Psittacosaurus
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2022/05/Psittacosaurus-standing-on-back-legs-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2022/05/Psittacosaurus-standing-on-back-legs-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2022/05/Psittacosaurus-standing-on-back-legs.jpg”);
}
}
Psittacosaurus
Psittacosaurus
These parrot-headed dinosaurs had beaks and feather-like quills on their tails!
Psittacosaurus Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Order
- Ornithiscia
- Family
- Psittacosauridae
- Genus
- Psittacosaurus
- Scientific Name
- Psittacosaurus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Psittacosaurus Conservation Status
Psittacosaurus Facts
- Group Behavior
-
- Herd
- Herds
- Fun Fact
- These parrot-headed dinosaurs had beaks and feather-like quills on their tails!
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Quills running up and down its back and its tail
- Distinctive Feature
- A toothless beak
- Habitat
- Dense forests
- Favorite Food
- Prehistoric plants like cycads
- Type
- Dinosaur
- Number Of Species
- 12
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2022/05/Psittacosaurus-standing-on-back-legs-1024×614.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the Psittacosaurus images!
Description and Size
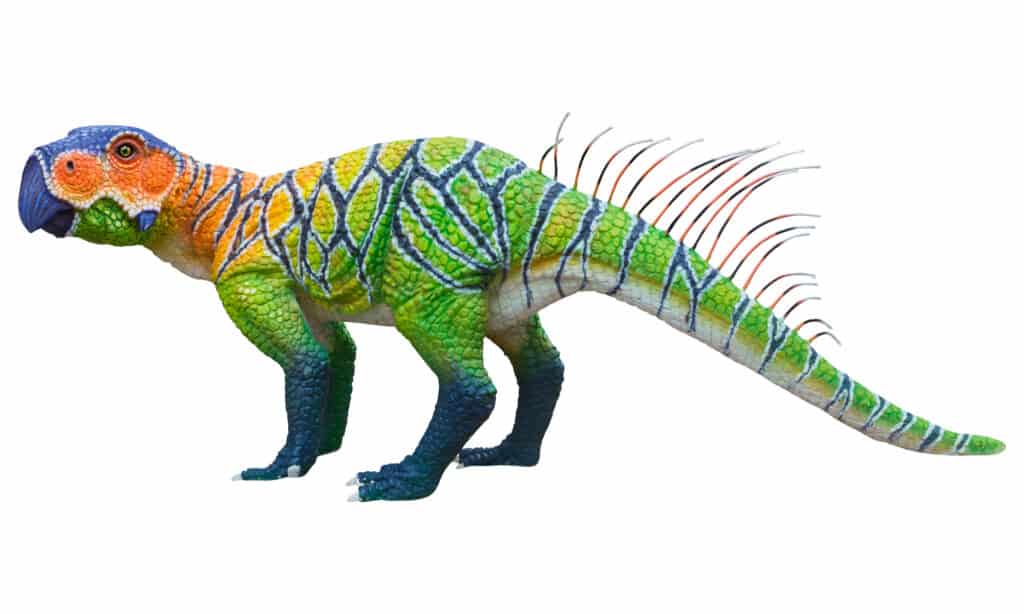
This dinosaur’s name means “parrot lizard” in Latin, and indeed the little dinosaur did resemble that colorful bird in certain key ways. Its skull extended into a toothless beak, and it had quills running up and down its back, and along its tail, which many scientists believe were an early precursor to feathers. The Psittacosaurus did have teeth in the very rear of its mouth, but it did not have molars for grinding the vegetation it fed on, leading paleontologists to infer that it swallowed stones to aid in its digestive processes, much as parrots do today.
The Psittacosaurus was a relatively small dinosaur and when fully mature, it was bipedal, moving on its two back limbs. It used its forelimbs for grasping and carrying objects. Scientists speculate this dinosaur may have been semi-aquatic since so many of its fossils have been found in the vicinity of lake residues.
Its leathery skin was covered with brown scales except along its abdomen and the underside of its tail. This two-toned color pattern, known as “countershading,” is thought to have served a camouflage function that allowed the dinosaur to blend more easily into its forest habitat. The Psittacosaurus was 2.6 to 6.5 feet long and 4 feet high; it weighed between 50 and 175 pounds.
YuRi Photolife/Shutterstock.com
Diet – What Did Psittacosaurus Eat?
The Psittacosaurus was an herbivore. Its beak-like mouth appears to have evolved to help it pluck leaves and nuts from low-growing trees in the deep forests it inhabited. Since its teeth were not adapted for grinding, it’s probable this dinosaur swallowed pebbles and small rocks to break up the food that passed through its digestive system. Such small stones are often found inside the abdominal cavities of fossilized Psittacosaurus.
Habitat – When and Where Did Psittacosaurus Live?
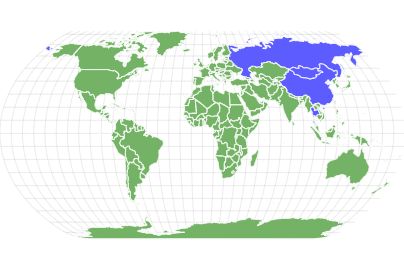
All Psittacosaurus fossils that have been excavated so far have been found in Early Cretaceous sediments throughout various parts of Asia, which would seem to indicate that Psittacosaurus roamed the earth between 126 million and 101 million years ago. Fossils have been unearthed in parts of Mongolia, Siberia, and Thailand.
Threats And Predators
Like many plant-eaters, Psittacosaurus appears to have had its fair share of predators. It was probably hunted by carnivorous dinosaurs and possibly by prehistoric crocodiles as well when it ventured into the water.
One of the most famous Psittacosaurus predators was a mammal called Repenomamus, which looked something like a three-foot-long badger. In 2005, paleontologists discovered a Repenomamus fossil with the remains of a juvenile Psittacosaurus in its gut. The juvenile Psittacosaurus showed unmistakable signs of having been masticated.
Discoveries and Fossils – Where Psittacosaurus Was Found
The first fossil to be identified as Psittacosaurus was discovered in 1923 by an American Museum of Natural History expedition to the Gobi Desert. The specimen was named “Psittacosaurus mongoliensis” by Henry Fairfield Osborn, the scientist who discovered it, after the country where it was discovered, Mongolia. Eleven other Psittacosaurus species have subsequently been excavated and identified.
Much is known about the Psittacosaurus because its fossil remains are so abundant. No fewer than 75 sets of fossil Psittacosaurus mongoliensis remains have been excavated, including representatives of every stage of the Psittacosaurus lifespan from juvenile specimens, newly hatched and measuring a mere five inches long, to elderly specimens, measuring six and a half feet long. Twenty complete Psittacosaurus mongoliensis specimens with skulls have been recovered in all. Nearly 400 fossils representing 11 other Psittacosaurus species have also been discovered.
Psittacosaurus species include:
- Psittacosaurus mongoliensis
- Psittacosaurus mazongshanensis
- Psittacosaurus meileyingensis
- Psittacosaurus neimongoliensis
- Psittacosaurus ordosensis
- Psittacosaurus sattayaraki
- Psittacosaurus sinensis
- Psittacosaurus xinjiangensis
One of the most spectacular of these fossil discoveries was made in 2014 when a joint research team of paleontologists from the Royal Tyrrell Museum of Alberta, Canada, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences unearthed a nest of six juvenile Psittacosaurus buried in a volcanic mudflow more than 120 million years ago. The differing age ranges of the specimens suggested that even though they were living together as a group, they were not members of the same brood. This observation offers valuable insights into the social behavior of these dinosaurs: It seems likely they congregated in flocks.
Extinction – When Did Psittacosaurus Die Out?
The time period within which the Psittacosaurus became extinct is not known with any degree of certainty. However, it’s likely extinction took place sometime within the mid- Cretaceous period.
Similar Animals to Psittacosaurus
Animals similar to Psittacosaurus include:
- Triceratops: Although Triceratops was a very large dinosaur and Psittacosaurus a small one, the two were both members of the group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs called Ceratopia that lived during the Cretaceous period.
- Archaeopteryx: Archaeopteryx is a genus of bird-like feathers. Like Psittacosaurus, anatomical structures strongly reminiscent of feathers have been found in Archaeopteryx fossils.
View all 117 animals that start with P
Psittacosaurus FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
When did Psittacosaurus live?
The Psittacosaurus was alive during the early part of the Cretaceous period, approximately 126 million and 101 million years ago.
How big was Psittacosaurus?
The Psittacosaurus was four feet high, between 2.6 to 6.5 feet long and weighed between 50 and 175 pounds.
Sources
- Enchanted Learning, Available here: https://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/dinosaurs/dinos/Psittacosaurus.shtml
- Prehistoric Wildlife, Available here: http://www.prehistoric-wildlife.com/species/p/psittacosaurus.html
- Reuters, Available here: https://www.reuters.com/article/us-science-dinosaur/scientists-decipher-color-of-super-cute-bristly-dinosaur-idUSKCN11L1OI
- Everything Dinosaur, Available here: https://blog.everythingdinosaur.co.uk/blog/_archives/2007/9/22/3245825.html
- Smithsonian Magazine, Available here: https://www.smithsonianmag.com/science-nature/when-mammals-ate-dinosaurs-129282708/