Toadfish
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/01/Toadfish-close-up-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/01/Toadfish-close-up-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/01/Toadfish-close-up.jpg”);
}
}
Toadfish
Can be heard out of water
Toadfish Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Toadfish Conservation Status
Toadfish Facts
- Prey
- Sea worms, crustaceans, mollusks, other fish
- Group Behavior
-
- Territorial
- Fun Fact
- Can be heard out of water
- Estimated Population Size
- Unknown
- Biggest Threat
- Hunting/trapping, pollution
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Toadlike appearance
- Other Name(s)
- Frogfish, dogfish
- Gestation Period
- Varies
- Habitat
- Worldwide
- Predators
- Marine mammals, sea turtles, other fish
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Type
- Vertebrate
- Common Name
- Frogfish
- Number Of Species
- 83
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/01/Toadfish-close-up-1024×535.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the Toadfish images!
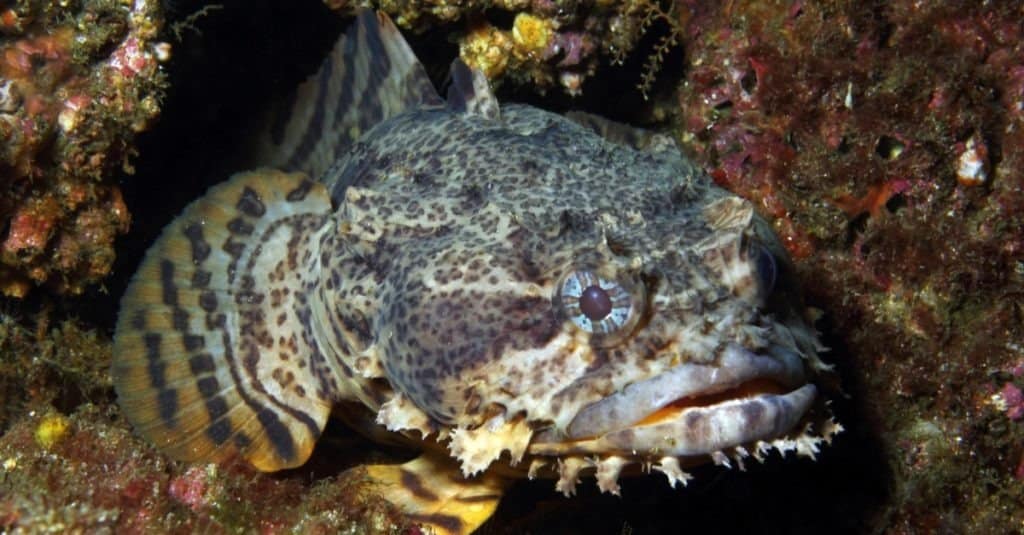
Unlike most fish, Toadfish are very vocal
Toadfish is the common name for all fish in the family Batrachoididae as well as some species in the families Tetraodontidae and Psychrolutidae. . Certain species along the Gulf coast are called dogfish. Its venom, textrodoxin, is the most dangerous poison in the world. Like pufferfish, it must be prepared and cooked correctly in order to be edible.
7 Incredible Toadfish Facts!
- The poison of these fishes is up to 100 times deadlier than black widow spider venom.
- There is no antidote for their poison.
- Sting treatment or first aid for these fish is similar to that of pufferfish.
- These fish is edible and surprisingly delicious when rendered safe to eat.
- These fish have many light-emitting cells (photophores) around the body.
- These fish are very vocal and their calls can be heard out of water.
- The fish’s call is a buzzing sound like the horn of a ship.
Toadfish Classification and Scientific Name
Toadfish is the common name for fish in the family Batrachoididae and some species in the families Tetraodontidae and Psychrolutidae. The genera Thalassophryne and Daector are of these fish. These fish are related to pufferfish, and some pufferfish are called toadfish, such as the pufferfish family Tetraodontidae. The common species (Tetractenos hamiltonii), also known as the common toado, or toado, and the smooth species (Tetractenos glaber) are both species in the family Tetraodontidae of order Tetraodontiformes. The oyster toadfish (Opsanus tau) is of the family Batrachoididae. The word “dogfish” refers to the gulf or orange species (Opsanus beta) which is also called mudfish or oysterdog.
These fish are divided into three groups: true toadfishes, including the oyster toadfish (Opsanus tau) in eastern North America; venomous species (Thalassophryne and Daector), found in Central and South America; and midshipmen (Porichthys), American fishes named for the rows of small, round light organs along their bodies.
Toadfish Species
“True” toadfish or frogfish are in the family Batrachoidinae in the ray-finned fish order Batrachoidiformes, with 83 species grouped into 21 genera. The family Tetraodontidae (order Tetraodontiformes) has 196 species worldwide grouped into 26 genera and 2 subfamilies, while Psychrolutidae has 40 species grouped into 9 genera.
Some examples of these fish species in the family Batrachoidinae are:
- Big-eyed toadfish (Thalassophryne megalops)
- Pacuma toadfish (Batrachoides surinamensis)
- Freshwater or grunting toadfish (Allenbatrachus grunniens)
Species in the pufferfish family Tetraodontidae are:
- The banded toadfish (Torquigener pleurogramma)
- The blackspotted toadfish (Arothron nigropunctatus)
- The common toadfish or toadfish (Tetractenos hamiltoni)
- The prickly toadfish (Contusus richei)
- The red striped toadfish (Tetraodon erythrotaenia)
- The smooth toadfish (Tetractenos glaber)
Fish in the blobfish family Psychrolutida are:
- The dark toadfish (Neophrynichthys latus)
- The frilled toadfish (Ambophthalmos magnicirrus)
- The pale toadfish (Ambophthalmos angustus)
Toadfish Appearance
True to their name, these fish look like toads. Plus, their swim bladders can create a sound like that of a toad. Their skin is scaleless and covered with mucus, with some species having spines within or protruding from the skin. Their coloring is usually drab, although there are exceptions. The gulf fish is light to dark orange and the splendid or coral toadfish (Sanopus splendidus) has bright yellow fins with distinctive patterns and white and dark stripes on its head.
Physically, these fish are heavy-bodied with broad, flat heads and large mouths containing strong teeth and surrounded by barbels. They are either scaleless or have small scales. Many grow to a maximum of about 40cm (16in) although their length can range anywhere from the 7.5cm (3in) to 57cm (22in) of the big-eyed (Thalassophryne megalops) to the 30cm (12in) of the freshwater or grunting toadfish (Allenbatrachus grunniens) to the 57cm (22in) of the Pacuma toadfish (Batrachoides surinamensis).
Another unique feature of these fish is a large number of photophores, or light-emitting cells, which are scattered around their bodies. They can have up to 700 of these specialized glands, thought to contain large numbers of luminescent bacteria, which possibly serve to attract prey and mates. Photophores are a common feature among the fishes inhabiting the deepest and darkest levels of the sea.

Joe Quinn/Shutterstock.com
Toadfish Distribution, Population, and Habitat
Most species of this fish live close to the shoreline but remain close to the sea bed, while others are purely bottom-dwelling. They are found worldwide, with most species being marine. Some live in brackish water, while the subfamily Thalassophryninae is exclusively in the freshwater habitats of South America. For example, Daector quadrizonatus and Thalassophryne amazonica are from the Atrato River in Colombia and the Amazon River, respectively.
The species Porichthys notatus, called Plainfin Midshipman, Humming Toadfish or California Canary fish has a habitat range from Alaska to the Gulf of California. The Pacuma toadfish (Batrachoides surinamensis) lives in the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, specifically along the coasts from Honduras to Brazil. The Lusitanian toadfish (Halobatrachus didactylus) lives along the Atlantic coast of Africa and the Mediterranean. Other species live in the Indian and Pacific oceans, such as the freshwater or grunting toadfish (Allenbatrachus grunniens) in Madagascar, India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Thailand, Cambodia, and Malaysia. Many species also live around Australia and New Zealand.
Toadfish Predators and Prey
These fish are slow swimmers. They are benthic ambush predators, meaning they are bottom-dwelling and sit and wait to hunt their prey. Their diets are carnivorous. When touched, sometimes they bite.
What do toadfish eat?
These fish eat sea worms, such as bloodworms. They also eat crustaceans, mollusks, and other fish.
What eats toadfish?
Dolphins are a major predator of these fish. Their calls alert each other. For example, the fish will decrease their mating calls by 50% to avoid alerting dolphins, while the dolphin “pop” sound alerts the fish to their nearby presence. Barracuda prey upon all species of these fish. Other potential predators are other marine mammals, sea turtles, and other fish.
Toadfish Reproduction and Lifespan
These fish use their swim bladders to create noise, especially males who “sing” their mating calls. They are said to sound like the horn of a ship or a motorboat-like drone using a “music muscle” to vibrate against their swim bladders. There are two types of these fish. Type 1 are large, prepare and guard rock nests, and can produce the sustained humming needed to attract females, while Type 2 are meek males who cannot create the “love song” and sneak in to fertilize eggs.
Even during breeding, these fish remain at deep sea levels. The female lays the eggs on the sticky top of the nest and then leave. The eggs are large and hatch after one month, after which the male guards the nest while the fry remain attached and grow for three to four weeks. The fry hide behind the female until they are old enough to feed themselves.
Toadfish in Fishing and Cooking
The venomous fishes of the genera Thalassophryne and Daector in Central and South America have hollow, venom-injecting spines which sometimes people step on. Other species like the gulf or orange toadfish likewise have venomous spines. The skin and ovaries also contain venom.
In order to prepare properly, it must be steamed, skinned, and thoroughly cooked. In spite of their repulsive appearance, however, these fish has a reputation for being delicious for people who are brave enough to cook or eat them.
Toadfish Population
The IUCN lists most species of these fish as Least Concern. However, the splendid, Cozumel splendid or coral toadfish, native to the Caribbean island of Cozumel, is listed as Endangered due to hunting/trapping and pollution.
View all 74 animals that start with T
Toadfish FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Can you eat toadfish?
Toadfish are edible if prepared properly but must be skinned and cooked thoroughly. Just a brief taste of a raw toadfish can be fatal.
Are toadfish poisonous?
Yes, toadfish are extremely deadly due to the poison in their skin.
Are toadfish dangerous to touch?
Yes, they are dangerous to touch or even step on.
How big do toadfish get?
They can get as long as 57cm (22in) and as heavy as 2.3kg (5.1lbs).
How do you treat a toadfish sting?
Sting treatment for toadfish does not have an antidote. However, immediate response is of the greatest importance in sting treatment and includes the following steps after calling the ambulance or before going to the doctor:
- Extract as much poison as possible by putting pressure on the wound.
- Place a tourniquet a few centimeters above the wound and loosen it for blood circulation. 3.) Use hot water at 50 degrees to alleviate pain, for an hour to an hour and a half.
- If the wound is not bleeding, make a small cut to help expel poison.
- A doctor will inject 0.1-0.5ml of 5% potassium permanganate, and for pain, an intramuscular injection of meperidine hydrochloride.
What is the lifespan of a Toadfish?
Toadfish live for 3-24 years.
In what type of habitat do Toadfish live?
Toadfish live in streams and oceans.
What is another name for the Toadfish?
The Toadfish is also called the frogfish or dogfish.
How many Toadfish are left in the world?
The population size of the Toadfish is unknown.
What is an interesting fact about the Toadfish?
Toadfish can be heard out of water.
How do Toadfish have babies?
Toadfish lay eggs.
Sources
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Toadfish
- Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/venomous-toadfish
- Florida Museum, Available here: https://www.floridamuseum.ufl.edu/discover-fish/species-profiles/opsanus-beta/
- All The Sea, Available here: http://www.allthesea.com/Deep-Sea-Fish-Toadfish.html
- Our Marine Species, Available here: https://ourmarinespecies.com/c-fishes/lusitanian-toadfish/-Toadfish.html
- Encyclopedia, Available here: https://www.encyclopedia.com/plants-and-animals/animals/vertebrate-zoology/toadfish
- Vedantu, Available here: https://www.vedantu.com/biology/benthic-zone
- SF Gate, Available here: https://www.sfgate.com/news/article/Toadfish-s-steamy-love-life-is-revealed-Singing-2525265.php.