African Wild Dog
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/african_wild_dog-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/african_wild_dog-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/african_wild_dog.jpg”);
}
}
Also known as the painted dog!
African Wild Dog Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Carnivora
- Family
- Canidae
- Genus
- Lycaon
- Scientific Name
- Lycaon pictus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
African Wild Dog Conservation Status
African Wild Dog Facts
- Prey
- Antelope, Warthog, Rodents
- Name Of Young
- Pup
- Group Behavior
-
- Pack
- Fun Fact
- Also known as the painted dog!
- Estimated Population Size
- Less than 5,000
- Biggest Threat
- Habitat loss
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Four toes on each foot rather than five
- Other Name(s)
- Hunting Dog, Painted Dog, Painted Wolf
- Gestation Period
- 70 days
- Habitat
- Open plains and savanna
- Predators
- Lions, Hyenas, Humans
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Average Litter Size
- 8
- Lifestyle
-
- Crepuscular
- Common Name
- African Wild Dog
- Number Of Species
- 1
- Location
- sub-Saharan Africa
- Slogan
- Also known as the painted dog!
- Group
- Mammal
African Wild Dog Physical Characteristics
- Color
-
- Brown
- Grey
- Red
- Black
- White
- Gold
- Tan
- Skin Type
- Fur
- Top Speed
- 45 mph
- Lifespan
- 10 – 13 years
- Weight
- 17kg – 36kg (39lbs – 79lbs)
- Length
- 75cm – 110cm (29in – 43in)
- Age of Sexual Maturity
- 12 – 18 months
- Age of Weaning
- 3 months
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/african_wild_dog4.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the African Wild Dog images!
African Wild Dog Classification and Evolution
The African Wild Dog (also known as the Painted Dog and the Cape Hunting Dog) is a medium sized species of canine found across sub-Saharan Africa. The African Wild Dog is most easily identified from both domestic and other wild Dogs by their brightly mottled fur, with its name in Latin aptly meaning painted wolf. The African Wild Dog is said to be the most sociable of all the canines, living in packs of around 30 individuals. Sadly however, this highly intelligent and sociable animal is severely under threat in much of its natural habitat, primarily due to habitat loss and having been hunted by Humans.
African Wild Dog Anatomy and Appearance
The most distinctive feature of the African Wild Dog is its beautifully mottled fur which makes this canine very easy to identify. The fur of the African Wild Dog is red, black, white, brown and yellow in colour with the random pattern of colours being unique to each individual. It is also thought to act as a type of camouflage, helping the African Wild Dog to blend into its surroundings. The African Wild Dog also has large ears, a long muzzle and long legs, with four toes on each foot. This is one of the biggest differences between the African Wild Dog and other canine species as they have five. They also have a large stomach and a long, large intestine which aids them in more effectively absorbing moisture from their food.
African Wild Dog Distribution and Habitat
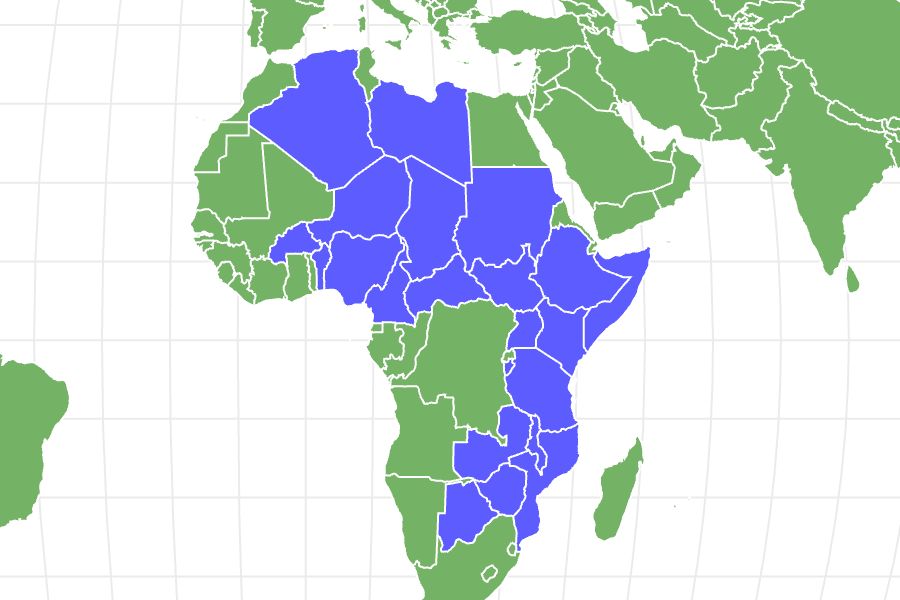
African Wild Dogs are found naturally roaming the deserts, open-plains and arid savanna of sub-Saharan Africa where the range of the African Wild Dog has decreased rapidly. It is thought that the African Wild Dog was once found in nearly 40 different African countries but that number is much lower today, at between 10 and 25. Now most African Wild Dog populations are primarily restricted to National Parks across southern Africa, with the highest populations found in Botswana and Zimbabwe. African Wild Dogs require large territories to support the pack, with pack sizes having in fact dropped in number with their decreasing home-ranges.
African Wild Dog Behaviour and Lifestyle
African Wild Dogs are highly sociable animals that gather in packs of generally between 10 and 30 individuals. There is a strict ranking system within the pack, led by the dominant breeding pair. They are the world’s most sociable Dogs and do everything as a group, from hunting for and sharing food, to helping sick members and assisting in raising young. African Wild Dogs communicate between one another through touch, movement and sound. Pack members are incredibly close, gathering together before a hunt to nose and lick each other, whilst wagging their tails and making high-pitched noises. African Wild Dogs lead a crepuscular lifestyle meaning that they are most active during dawn and dusk.
You can check out incredible facts about African wild dogs.
African Wild Dog Reproduction and Life Cycles
In African Wild Dog packs, there is usually only one breeding pair, which are the dominant male and female members. After a gestation period of around 70 days, the female African Wild Dog gives birth to between 2 and 20 pups in a den, which she remains in with her young for the first few weeks, relying on the other pack members to provide her with food. The African Wild Dog cubs leave the den at between 2 and 3 months old and are fed and cared for by the entire pack until they are old enough to become independent and generally leave to join or start another African Wild Dog pack. It is thought that the more looked after the pups are, the higher their chances of survival.
African Wild Dog Diet and Prey
The African Wild Dog is a carnivorous and opportunistic predator, hunting larger animals on the African plains in their big groups. African Wild Dogs primarily prey on large mammals such as Warthogs and numerous species of Antelope, supplementing their diet with Rodents, Lizards, Birds and Insects. They are even known to hunt much larger herbivores that have been made vulnerable through sickness or injury, such as Wildebeest. Although the African Wild Dog’s prey is often much faster, the chase can last for miles, and it is this Dog’s stamina and perseverance that makes them so successful, along with their ability to maintain their speed. Hunting as a pack also means that the African Wild Dogs can easily corner their prey.
African Wild Dog Predators and Threats
Due to the relatively large size and dominant nature of the African Wild Dog and their pack, they have few natural predators within their native habitats. Lions and Hyenas have been known on occasion, to prey on African Wild Dog individuals that have been separated from the rest of the group. One of the biggest threats to the African Wild Dog are farmers that hunt and kill the African Wild Dog in fear that they are preying on their livestock. A drastic decline in their natural habitats has also pushed the remaining African Wild Dog populations into small pockets of their native regions, and they are now most commonly found within National Parks.
African Wild Dog Interesting Facts and Features
The long large intestine of the African Wild Dog means that they have a very efficient system for absorbing as much moisture from their food as possible. This gives these canines an advantage in such arid climates as they do not need to find such a regular supply of water. African Wild Dogs are therefore able to go for long periods of time without needing to drink. Unlike many other carnivores, African Wild Dogs kill their prey by starting to bite it when it is still alive. Although this may sound cruel, the animal actually dies more quickly and less painfully than if it was killed in the generally preferred way.
African Wild Dog Relationship with Humans
African Wild Dog populations have been declining rapidly across the southern African countries mainly due to loss of much of their natural habitat and the fact that they are commonly hunted by farmers in particular. The slightly savage nature of the African Wild Dog has led to a great deal of superstition regarding it, with locals having almost wiped out entire populations in certain areas. The loss of their historical ranges generally due to growing Human settlements has also led to drastic declines in populations throughout much of their environment. Although the majority of the African Wild Dog population is today confined to National Parks, they tend to require much larger territories and come into conflict with Humans when they leave these protected areas.
African Wild Dog Conservation Status and Life Today
Today, the African Wild Dog is listed as an Endangered species by the IUCN as African Wild Dog population numbers have been rapidly declining, particularly in recent years. There are thought to be less than 5,000 individuals left roaming sub-Saharan Africa today, with numbers still declining. Hunting, habitat loss and the fact that they are particularly vulnerable to the spread of disease by livestock, are the main causes for the continent’s African Wild Dog loss.
View all 127 animals that start with A
African Wild Dog FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are African Wild Dogs herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
African Wild Dogs are Carnivores, meaning they eat other animals.
What Kingdom do African Wild Dogs belong to?
African Wild Dogs belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What phylum to African Wild Dogs belong to?
African Wild Dogs belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do African Wild Dogs belong to?
African Wild Dogs belong to the family Canidae.
What order do African Wild Dogs belong to?
African Wild Dogs belong to the order Carnivora.
What type of covering do African Wild Dogs have?
African Wild Dogs are covered in Fur.
What genus do African Wild Dogs belong to?
African Wild Dogs belong to the genus Lycaon.
Where do African Wild Dogs live?
African Wild Dogs live in sub-Saharan Africa.
In what type of habitat do African Wild Dogs live?
African Wild Dogs live in open plains and savannas.
What are some predators of African Wild Dogs?
Predators of African Wild Dogs include lions, hyenas, and humans.
How many babies do African Wild Dogs have?
The average number of babies an African Wild Dog has is 8.
What is an interesting fact about African Wild Dogs?
The African Wild Dog is also known as the painted dog!
What is the scientific name for the African Wild Dog?
The scientific name for the African Wild Dog is Lycaon pictus.
What is the lifespan of an African Wild Dog?
African Wild Dogs can live for 10 to 13 years.
How many species of African Wild Dog are there?
There is 1 species of African Wild Dog.
What is the biggest threat to the African Wild Dog?
The biggest threat to the African Wild Dog is habitat loss.
What is another name for the African Wild Dog?
The African Wild Dog is also called the hunting dog, painted dog, or painted wolf.
How many African Wild Dogs are left in the world?
There are less than 5,000 African Wild Dogs left in the world.
How fast is an African Wild Dog?
An African Wild Dog can travel at speeds of up to 45 miles per hour.
How to say African Wild Dog in …
Хиеново куче
Gos salvatge africà
Pes hyenovitý
Hyænehund
Afrikanischer Wildhund
African Wild Dog
Lycaon pictus
Hyeenakoira
Lycaon (mammifère)
Lycaon pictus
זאב טלוא
Afrički divlji pas
Afrikai vadkutya
Lycaon pictus
リカオン
Afrikaanse wilde hond
Afrikansk villhund
Likaon (pies)
Mabeco
Afrikansk vildhund
Afrika yaban köpeği
非洲野犬
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World’s Wildlife
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David W. Macdonald, Oxford University Press (2010) The Encyclopedia Of Mammals
- African Wild Dog Behaviour, Available here: http://animals.nationalgeographic.com/animals/mammals/african-hunting-dog/
- African Wild Dog Habitats, Available here: http://www.predatorconservation.com/wild%20dog.htm
- About African Wild Dogs, Available here: http://www.honoluluzoo.org/african_hunting_dog.htm
- African Wild Dog Packs, Available here: http://www.outtoafrica.nl/animals/engafricanwilddog.html?zenden=2&subsoort_id=4&bestemming_id=1