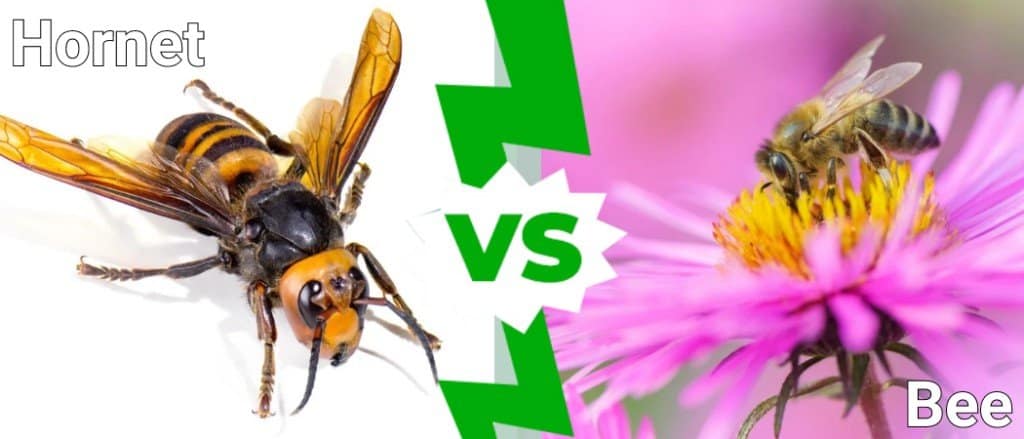
Hornet vs Bee: What Are the Differences?
We automatically think of bees whenever we see a bee-like insect. But there are plenty of other insect species that look like bees but aren’t bees. You may encounter a honey bee, which differs from a bumblebee. You can also encounter a wasp, an entirely different species. And lastly, you may come in close contact with what you may think of as bees but are actually hornets. Bees and hornets almost look the same, except that they are two different insects. So, what are the differences between hornets vs bees? Below, we will take a deep dive into each of their hives.
Comparing a Hornet and a Bee

A-Z-Animals.com
| Hornet | Bee | |
| Appearance | – usually have longer and more slender bodies – mostly have brown bodies striped with yellow lines or tinge of red – smooth skin texture with less to no hair |
– stouter and rounder body shape- have orange-yellow, tan, or black stripes- fuzzy or furry skin |
| Nests/Hives | – often build colonies in wall voids or attics- also nests in roof eaves or tree hollows | – typically ground nesters; will take shelter in underground burrows created by rodents or moles- prefer natural cavities than home spaces |
| Behavior | – hangs its legs down during flight- have a reputation of being aggressive; will sting readily, specifically when their hive is threatened or destroyed | – legs are hidden during flight- non-aggressive at all; will less likely sting unless deeply threatened – generally gentle in nature and will rather escape than sting |
| Sting | – more painful but is 50 times less toxic than a bee sting- smooth stingers that won’t break or fall out after stinging | – less painful but has more potent venom than hornets- barbed stingers that can be lost after stinging |
| Diet | – scavengers feeding on other insects, leftover food on the ground, and decaying fruit | – consume nectar from flowers and collect pollen for their young’s food |
The 5 Key Differences of Hornets and Bees
No matter how alike you think they are, the main differences between hornets and bees include their appearances, where they live, behavior, diet, and their stings. While both have stingers, bees and hornets have many different features that set them apart. Bees are often considered beneficial to humans and the environment because they make honey and pollinate flowers. On the other hand, hornets are not associated with honey and are considered a nuisance. Apart from the fact that you can spot them in entirely different habitat types, we will review each of the differences that untie them apart.
Hornet vs Bee: Appearance
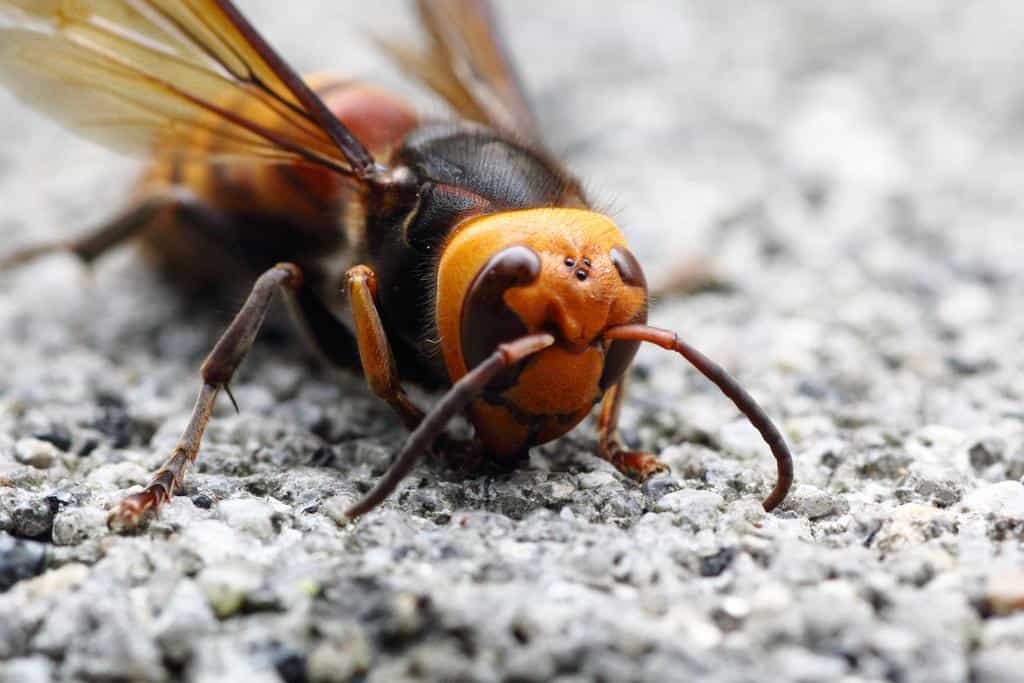

Hornets and bees may look exactly alike from afar, but looking closely, you’ll realize they have a lot of differences. Depending on the species, the key features defining hornets and bees may vary, but common grounds help quickly identify the two. Most bees, particularly bumblebees, have hefty, spherical bodies, while hornets have a thinner and longer physique. Bees are also described by their distinct colors, usually sporting black or tan stripes. For bumblebees, they have a unique yellow and black pattern.
On the other hand, hornets have brown bodies striped with yellow lines or a tinge of red. Bees are also recognizable through their furry bodies. They seem to have hair or thin fur covering their bodies, while hornets are often hairless.
Hornet vs Bee: Nests/Hives
When it comes to distinguishing between bee and hornet infestations, the position of the nest can be helpful. Knowing where to look can also help prevent homeowners from accidentally disrupting a colony, resulting in insect attacks. Hornet nests are often found in wall voids or attics. Their preference is based on the species of hornets, but they can also be commonly found nesting in tree hollows and roof eaves.
In contrast, bees prefer nesting in natural cavities rather than home spaces. Most bees build their nests on the ground. Bumblebees, for instance, commonly seek refuge in abandoned underground burrows.
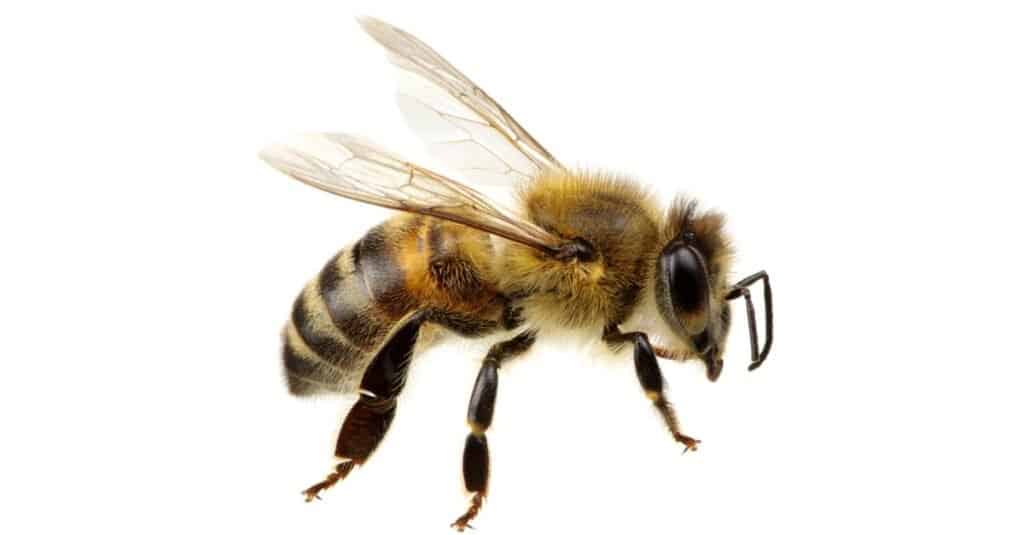
Hornet vs Bee: Behavior

iStock.com/Ale-ks
Hornets and bees are drastically different when it comes to aggressiveness. Hornets are way more aggressive than bees, which is why hornets are often more feared than bees. They are always ready to sting, especially when they feel threatened. Hornets do not lose their stingers after they sting, making them more aggressive than bees. While flying, hornets also like to hang their legs down, which is another distinct indicator.
Bees, on the other hand, hide their legs while flying. Unlike hornets, bees can lose their stingers after a sting incident, and stinging is more dangerous for them than it is to the victim. This makes bees less dangerous and less aggressive compared to hornets. Bees are generally gentle and will often escape rather than attack.
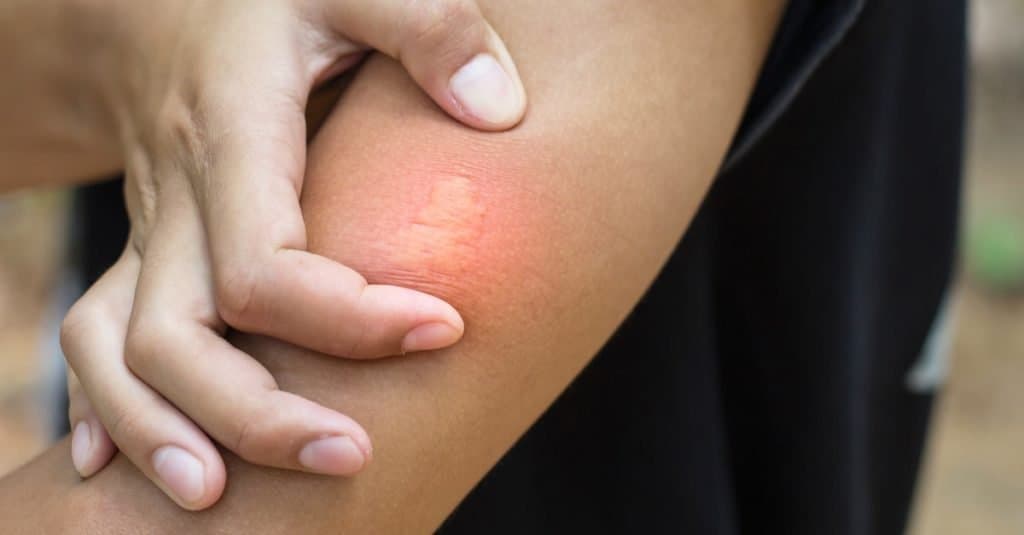
Hornet vs Bee: Sting
WIRACHAIPHOTO/Shutterstock.com
Their ability to sting is the only serious issue about these insects. Yet, hornets are more likely to sting than bees. Since they are more aggressive, they use their stingers to empower them against threats. However, for bees, stinging can be fatal for them, so they avoid stinging if unnecessary. Since bees’ stingers have barbs, they can lose it after a sting, whereas hornets can sting as often as they need to.
Both bees and hornets have venom in their stingers, but a bee’s venom is stronger than a hornet’s. Despite this, hornet stings are still more painful than a bee sting. In the Schmidt sting pain index, the bald-faced hornet was measured at 2.0 in the scale while the sweat bee was scaled at 1.0. The scale’s highest is 4.0, which indicates that the hornet’s sting is a scale more painful than a bee sting.
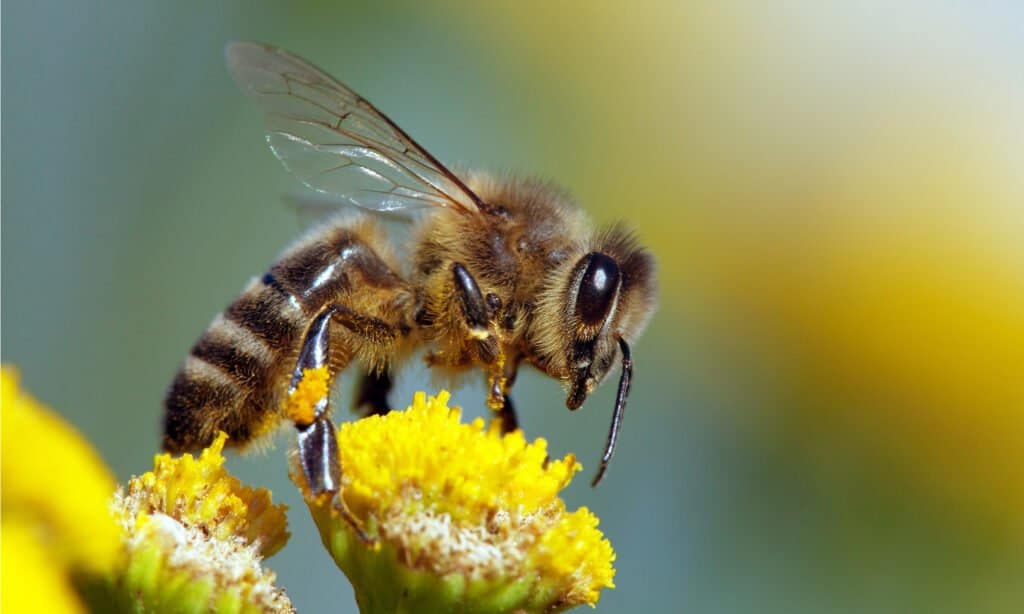
Hornet vs Bee: Diet

Daniel Prudek/Shutterstock.com
Bees only feed on limited materials, including nectar, pollen, and honey. However, hornets do not eat the same diet as bees. They can sometimes eat leaves and sap. But as they are accomplished predators, hornets prefer consuming smaller insects, drawing a huge difference between them. Hornets also eat decaying fruits and often scavenge leftover food on the ground.
More from A-Z Animals
We automatically think of bees whenever we see a bee-like insect. But there are plenty of other insect species that look like bees but aren’t bees. You may encounter a honey bee, which differs from a bumblebee. You can also encounter a wasp, an entirely different species. And lastly, you may come in close contact with what you may think of as bees but are actually hornets. Bees and hornets almost look the same, except that they are two different insects. So, what are the differences between hornets vs bees? Below, we will take a deep dive into each of their hives.
Comparing a Hornet and a Bee

A-Z-Animals.com
| Hornet | Bee | |
| Appearance | – usually have longer and more slender bodies – mostly have brown bodies striped with yellow lines or tinge of red – smooth skin texture with less to no hair |
– stouter and rounder body shape- have orange-yellow, tan, or black stripes- fuzzy or furry skin |
| Nests/Hives | – often build colonies in wall voids or attics- also nests in roof eaves or tree hollows | – typically ground nesters; will take shelter in underground burrows created by rodents or moles- prefer natural cavities than home spaces |
| Behavior | – hangs its legs down during flight- have a reputation of being aggressive; will sting readily, specifically when their hive is threatened or destroyed | – legs are hidden during flight- non-aggressive at all; will less likely sting unless deeply threatened – generally gentle in nature and will rather escape than sting |
| Sting | – more painful but is 50 times less toxic than a bee sting- smooth stingers that won’t break or fall out after stinging | – less painful but has more potent venom than hornets- barbed stingers that can be lost after stinging |
| Diet | – scavengers feeding on other insects, leftover food on the ground, and decaying fruit | – consume nectar from flowers and collect pollen for their young’s food |
The 5 Key Differences of Hornets and Bees
No matter how alike you think they are, the main differences between hornets and bees include their appearances, where they live, behavior, diet, and their stings. While both have stingers, bees and hornets have many different features that set them apart. Bees are often considered beneficial to humans and the environment because they make honey and pollinate flowers. On the other hand, hornets are not associated with honey and are considered a nuisance. Apart from the fact that you can spot them in entirely different habitat types, we will review each of the differences that untie them apart.
Hornet vs Bee: Appearance

Hornets and bees may look exactly alike from afar, but looking closely, you’ll realize they have a lot of differences. Depending on the species, the key features defining hornets and bees may vary, but common grounds help quickly identify the two. Most bees, particularly bumblebees, have hefty, spherical bodies, while hornets have a thinner and longer physique. Bees are also described by their distinct colors, usually sporting black or tan stripes. For bumblebees, they have a unique yellow and black pattern.
On the other hand, hornets have brown bodies striped with yellow lines or a tinge of red. Bees are also recognizable through their furry bodies. They seem to have hair or thin fur covering their bodies, while hornets are often hairless.
Hornet vs Bee: Nests/Hives
When it comes to distinguishing between bee and hornet infestations, the position of the nest can be helpful. Knowing where to look can also help prevent homeowners from accidentally disrupting a colony, resulting in insect attacks. Hornet nests are often found in wall voids or attics. Their preference is based on the species of hornets, but they can also be commonly found nesting in tree hollows and roof eaves.
In contrast, bees prefer nesting in natural cavities rather than home spaces. Most bees build their nests on the ground. Bumblebees, for instance, commonly seek refuge in abandoned underground burrows.
Hornet vs Bee: Behavior

iStock.com/Ale-ks
Hornets and bees are drastically different when it comes to aggressiveness. Hornets are way more aggressive than bees, which is why hornets are often more feared than bees. They are always ready to sting, especially when they feel threatened. Hornets do not lose their stingers after they sting, making them more aggressive than bees. While flying, hornets also like to hang their legs down, which is another distinct indicator.
Bees, on the other hand, hide their legs while flying. Unlike hornets, bees can lose their stingers after a sting incident, and stinging is more dangerous for them than it is to the victim. This makes bees less dangerous and less aggressive compared to hornets. Bees are generally gentle and will often escape rather than attack.
Hornet vs Bee: Sting

WIRACHAIPHOTO/Shutterstock.com
Their ability to sting is the only serious issue about these insects. Yet, hornets are more likely to sting than bees. Since they are more aggressive, they use their stingers to empower them against threats. However, for bees, stinging can be fatal for them, so they avoid stinging if unnecessary. Since bees’ stingers have barbs, they can lose it after a sting, whereas hornets can sting as often as they need to.
Both bees and hornets have venom in their stingers, but a bee’s venom is stronger than a hornet’s. Despite this, hornet stings are still more painful than a bee sting. In the Schmidt sting pain index, the bald-faced hornet was measured at 2.0 in the scale while the sweat bee was scaled at 1.0. The scale’s highest is 4.0, which indicates that the hornet’s sting is a scale more painful than a bee sting.
Hornet vs Bee: Diet

Daniel Prudek/Shutterstock.com
Bees only feed on limited materials, including nectar, pollen, and honey. However, hornets do not eat the same diet as bees. They can sometimes eat leaves and sap. But as they are accomplished predators, hornets prefer consuming smaller insects, drawing a huge difference between them. Hornets also eat decaying fruits and often scavenge leftover food on the ground.






