Gopher Tortoise
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/09/Gopher-tortoise-header-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/09/Gopher-tortoise-header-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/09/Gopher-tortoise-header.jpg”);
}
}
Gopher Tortoise
Gopherus polyphemus
It is the only species of tortoise native to Florida.
Gopher Tortoise Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Reptilia
- Order
- Testudines
- Family
- Testudinidae
- Genus
- Gopherus
- Scientific Name
- Gopherus polyphemus
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Gopher Tortoise Conservation Status
Gopher Tortoise Facts
- Prey
- Insects (occasionally)
- Name Of Young
- neonate, hatchling
- Group Behavior
-
- Solitary/Group
- Fun Fact
- It is the only species of tortoise native to Florida.
- Estimated Population Size
- 700,000
- Biggest Threat
- habitat destruction
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Front legs resembling shovels
- Other Name(s)
- Florida gopher tortoise
- Gestation Period
- 90 days
- Litter Size
- 1-23
- Habitat
- Pine Flatwoods, Pine-Oak sandhills, Rocklands, grasslands
- Predators
- humans, birds of prey, cats and dogs, coyotes, raccoons, wild boars, bobcats
- Diet
- Herbivore
- Type
- Reptile
- Common Name
- gopher tortoise
- Number Of Species
- 1
- Location
- southeastern United States
- Group
- colony, pod
Gopher Tortoise Physical Characteristics
- Color
-
- Brown
- Yellow
- Grey-Brown
- Skin Type
- Leather
- Top Speed
- 4.9 mph
- Lifespan
- 40-60 years
- Weight
- 8-15lbs
- Length
- 9in-11in
- Age of Sexual Maturity
- 9-21 years
- Age of Weaning
- 3-5 days
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2021/09/Gopher-tortoise-in-tunnel-1024×535.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the Gopher Tortoise images!
“ The gopher tortoise is a real Keystone species”
The gopher tortoise is quite an interesting animal. It is land-dwelling and spends most of its time underground in burrows. The front limbs are built for digging these burrows and do an excellent job at the excavation. It is the state tortoise of Florida.
5 Incredible Gopher Tortoise Facts!
- They live on land and do not swim.
- It is the state reptile of Georgia.
- They are ectothermic, or cold-blooded.
- Protected by Florida laws, it is illegal to keep a gopher tortoise as a pet.
- They are diurnal, with most of their activity occurring in the daytime.
Gopher Tortoise Scientific Name
The scientific name for the gopher tortoise is Gopherus polyphemus. It is sometimes called the Florida gopher tortoise or gopher turtle. The word “Gopherus” stems from the French word “guafre” meaning waffle. It references small animals that make burrows looking like waffles or honeycomb shapes. “Polyphemus” comes from a giant in Greek mythology with the same name who lived in a cave.
This species is in the Animalia kingdom and the Chordata phylum. It belongs to the reptilia class, a group of reptiles. It is in the Testudinidae family under the order Testudines. It is a member of the Gopherus genus which includes six subspecies. The five other Gopherus subspecies that are closely related to Gopherus polyphemus are: Gopherus agassizii (Mojave desert tortoise), G. berlandieri (Texas tortoise), G. evgoodei (Sinaloan desert tortoise), G. flavomarginatus (Bolson tortoise) and G. morafkai (Sonoran desert tortoise). There are two additional species that became extinct many millennia ago. These non-extant species are Gopherus depressus and Gopherus donlaloi.
Gopher Tortoise Appearance & Behavior
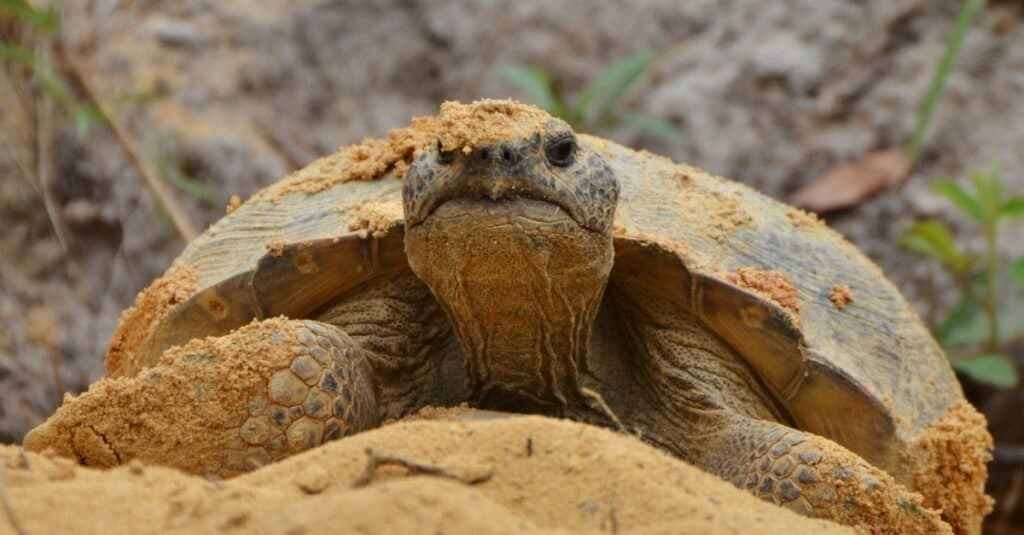
The gopher tortoise, like all tortoise species, has a hard outer shell. The upper part of the shell is the carapace and the bottom shell is the plastron. It’s hard carapace is typically light brown to dark brown colored. The plastron has a muted yellow hue. The skin is grayish brown, leathery and has scales.
The gopher tortoise generally weighs between eight and 15 pounds. The average weight is about equal to one-half to a whole bowling ball’s weight. Nine to 11 inches is the average length of this animal but some reach 15 inches. Females are often larger than males. In 2018, the record for largest specimen was noted at the Clinic for the Rehabilitation of Wildlife (CROW) in Florida. It was a male with a carapace length of 17.3 inches. He was also the heaviest of his kind recorded, weighing in at 33 pounds. His impressive weight is about half as heavy as a Dalmatian.
All of the tortoise species in the Gopherus genus are moderately similar in appearance to the gopher tortoise. They all have shovel-like front limbs made for digging and elephant-like hind legs.
Gopher tortoises are ectothermic. This means they are cold-blooded and cannot regulate their body temperature. Instead, they rely on thermoregulation from their surrounding environment. They bask above-ground in the warm sun to elevate their temperature, and they burrow into the ground to cool down.
These tortoises are mostly solitary creatures but will sometimes coexist in small groups. The groups are called pods. Many pods in the same area make up a colony. Colonies may contain more than 50 tortoises. It is not uncommon for 2 or more individuals to occupy the same burrow. They are typically docile but can become aggressive if threatened or during mating. These reptiles are not migratory and generally do not travel long distances.

iStock.com/mjf795
Gopher Tortoise Habitat
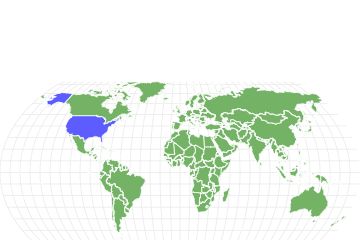
Gopher tortoises are native to the southeastern United States on the continent of North America. They live in Florida, South Carolina, Georgia, Louisiana, and Mississippi. They live in a humid, subtropical climate. About 80% of this animal’s habitat is in longleaf pine environments including pine Flatwoods and pine-oak sandhills. Other types of habitats they occupy are Rocklands, grasslands, forests, sandy ridges and pastures.
These reptiles can sometimes be found grazing in vegetation that is low to the ground. Most of the time, they are out of sight in their burrows. In fact, they spend about 19 hours a day underground.
The gopher tortoise uses its front limbs like shovels to dig deep, elaborate burrows. Their burrows are quite important to the ecosystem as many other animals benefit from them. They will sometimes reconstruct older burrows that have been damaged. They prefer to make their burrows in sandy soil but will also dig in clay soil. They create a tunnel that leads underground and opens up into a chamber. These burrows have average depths of six and a half feet and lengths of 15 feet. At the entrance of the burrow, the excavated dirt formed into a mound called the apron. Gopher tortoises spend up to 80% of their lives within the burrows. There, they are protected from predators, temperature extremes and fires.
More than 350 species use the burrows made by gopher tortoises. They are of great importance to the ecosystem. This is why they are referred to as a “keystone species.” Gopher frogs, gopher crickets, burrowing owls, snakes, opossums and raccoons are just some of the animals that utilize these burrows.
Gopher Tortoise Predators & Threats
Gopher tortoises are primarily herbivores. They are known to consume insects sometimes as well. They forage for their food in the daytime. Water does not have much importance to them unless there is a drought or dry season. They rarely drink water because the plants in their diet contain enough to sustain them.
Gopher tortoises are threatened by natural predators as well as environmental dangers. There is a fairly low survival rate for their vulnerable eggs due to predators. Extreme weather, fragmentation, and disease are hazards for these animals. Some become afflicted with a common upper respiratory tract disease caused by bacteria. They can also fall victim to parasites such as ticks and botflies. Humans are also a threat to gopher tortoises. Humans hunted them copiously before they were protected. Traffic accidents claim the lives of a number of them in their native range. Habitat destruction caused by urban development is undoubtedly one of the biggest negative impacts on the population.
Gopher tortoises are listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List. They are at risk of becoming endangered in the near future. It is also listed on CITES (the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora) Appendix II. This category contains species that are not currently facing extinction. However, they are species that need control on their trade to prevent their demise. Currently, they are protected under Florida law. They also receive protection through the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission and the US Fish and Wildlife Service. It is illegal to have a gopher tortoise as a pet as well as to handle or harm them.
What eats the gopher tortoise?
Adult gopher tortoises are preyed upon by a number of natural predators. Some species that eat these tortoises include hawks, eagles, raccoons, coyotes, bobcats, wild boars and domestic cats and dogs. Eggs, neonates and hatchlings are also eaten by additional species such as the common gray fox, skunks, armadillos and opossums. They are also preyed upon by a number of snake species including rattlesnakes, common kingsnakes, Florida cottonmouths, eastern diamondbacks and more.
What does the gopher tortoise eat?
Grasses make up a large portion of the gopher tortoise’s diet. It also eats leaves, mosses, fruits, flowers and occasionally insects.
Gopher Tortoise Reproduction, Babies & Lifespan
The mating season occurs from March to October. During this time, males will use calls to attract females. The male will fight other male tortoises as well as his chosen mate. These reptiles exhibit polygyny, which means that males will mate with multiple females rather than mating with one partner for life.
The gestation period is around 90 days. Nesting takes place between the months of April and July. Females lay an average of five to eight eggs, though the number could range from one to 25. They have one clutch per year. They make their nests in a clear area where the sun shines, often on the burrow’s apron or in close proximity to it. The nests are usually about six to 12 inches deep in the sand or dirt.
Because they have “temperature-dependant sex determination,” eggs are non-gendered when laid. Before hatching, the animal’s sex is defined by the temperature of the dirt or sand they are nested in. Temperatures above 85 degrees Fahrenheit will produce a female and below that, a male.
A related species, the Texas tortoise (Gopherus berlandieri), has a mating ritual and gestation period that is similar to the gopher tortoise. The male will engage in a physical altercation with the female where he will ram her and bite her. The female also has a gestation period comparable to that of a gopher tortoise. It lasts between 88 and 118 days.
Baby gopher tortoises are called neonates. After a period of a few days, the yolk sac is absorbed and the baby is then considered a hatchling. After this transition, the hatchling will begin foraging like the older tortoises. Hatchlings have soft shells and are therefore more vulnerable to predators. Gopher tortoises do not provide any parental care for the baby.
These animals have an average lifespan of around 40 to 60 years. It is suggested that they can live even longer in captivity. Adulthood is reached between 10 and 21 years for females and nine to 12 years for males. The oldest recorded gopher tortoise is a male named Gus. He resides at the Museum of Natural History in Nova Scotia. Gus turned 99 years old in August 2021.
Gopher Tortoise Population
Scientists estimate that there are about 700,000 gopher tortoises left in the wild. A large portion of them occupies Florida. The population is declining. Between the 1800s and 1900s, the population had declined by a whopping 80%. Although there has been a push to recategorize them as endangered, they are still classified as vulnerable at this time.
View all 115 animals that start with G
Gopher Tortoise FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is a gopher tortoise?
It is a land-dwelling reptile that burrows into the ground.
Are Gopher tortoises carnivores, herbivores or omnivores?
They are primarily herbivores, but will sometimes eat insects as well as plants.
Is it illegal to pick up a gopher tortoise?
Yes, it is illegal to handle it in any way.
Are gopher tortoises protected in Florida?
Yes, they are protected by Florida law.
How many gopher tortoises are left?
There are around 700,000 left in the wild.
How do I get rid of a gopher tortoise?
The only legal method of getting rid of a gopher tortoise is to use non-toxic repellants. It is against the law to harm them.
What do you do if you find a gopher tortoise?
If you find one, you should leave it alone. If it is harmed, you can call your local wildlife service for help.
Why is the gopher tortoise endangered?
The gopher tortoise is not yet classified as endangered. However, due to hunting and habitat destruction, it could become endangered very soon.
What is the gopher tortoise’s scientific name?
Gopherus polyphemus
What is the importance of gopher tortoises?
They contribute positively to their environment. Their burrows benefit many species that use them.
Sources
- EOL, Available here: https://eol.org/pages/456481
- U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service, Available here: https://www.fws.gov/northflorida/gophertortoise/gopher_tortoise_fact_sheet.html
- Florida State Parks, Available here: https://www.floridastateparks.org/learn/gopher-tortoise
- Fire Effects Information System (FEIS), Available here: https://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/animals/reptile/gopo/all.html
- Zoo Miami, Available here: https://www.zoomiami.org/gopher-tortoise-ecology-in-pine-rockland
- Chattahoochie Nature Center, Available here: https://www.chattnaturecenter.org/visit/experience/wildlife/animal-facts/gopher-tortoise/