Gecko
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2018/09/Gecko-header-2-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2018/09/Gecko-header-2-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2018/09/Gecko-header-2.jpg”);
}
}
Gecko
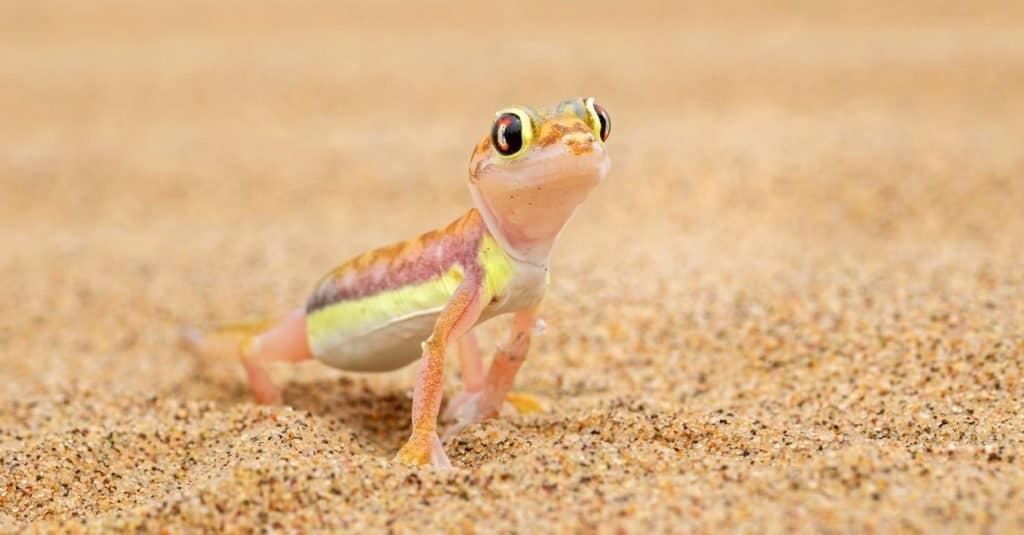
Geckos can climb up vertical surfaces
Gecko Scientific Classification
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Gecko Conservation Status
Gecko Facts
- Main Prey
- Insects, Worms, Small Birds
- Fun Fact
- Geckos can climb up vertical surfaces
- Habitat
- Rocky deserts and mountainous regions
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Average Litter Size
- 2
- Lifestyle
-
- Solitary
- Favorite Food
- Insects
- Type
- Reptile
- Slogan
- There are thought to be over 2,000 species!
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/2018/09/Gecko-on-stump-1024×535.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
“Geckos can climb vertical walls and stroll across ceilings.”
Geckos have been around for at least 300 million years. Scientists have found geckos preserved in amber that dates back to the Cretaceous Period, and those specimens look remarkably like the gentle little lizards you’ll find in so many parts of the world today.
See all of our expert product reviews.
There are approximately 1,500 gecko species, and they vary in size from the Jaragua Sphaero dwarf gecko, which measures just three-quarters of an inch long and weighs less than one-hundredth of an ounce, to the New Caledonian giant gecko, which can grow to 17 inches and tips the scales at 10 ounces. Geckos thrive in practically every habitat, including rain forests, mountains, and deserts, so long as average temperatures reach 72 degrees Fahrenheit.
5 Incredible Gecko Facts!
Geckos are standouts among the reptile class in a number of respects:
- These reptiles can climb practically every vertical surface effortlessly thanks to the tensile suction created by hundreds of thousands of tiny hairs on their toes.
- Geckos are the only lizards with true vocal cords.
- These reptiles clean their eyes by licking them.
- When they lose their tails to predators, they can regenerate new tails.
- These reptiles replace their teeth by growing new ones every three to four months.
Gecko Scientific name
These animals belong to a taxonomic group that shares the designation “squamate reptiles.” “Squamate” is derived from the Latin word “squamatus,” which means scaly, although these reptiles themselves don’t have scales. They belong to the infraorder Gekkota, a name thought to derive from the Indonesian-Malay “gēkoq,” which is a transliteration of the sound this animal makes.
The infraorder Gekkota is comprised of seven families:
- Diplodactylida: This family includes 137 species in Australia, New Zealand, and New Caledonia. Its scientific name is derived from the Greek words for double (“diplo”) and finger (“daktylos.”) The crested gecko, a popular pet, is a member of this family.
- Carphodactylidae: Carphodactylidae is another family of Australian geckos, comprising 30 species. Its scientific name derives from the Greek words for finger and straw (“karphos”.)
- Pygopodidae: Pygopodidae look like snakes but are really geckos. The family consists of 35 species, native to Australia and New Guinea. “Pygo” is a Greek word for rump while “podi” is the Greek word for feet, so the family’s name roughly means “feet in their bottom.”
- Eublepharidae: Eublepharidae is a family of 30 species found in Asia, Africa, and North America. They are distinguished from other species by their moveable eyelids and their lack of adhesive toepads. This genus includes the leopard, the fat-tailed, and the clawed gecko.
- Sphaerodactylidae: The Sphaerodactylidae family includes more than 200 species distributed throughout all parts of the world. The scientific name derives from the Greek words for round (“sphaero”) and finger (“dactyl.”)
- Phyllodactylidae: “Phyllo” is the Greek word for leaf, and many of the 148 species that belong to this family are known as leaf-toed geckos. Phyllodactylidae is found in all parts of the world.
- Gekkonidae: Gekkonidae, or the common gecko, is the most widespread family, containing more than 950 species. Well-known species include the house, the tokay, the leaf-tailed, and the day gecko.
Gecko Appearance
These reptiles are small lizards with stubby bodies, large heads, tails, and—except for members Pygopodidae family—prominent limbs. The animal’s color varies widely across species. The majority are grey or brown, the better to blend in with the rocks, sand, and dirt around them and so, to escape the notice of predators. However, the leopard gecko has bright yellow skin covered with brown spots, some day geckos are an electric blue, the crested gecko is orange or red while the tokay gecko has bright orange spots.
Health and Entertainment for your Gecko
See all of our expert product reviews.
Their tails also vary widely in shape and morphology, depending upon the species. Some are long and tapering while others are shorter and blunter, or even globular. These reptiles store fat in their tails so they’ll have access to calories when food sources are scarce. Their tails have evolved to fall off easily when the animal is pursued by predators. When this happens, the animal will regenerate its tail. Their tails actually have their own nerve control center that allows the tail to move and lunge independently for up to half an hour after its separation from the body.
These reptiles have approximately 100 teeth. Their teeth don’t grind down because they replace their teeth every three to four months.
Their skin is covered with millions of infinitesimal, hairlike spines that are very soft to the touch. These spines trap water droplets that keep dust and other air contaminants away from the gecko’s skin. The microscopic hairs that cover their toes are called “setae.” These hairs work differently than the hair that covers the animal’s body. Setae are actually tiny enough to activate molecular Van der Waals forces that enable geckos to easily climb vertical surfaces, like walls, and even to move comfortably on ceilings.
Although a few species are active during the day, they are primarily nocturnal animals, and the design of their eyes shows it. All but a few species have translucent membranes covering their eyes instead of eyelids. They lick their eyeballs to keep them clean! (The leopard gecko is unique here in having moveable eyelids.) Their pupils are vertical, and their eyes can be up to 350 times as sensitive to light as human eyes. These lizards also have a sophisticated auditory system; they’re capable of hearing sounds pitched at high frequencies that other reptiles cannot hear.

David Havel/Shutterstock.com
Gecko Behavior
Though these reptiles are not particularly social animals, they have a sophisticated vocal communication system when compared with other lizards. They have true vocal cords. They bark and chirp to define their territory, to attract mates, and to elude predators; they also hiss and emit high-pitch squeaks. The New Caledonian gecko has such a distinctive growl that native tribes of those islands dubbed it “the devil in the trees.” The leaf-tailed gecko of Madagascar emits a distress call that many liken to a child’s scream.
They also use their tails to communicate with other geckos. Slow, wiggling movements indicate awareness of another animal’s presence while more vigorous shakes are defensive maneuvers designed to distract or evade predators.
Another characteristic of their behavior is head shaking. This movement is associated with feeding, and it helps the animal pass food from its throat to its stomach.
Most species are nocturnal. The night is the time when they climb most actively. They kos are swift runners, too; flat-tailed house geckos have been clocked at three feet per second, and they can scamper over the surface of the water.
Gecko Habitat
These reptiles live in a variety of warm habitats on every continent of the globe except Antarctica. The immense amount of morphological variation found in different species reflects the ways that they have evolved to fit into their specific habitats. The Northland tree species, for example, owes its bright green color to the New Zealand forests and scrublands it inhabits. The leopard gecko with its yellowish skin and black spots blends in well with the semi-desert terrain of its native Pakistan, India, and Afghanistan. Red-spotted tokay species are well concealed in the lowland or submontane rainforests of southeast Asia while black-spotted tokay species have adapted to the rockier regions of Vietnam and China.
Gecko Diet
These reptiles are primarily insectivores, but they also eat worms, fruit, and flower nectar. Leaf-tailed geckos like to snack on land snails. Large species kos such as the New Caledonian gecko have even been known to eat small birds and rodents.
What eats geckos?
Snakes, birds, spiders and cats.
What do geckos eat?
Insects, worms, fruit and flower nectar. For a complete guide on what geckos eat, give ‘What Do Geckos Eat: 15 Foods in their Diet‘ a read!
Gecko Predators and Threats
Predators include snakes, birds, spiders, and species introduced by humans such as dogs and cats. In the tropical rainforests of northern South America, these animals are stalked by the much smaller goliath tarantula, which uses its venom to paralyze the gecko and liquefy its flesh. Raptor birds such as hawks and owls typically live in climates too cold for geckos, but when temperatures drop below freezing and these birds travel south, these reptiles become a favorite prey.
Most species aren’t in danger of extinction, but a few species are on the International Union for Conservation of Nature’s Red List. The crested gecko of New Caledonia, for example, was thought to be extinct for many years after its initial sighting in 1866 until it was rediscovered in 1994. Two other New Caledonian species, Bavayia goroensis and Bavayia ornate, are on the Red List because mining activities are shrinking their habitats.
Gecko Reproduction and Life Cycle
Males attract females by making distinct mating sounds and by vibrating his tail. While mating, the male grasps the skin at the back of the female’s neck in his jaws and tucks his tail beneath her abdomen, bringing the animals’ cloacal openings in close proximity so that fertilization can occur. Some species, however, such as the mourning gecko found in Central and South America, can reproduce through parthenogenesis.
Most of these animals lay eggs. Gestation periods vary widely in length: The leopard gecko may lay her eggs 16 to 22 days after mating while a harlequin gecko’s pregnancy can last three to four years. Forty-three species endemic to New Zealand give birth to live young.
The typical egg clutch size is two, and the eggs are laid on the ground beneath rocks and tree bark. Their eggs can take between 35 and 90 days to hatch. Females show no interest in eggs or hatchlings once they’ve laid their eggs. Though many hatchlings have body markings that are different from those of adults, they move, behave and respond to their environments exactly like adults.
In captivity, these reptiles have relatively long lifespans. Leopard geckos, for example, typically live between 15 and 20 years. In the wild, they live for approximately five years if they aren’t preyed upon. A study in New Zealand found wild geckos that were believed to be at least 36 years old, which is substantially past the average lifespan of a gecko.
Gecko Population
Scientists believe that these retiles originated in Southeast Asia some time during the Lower Cretaceous, but they are now found in large numbers in practically every place in the world where the average temperature is 72 degrees Fahrenheit or larger. It would be impossible to estimate the number of them currently on the planet.
Geckos In the Zoo
Every zoo that has a reptile house is likely to be exhibiting at least a few specimens. Zoos with noteworthy reptile collections include the San Diego Zoo, the Fort Worth Zoo, the Saint Louis Zoo, the Los Angeles Zoo, and the Bronx Zoo.
View all 115 animals that start with G
Gecko FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are Geckos herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
Geckos are Carnivores, meaning they eat other animals.
What Kingdom do Geckos belong to?
Geckos belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do Geckos belong to?
Geckos belong to the class Reptilia.
What phylum to Geckos belong to?
Geckos belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do Geckos belong to?
Geckos belong to the family Gekkonidae.
What order do Geckos belong to?
Geckos belong to the order Squamata.
What type of covering do Geckos have?
Geckos are covered in scales.
In what type of habitat do Geckos live?
Geckos live in rocky deserts and mountainous regions.
What is the main prey for Geckos?
Geckos prey on insects, worms, and small birds.
What are some predators of Geckos?
Predators of Geckos include snakes, birds, and spiders.
How many babies do Geckos have?
The average number of babies a Gecko has is 2.
What is an interesting fact about Geckos?
There are thought to be over 2,000 species of Gecko!
What is the lifespan of a Gecko?
Geckos can live for 2 to 9 years.
How fast is a Gecko?
A Gecko can travel at speeds of up to 30 miles per hour.
What is a gecko?
Geckos are small, nocturnal lizards found in all the warm parts of the world. They are known for their ability to scurry up vertical surfaces, and they are the only lizard species with true vocal cords.
Where are geckos from?
Geckos are thought to have evolved in Southeast Asia some time during the Lower Cretaceous, but today, they can be found on every continent except Antarctica.
What eats geckos?
Snakes, birds, and spiders eat geckos.
Are geckos dangerous?
No! Geckos are gentle creatures, though, in captivity, they have been known to nip humans from time to time if they’re feeling threatened because they’re being handled roughly.
Are geckos good pets?
Yes. Geckos make excellent terrarium pets. Crested geckos, leopard geckos, African fat-tailed geckos, gargoyle geckos, and the giant New Caledonian gecko are particularly popular.
What is the difference between a gecko and a salamander?
The main differences between a salamander and a gecko include their size, skins, diet, habitat, and training. Geckos may be very similar to salamanders in body shape and color patterns, but that is where their similarities end. Geckos are reptiles with over 1,500 species, while salamanders are amphibians with over 550 species. Since the two animals are from different classes, they are expected to vary in reproduction processes. Unlike salamander eggs with no shell, geckos produce shelled, amniotic eggs that prevent them from desiccating.
What geckos live in Texas?
There are a variety of gecko species across Texas that include:
- Rough-tailed geckos
- Common house geckos
- Reticulated Geckos
- Mediterranean Geckos
- Texas banded geckos
Sources
- Wikipedia, Available here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gekkota
- Live Science, Available here: https://www.livescience.com/60242-gecko-facts.html
- News BBC, Available here: http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/1689313.stm
- National Geographic Kids, Available here: https://kids.nationalgeographic.com/animals/reptiles/facts/gecko#
- Pets on Mom, Available here: https://animals.mom.com/colors-geckos-2093.html
- Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/gecko
- Treehugger, Available here: https://www.treehugger.com/surprising-facts-about-geckos-4864284#
- National Geographic, Available here: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/article/151024-animal-behavior-lizards-reptiles-geckos-science-anatomy
- Inside Science, Available here: https://www.insidescience.org/news/how-geckos-run-water
- Smithsonian’s National Zoo & Conservation Biology Institute, Available here: https://nationalzoo.si.edu/animals/giant-leaf-tailed-gecko
- Pethelpful, Available here: https://pethelpful.com/reptiles-amphibians/Natural-Habitat-of-the-Leopard-Gecko
- Most New Zealand, Available here: https://mostnewzealand.com/pregnant-geckos.html
- JRank Science & Philosophy Encyclopedia, Available here: https://science.jrank.org/pages/2938/Geckos.html#
- Reptiles Magazine, Available here: https://www.reptilesmagazine.com/which-gecko-species-is-right-for-you/