Lemming
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/lemming-1-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/lemming-1-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/lemming-1.jpg”);
}
}
Lemming
Lemmus Lemmus
Does not hibernate during the bitter Arctic winter!
Lemming Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Mammalia
- Order
- Rodentia
- Family
- Cricetidae
- Genus
- Lemmus
- Scientific Name
- Lemmus Lemmus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Lemming Conservation Status
Lemming Facts
- Main Prey
- Seeds, Grass, Berries
- Habitat
- Arctic tundra and woodland areas
- Predators
- Owls, Foxes, Wolves
- Diet
- Herbivore
- Average Litter Size
- 7
- Lifestyle
-
- Solitary
- Favorite Food
- Seeds
- Type
- Mammal
- Slogan
- Does not hibernate during the bitter Arctic winter!
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/lemmings1.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the Lemming images!
The lemming is a tiny rodent that is found in or near the Arctic Circle
One of the tiniest rodents, lemmings are animals that are known to exist in or around the Arctic circle and is also known to be closely related to muskrats and voles. They can also be found in the Tundra biomes. The smallest of them are as tiny as only 8 cm long. The largest of these species have known to be three times the smallest one. Interestingly, a popular legend says that these rodents commit mass suicide.
Lemmings have about six different subspecies that further have sub-sub species, including true lemmings, collared lemmings, wood lemmings, bog lemmings, yellow steppe lemmings, and southern bog lemmings.
Incredible Lemming Facts!
- Usually small in size, lemmings are animals that can very well reach 3-6 inches in length.
- Lemmings can reproduce within less than a month of being born themselves
- There are about 20 different types of lemmings
- Lemmings do not hibernate at all
- Most of their lives are spent alone. They come together only when they need to mate.
Lemming Scientific Name
Commonly known as a lemming, this small rodent belongs to the kingdom ‘Animalia‘ and class ‘Mammalia’. Lemming belongs to the family ‘Cricetidae’ and goes by the scientific name ‘Lemmus lemmus.
The word “lemming” is often used to describe someone who joins a mass movement without thinking about the consequences of anything.
Lemming Appearance and Behavior
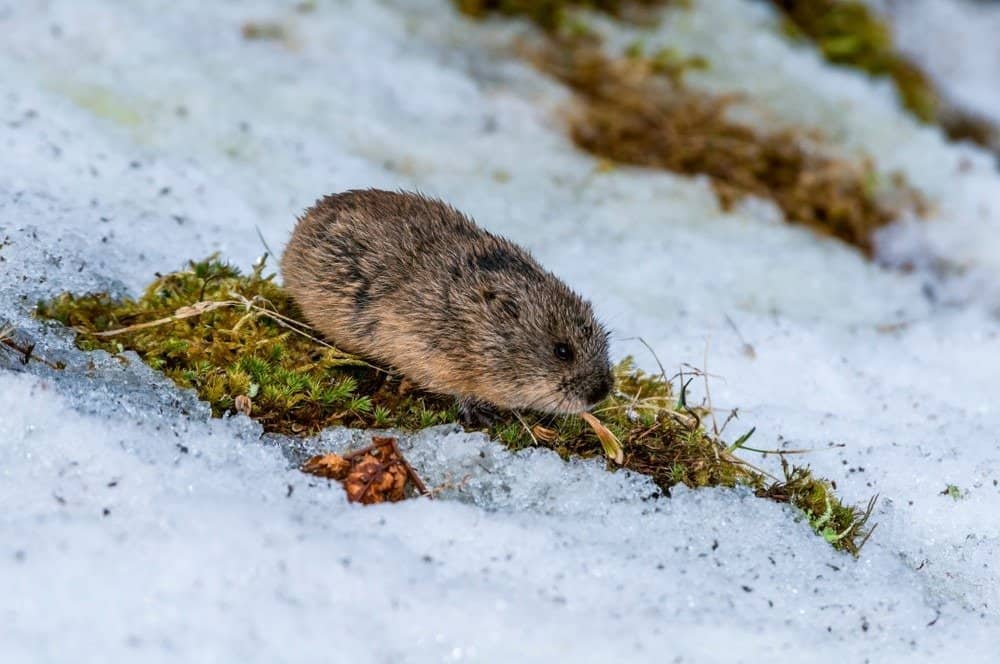
Lemmings are very small animals, usually, just three to six inches long and they weigh around 23–34 grams. They are usually round in shape. Their bodies are covered in thick fur, the color of which can carry from species to species. However, it is mostly brown or grey.
These animals have stout bodies and their limbs, tails and ears are usually very tiny. The small ears help them to conserve their body’s heat. They also have very sharp teeth as well along claws to help them tear out and feed on roots. These rodents are impressive swimmers with their waterproof fur, but it may be difficult for them to swim when multiple animals reach the water at once. With all of the confusion and little extra room, some lemmings die of drowning.
Lemmings are usually solitary animals. However, they also spend some part of their day socializing with others in colonies with rodents similar to them. Usually, the only time when they come together only for migration purposes or when they have to mate.
Upon sensing danger, these animals turn very aggressive towards their predators – sometimes leading them into trouble with larger animals. It is also said that the thing about lemmings committing mass suicide is just a myth and does not happen.
These rodents spend most of their summertime under the ground and in various tunnels. However, around autumn, the ground gets cold and becomes difficult to dig into – forcing them to come up to the surface.
Living underground and in tunnels help them survive the harsh conditions and eliminates their need to hibernate. It also protects them from large wild animals, which usually prey on these tiny rodents.

Nick Pecker/Shutterstock.com
Lemming Habitat
As said earlier, these rodents are usually found in the Arctic region and Tundra. They are commonly found in Alaska, northern Canada, Norway, Asia, and Europe. Sometimes, they can also be found in Taiga, which is another region with a cold atmosphere.
These rodents, especially in the summer months, live underground in tunnels. During autumn, they usually come to the surface as the weather starts getting cold because digging out food in cold becomes very difficult.
Their underground tunnel habitat helps them stay warm and also eliminates the need for them to hibernate. It also protects them from any possible predator that would usually prey on them above the ground.
Lemmings usually make up nests out of ox wool, grasses, and feathers as both a shelter and a way to stay warm. During the spring season, these rodents move further up and start living in mountain heaths and forests for the warm weather, returning to the Alpine zone during the autumn season.
Lemming Diet
These rodents are known to be herbivorous. Their diet comprises mainly of grass and moss. In addition to that, especially during the colder months, these rodents usually find leaves, roots, bulbs, berries, and shoots to feed and survive on. Since these foods don’t offer many calories, lemmings spend six hours of their day eating these foods.
The majority of their diet will consist of leafy plants, but very little fruit. Lemmings cannot process the glucose in sugar, even if it comes from a natural source. When kept in captivity as a pet, the owner should never substitute their food with pre-made assortments for other rodents, like hamsters and mice.
Their teeth, especially incisors, consistently keep growing, which means that they can bite and munch on the more solid things smoothly.
Lemming Predators and Threats
Much like every other animal, lemmings are a vital part of the natural food chain, which means that some animals feed on them. Their small size is a major disadvantage since it makes them more likely to be a source of meat for any carnivorous animal.
Lemmings have a vast number of predators like wolverines and snowy owls, but almost any carnivore will consume a lemming as a small meal. These rodents are a major source of protein for these animals and are very important for the ecosystem. According to sources, whenever the lemming population decreases, there is usually a decline in the number of arctic foxes as well.
Meanwhile, there is no threat to the population of these animals generally as they are found very commonly and the IUCN has declared the species as “least concerned.” Without much of a threat from humans, there are no broadly publicized conservation efforts. In fact, people in some parts of Europe even keep them as pets.
Lemming Reproduction, Babies, and Lifespan
Lemmings are known to fast mature and the maturity usually sets in around 5 to 6 weeks of their age. They start reproducing as early as within one month of being born and are known to be enthusiastic breeders. Most lemmings follow the same mating rituals. However, the southern bog is known to be a little different and very little is currently known about its reproductive process.
In the course of their lifetime, each lemming can produce 8 litters of 6 each. The gestation period is about 20 days. Meanwhile, these animals usually live for only about two years.
The mother usually gives birth to the babies in burros which helps them survive the cold conditions of the arctic. She also feeds them until they are mature enough to start venturing out and looking for food themselves.
Lemming Population
The lemming population varies from area to area and also from time to time. At some places, they might be nearing extinction, while in some other places, the population is booming. Likewise, some years are great for the lemming populations and some are not. In some areas, there might be as many as 3000 lemmings per one million square feet.
However, there is hardly any extinction threat to the overall lemmings’ population. The IUCN has put the species under the ‘least concerned’ category.
Lemming In the Zoo
Lemmings are solitary creatures but are usually not kept in zoos. If too many of these rodents are kept together for a longer period of time, they might turn hostile towards each other and they usually come together only for migration purposes.
As stated above, while not in captivity in zoos, lemmings are often kept as pets in Europe, though they are a less common pet in the United States. To keep them healthy, pet owners provide them with much of the same diet that they have in the wild, offering about a cup a day of leafy greens. They require a terrarium as their home since the wired cages for other rodents are too easy to escape.
View all 56 animals that start with L
Lemming FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are lemmings’ carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores?
Lemmings are herbivores. Their diet primarily includes grass and moss.
What is a lemming?
Lemmings are very tiny rodents that are covered in thick fur. They are usually found in cold regions like the Arctic and Tundra. They usually live in tunnels under the ground, especially in the summertime.
Where do lemmings live?
They are usually found in the Arctic area and the Tundra region. They can also be found in northern Canada, Alaska, Norway, and Asia.
What do lemmings eat?
Lemmings’ diet usually comprises of grass and moss. In colder environments, they can search for berries, leaves, and roots to feed on.
What does a lemming look like?
Lemming is very tiny in appearance and is covered in thick fur. They are usually three to six inches long. Their fur comes in a variety of colors. However, the fur is usually grey or brown.
What hunts lemmings?
Many animals prey on lemmings. Some of them include the snowy owl, wolverines, and the Arctic. Lemmings make an important part of the ecosystem and many predators depend on them for survival.
What Kingdom do Lemmings belong to?
Lemmings belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do Lemmings belong to?
Lemmings belong to the class Mammalia.
What phylum to Lemmings belong to?
Lemmings belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do Lemmings belong to?
Lemmings belong to the family Cricetidae.
What order do Lemmings belong to?
Lemmings belong to the order Rodentia.
What type of covering do Lemmings have?
Lemmings are covered in Fur.
What genus do Lemmings belong to?
Lemmings belong to the genus Lemmus.
How many babies do Lemmings have?
The average number of babies a Lemming has is 7.
What is an interesting fact about Lemmings?
Lemmings do not hibernate during the bitter Arctic winter!
What is the scientific name for the Lemming?
The scientific name for the Lemming is Lemmus Lemmus.
What is the lifespan of a Lemming?
Lemmings can live for 1 to 3 years.
How fast is a Lemming?
A Lemming can travel at speeds of up to 3 miles per hour.
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World’s Wildlife
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David W. Macdonald, Oxford University Press (2010) The Encyclopedia Of Mammals
- Soft Schools, Available here: https://www.softschools.com/facts/animals/lemming_facts/2602/