insects
• The biggest type of bat in the world is known as the Pteropus
• Bats have been known to survive for over 20 years
• A bat is a mammal that can fly without ever gliding. Some bats are extremely fast. The Mexican free-tailed bat can reach speeds of more than 100 miles per hour making it the fastest animal in North America.
Bat Scientific Name
Bat is the common name of this remarkable animal while Chiroptera is its scientific name. The bat has a classification of Mammalia and is in the Microchiroptera family.
The Brazilian free-tailed bat has a subspecies called the Mexican free-tailed bat that lives the southern part of the United States. Also, the Virginia big-eared bat is a subspecies of the Townsend’s big-eared bat.
A bat’s scientific name is taken from the Greek words cheir, meaning hand and pteron meaning wing. This is because the parts of a bat’s wing resemble that of a hand with four ‘fingers’ covered with a thin membrane.
Bat Appearance and Behavior
A bat has a thin layer of brown, black or gray fur. They have small or large ears and small black eyes. Depending on its species, a bat can weigh as little as .07 ounces. Think of a bat that weighs .07 ounces as being lighter than a single penny. The largest species of bat can weigh up to 3.3 pounds. A bat weighing 3.3 pounds is about as heavy as half of an average sized brick.
The wings of a bat are its most memorable feature. A bat’s wing has four bones that you can think of as its fingers as well as a bone serving as a thumb. A thin layer of skin called a membrane connects these bones creating a bat’s flexible wing. If you’ve ever watched a bat fly, you know it can change direction in an instant. It’s these flexible finger bones in their wings that give them that skill. A bat’s wings also give it speed. The fastest bat can travel 99 mph.
When it comes to wingspan, the largest species of bat known as a flying fox, has a wingspan of five feet! When a flying fox stretches its wings to full length they would be almost a long/tall as a home’s refrigerator. The smallest species of bat, the Kitti hognosed bat, has a wingspan of a little less than six inches. This is less than half the length of a ruler you may use in school.
Bats are social animals and live in groups called colonies. (Though they like being around other bats, they are shy and will avoid people.) Sometimes a colony of bats can number in the hundreds of thousands. Living together is how a bat protects itself from predators. If an owl invades a colony of bats, most of the bats will be able to escape. The largest colony of bats is located in the Philippines. The Monfort bat colony there has 3 million bats and counting. Safety in numbers!

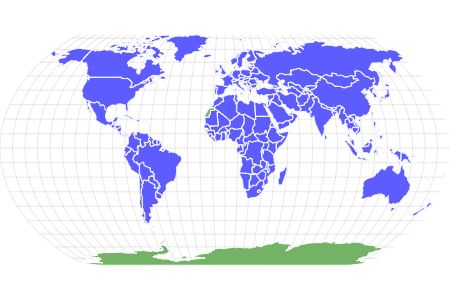
Bat Habitat
Bats live on many continents including Asia, North America, South America, Africa, Europe and Australia. However, there are no bats living in Antarctica because they prefer warm climates.
When you think of a bat’s home, you may imagine a colony of bats hanging from the ceiling of a cave. Bats also live in trees, under bridges, in burrows and even in manmade bat houses. They choose a place to roost where they’ll be hidden from predators and able to sleep during the day. Bats wrap their flexible wings around them when they sleep.
Some bats migrate to warmer places for the winter months. These flying mammals hibernate from about October or November until spring arrives in March. A bat living in a place where the temperature doesn’t fall below 45 degrees may not migrate to a warmer climate.
Learn more about other animal species that hibernate here.
Bat Diet
What do bats eat? Many bats eat insects such as mosquitoes,moths, cockroaches and beetles. A little brown bat can eat 500 insects in one hour. A colony of bats can consume 500,000 pounds of bugs per night. 500,000 pounds of bugs is equal to the weight of two blue whales!
Bats use echolocation to find their prey. As a bat flies, it lets out high-pitched squeaks and clicks that humans can’t hear. When the soundwaves created by a bat’s squeak hit an object, the sound echoes back to the bat. Think of echolocation as a bat’s personal radar system.
Other bats have a diet of nectar. These bats drink nectar from flowers just as hummingbirds do. Some bats eat fruit by sucking the juices of a ripe piece of fruit and spitting out the seeds. In addition, there are bats that eat fish. They fly over the water grabbing fish with their claws.
You’re probably familiar with the vampire bat. There are three types of these bats that drink blood from mammals such as cows or birds. They are found in South America and Mexico. It’s a myth that vampire bats suck the blood from these animals. Instead, they bite a cow, a sheep or a bird while it’s sleeping and lick the blood as it seeps out of the animal’s leg or other body part. This bat only takes in about two teaspoons of an animal’s blood.
Bat Predators and Threats
Bats have a few predators including owls, falcons, eagles, snakes, raccoons and cats. An owl may sit on a tree near a cave or bridge where a bat is sleeping and capture it as it flies out to hunt in the evening. Alternatively, a raccoon or snake may pick up a baby bat that’s fallen from its mother’s grasp and landed on the ground.
Bats face the threat of loss of habitat due to people clearing trees to build homes and businesses. If they’re disturbed during the hibernation period they can starve or die due to exposure to the cold. Also, when land and crops are cleared it can remove the food source of bats. Some bats are threatened in cultures that use them for food or medicine.
The conservation status of bats is: Least Concerned. Many bat conservation groups offer suggestions to the public on how they can help make sure bats continue to thrive and grow in population. Some of those suggestions include avoiding the use of pesticides in gardens and building a bat house to provide protection for local bats. Also, if you find a bat in hibernation, don’t disturb it.
Bat Reproduction, Babies and Lifespan
Did you know a bat can sing? Male bats sing and unfold their wings to attract female bats during mating season. Unfortunately, people can’t hear the high-pitched song of bats. A male bat marks its territory during mating time with liquid from its scent glands. Bats swarm during this time allowing them to find a mate. A female bat can be pregnant for 40 days or six months depending on its species. Most have one baby, once a year.
A mother bat gives birth to its baby or pup while she is hanging upside down. She must catch her pup with her wings after it’s born! A pup weighs about ¼ of the total weight of its mother. So, if a pup’s mom weighs one pound, the baby weighs just ¼ of a pound. A pup of this size is not quite as heavy as a hamster. A pup is born blind and without hair. It drinks milk from its mother for up to six months and clings to her as she flies. After six months, a mother teaches its pup to fly and hunt for food. Once a pup learns these skills, it’s able to survive on its own.
Depending on its species, a bat can live from 5 to 30 years. Scientists have observed that hibernating bats have a tendency to live longer than non-hibernating ones. In many species of bat, females live longer than males. The oldest bat on record lived to be 41 years old!
A disease known as White-nose syndrome is responsible for killing both young and older bats as they hibernate. This disease takes away from a bat’s store of fat as it sleeps. This can cause the bat to wake up and fly out of the cave in search of food. Chances are that the weakened bat will starve because the supply of insects is low in the wintertime.
Bat Population
There are over 1,300 species of bats throughout the world. The highest concentration of bat species live near the equator. The conservation status of bats is: Least Threatened and the population is holding fairly steady. However, conservation efforts are always in place for bats because most have just one pup per year.
View all 192 animals that start with B
Bat FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are bats carnivores, herbivores or omnivores?
Bats are omnivores. Fruit bats eat avocados, mangoes, bananas, wild dates and more. Three species of vampire bats live on blood from other mammals. Some bats drink nectar from flowers including honey suckle, yucca and evening primrose. Not surprisingly, these bats especially love the nectar of moonflowers! Some species of bats eat fish, mice and frogs.
Do bats bite?
Yes, bats do bite. Vampire bats usually bite the leg of a cow or goat to get the blood to leak out so it can drink a little of it. A bat would only bite a human if it felt threatened. But, bats are known to keep away from people.
Are bats blind?
No, bats aren’t blind. This is one of the biggest myths out there. Bats are nocturnal so they look for food when it’s dark. They don’t see well in the dark, but they aren’t blind.
Are bats dangerous?
No, bats aren’t dangerous. In fact, just the opposite! Like butterflies and bees, bats are important pollinators that help trees and flowers to grow. They spread seeds that help to grow breadfruit, figs, peaches, dates, bananas, avocados and other fruits. Plus, they eat insects helping to keep the bug population to a manageable number. As a note, bats have a reputation for carrying rabies. In reality, a very small number of bats carry this disease. Still, if you come into contact with a bat it’s good to see medical help. In the United States, five people died from contracting rabies from a bat in 2021, none received a PEP vaccination that could have prevented the spread of rabies if applied shortly after exposure.
What does it mean when you see a bat?
When you see a bat you know that the sun has gone down and it’s time to find food. If you see a bat in your backyard, you know the bat has made its home in a nearby tree or has found a cozy place in an attic. Finally, you know the bat has found its food source in your area. Whether it’s nectar, insects or fruit, the bat will stick around just as long as it finds its dinner each night!
What Kingdom do Bats belong to?
Bats belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum do Bats belong to?
Bats belong to the phylum Chordata.
What class do Bats belong to?
Bats belong to the class Mammalia.
What family do Bats belong to?
Bats belong to the family Microchiroptera.
What order do Bats belong to?
Bats belong to the order Chiroptera.
What genus do Bats belong to?
Bats belong to the genus Emballonuridae.
What type of covering do Bats have?
Bats are covered in Fur.
In what type of habitat do Bats live?
Bats live in woodlands and caves.
What is the main prey for Bats?
Bats prey on mice, frogs, and fruit.
What are some distinguishing features of Bats?
Bats have strong, flexible wings and large ears that detect prey using echolocation.
What are some predators of Bats?
Predators of Bats include owls, eagles, and snakes.
What is the average litter size for a Bat?
The average litter size for a Bat is 1.
What is an interesting fact about Bats?
Bats detect prey using echolocation!
What is the scientific name for the Bat?
The scientific name for the Bat is Chiroptera.
What is the lifespan of a Bat?
Bats can live for 10 to 30 years.
How fast is a Bat?
A Bat can travel at speeds of up to 25 miles per hour.
What are the key differences between mouse poop and bat poop?
The key differences between mouse poop and bat poop are appearance and characteristics.
How to say Bat in …
Прилепи
Ratapinyada
Letouni
Flagermus
Fledertiere
Bat
Murciélago
Ĥiropteroj
Lepakot
Chauve-souris
עטלפים
Netopiri
Kelelawar
Chiroptera
Vliermuis
Vleermuis
Flaggermus
コウモリ
Nietoperze
Morcego
Fladdermöss
yarasa
蝙蝠
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World’s Wildlife
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David W. Macdonald, Oxford University Press (2010) The Encyclopedia Of Mammals