Cuttlefish
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/cuttlefish-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/cuttlefish-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/cuttlefish.jpg”);
}
}
Found throughout the world’s oceans!
Cuttlefish Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Mollusca
- Class
- Cephalopoda
- Order
- Decapodiformes
- Family
- Sepiida
- Scientific Name
- Sepiida
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
Cuttlefish Conservation Status
Cuttlefish Facts
- Main Prey
- Crab, Shrimp, Fish
- Distinctive Feature
- Long body shape and large eyes
- Habitat
- Coastal and deeper waters
- Predators
- Fish, Sharks, Cuttlefish
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Average Litter Size
- 200
- Favorite Food
- Crab
- Common Name
- Cuttlefish
- Number Of Species
- 120
- Location
- Worldwide
- Slogan
- Found throughout the world’s oceans!
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/cuttlefish3.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the Cuttlefish images!
Equipped with flexible tentacles, ink production capabilities, and a keen intelligence, the cuttlefish is a remarkable creature of the sea.
Despite the name, it is not really a fish at all, but a type of cephalopod. This puts it in the same class as the squid, nautilus, and octopus. It is often said that the cephalopods resemble aliens on Earth in the sense that it’s a remarkably intelligent but very different type of lifeform from us. They last shared a common ancestor with land animals some hundreds of millions of years ago.
5 Incredible Cuttlefish Facts
- All cuttlefish feature a thick internal shell called a cuttlebone, from which the name obviously derives. The cuttlebone is composed of the mineral aragonite with calcium, carbon, and oxygen atoms.
- This creature evolved 21 million years ago in the Miocene Epoch. Its ancestor probably came from an extinct cephalopod order known as the belemnitida. Unlike many modern cephalopods, the belemnitida had a full skeleton.
- The ink of the cuttlefish has been used as both dye and medicine throughout human history.
- With its curvy W-shaped eye, this fish has the remarkable ability to perceive extremely high contrasts in light that is normally invisible to the human eye. Contrast is the difference between white and dark light. As a tradeoff, however, the cuttlefish is unable to see color.
- A few cuttlefish species are able to produce a toxic venom to ward off predators.
Want more cuttlefish facts? Check out ‘10 Impressive Cuttlefish Facts‘ that has much more on their color changing and intelligence!
Cuttlefish Scientific Name
The scientific name of the cuttlefish is Sepiida, which refers to the entire order. The term Sepiida derives from the Greek and Latin word sepia, which is a reference to the name of the dye produced from its ink. Sepia is now the English word for a type of reddish brown color.
Cuttlefish Species
There are approximately 100 species of cuttlefish still alive. Here is just a small sample of them:
- Common Cuttlefish: As the name implies, this is one of the most widespread species of cuttlefish in the world. Measuring no more than 19 inches in size, the common cuttlefish primarily inhabits the waters of the Mediterranean Sea, North Sea, and Baltic Sea.
- Pharaoh Cuttlefish: This is a large species of cuttlefish that inhabits the Pacific region between Japan and Australia and as far west as the Red Sea. It is commonly hunted in the Philippines, India, and Persia for food.
- Flamboyant Cuttlefish: This species is well-named for the rather bright and exuberant pattern of colors on its mantle. Endemic to the waters of Australia and Southeast Asia, this species produces an acid that makes it unsuitable for human consumption. This small species is only a few inches in length.
Cuttlefish Appearance and Behavior
One look at this fish will tell you that it’s a true cephalopod. Its body resembles the closely related squid and octopus, except it is much smaller in size. The smallest cuttlefish species only measure an inch or two. The largest species is the Australian giant cuttlefish, which can measure up to 20 inches and weigh about 23 pounds.
The cuttlefish is characterized by the gas-filled internal cuttlebone (which actually provides buoyancy and control rather than protection), a long and relatively flat body, a parrot-like beak, and long fins running along both sides. It also features eight arms and two tentacles containing a series of suction pads that are used to capture prey. The arms and tentacles can be withdrawn into two pouches at any time. Cuttlefish are also one of the few animals that have multiple hearts. In total they have three different hearts!
The cuttlefish moves at incredible speeds through the water via jet propulsion. It does this by sucking in water through a body cavity and then expelling the water out with its powerful muscles. The fins allow it to maneuver at high speeds. This method of transportation is necessary to evade very fast and agile predators.
Another incredible ability is the color change. The cuttlefish body contains millions of small pigment cells called chromatophores that allow the creature to alter its color and pattern at any time. When the cuttlefish flexes its muscles, the pigment is released into the outer skin to blend in with the surroundings. This is used for many purposes such as to camouflage itself, attract mates, and communicate with other cuttlefish. The color change may also serve the purpose of stunning prey with quick and debilitating flashes.
The cuttlefish has a rather large brain to body size compared to most invertebrate. Studies reveal that it is capable of various degrees of problem solving and object manipulation. This intelligence may be necessary to manipulate the incredibly complex tentacles and arms, which contain a large number of neurons like the brain.
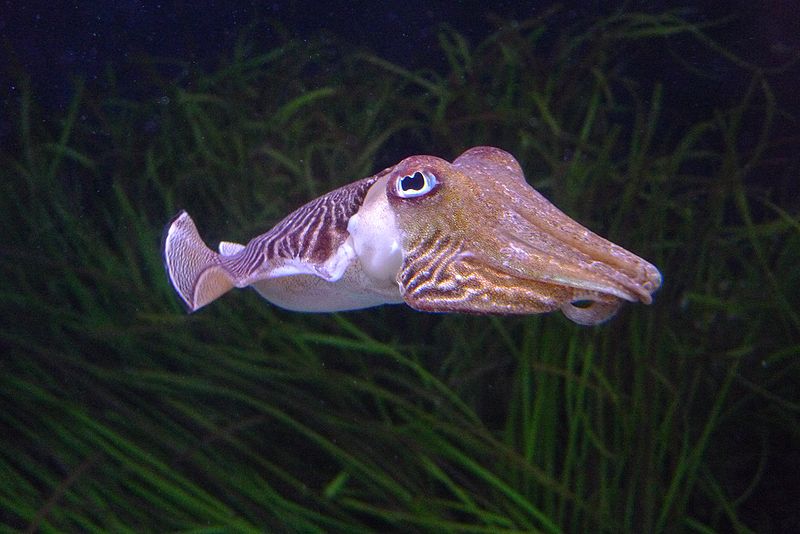

Cuttlefish Distribution, Population, and Habitat
The cuttlefish is found throughout the oceans and seas of Europe, Africa, Asia, and Australia, but it is largely absent from the Americas. Throughout its natural range, this animal exhibits a yearly migratory pattern. In the summer, it inhabits the coastal waters in tropical or temperate regions. In the winter, it migrates to the deeper water of the oceans.
According to the IUCN Red List, which keeps track of the conservation status for many animals, data about population numbers is unfortunately not available for many cuttlefish species. When data is known, almost all species are categorized as least concern. Only a few species are at risk of endangerment.
Cuttlefish Predators and Prey
The cuttlefish has a rather simple diet consisting of fish, crab, and other molluscs. Larger cuttlefish also have the tendency to prey on juveniles or smaller species of cuttlefish. They use the beak located in the mantle between their arms to crack open the tough shells of their prey and feast on the tasty meat within. For a full analysis of what cuttlefish eat, we’ve published ‘What Do Cuttlefish Eat? The 10 Favorites of Their Diets.’
Due to its small size, the cuttlefish is hunted by all kinds of larger fish, dolphins, seals, birds, and other molluscs. But it does have several defensive mechanisms to help it survive. When threatened, the cuttlefish can release a cloud of ink to confuse predators and then make its daring escape. The speed is a distinct advantage over slower predators. The venom of some species also provides a useful defense.
Cuttlefish Reproduction and Lifespan
The cuttlefish has a very organized and straightforward reproduction cycle. During the breeding season, which lasts between the spring and summer of every year, the male puts on a brilliant mating display in which it transforms colors and patterns to impress the female. Once accepted, the male uses its modified arm to transfer sperm into the female’s mantle near the mouth to fertilize the eggs.
The impregnated female then deposits some 100 to 300 eggs at a time on rocks, seaweed, or some other surfaces. She alone watches over the eggs until they hatch after a period of one or two months on average. Shortly after their duties are fulfilled, both the male and female will die, ceding the way to the next generation. Cuttlefish reach sexual maturity after a period lasting up to 18 months, but their life expectancy is a mere one or two years of age. This means they tend to perish after only a single mating season.
Cuttlefish in Fishing and Cooking
The cuttlefish is a popular dish throughout the coastal regions of Europe and East Asia. It is prepared in various ways: breaded, deep fried, grilled, or shredded. The ink can be served alone or with the rest of the cuttlefish as well.
View all 157 animals that start with C
Cuttlefish FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What do cuttlefish eat?
The cuttlefish regularly consumes all kinds of fish, crab, and molluscs. It is not shy about consuming other species of cuttlefish as well.
What phylum do cuttlefish belong to?
The cuttlefish belongs to the phylum of mollusca. This is the second largest phylum of invertebrates (meaning animals that lack a spine) in the world. Approximately 85,000 living species of molluscs have been discovered in the major classes of snails, cephalopods, and bivalves.
Where do cuttlefish live?
The cuttlefish inhabits the coastal region of Europe, Africa, Asia, and Australia. They migrate out to the deep waters in the colder seasons.
Are cuttlefish dangerous to humans?
The humble cuttlefish poses almost no danger to humans. A few species can inject venom into their victims, but due to minimal contact with humans, this is not a significant risk.
Can you eat cuttlefish?
The cuttlefish is considered to be a delicacy in many parts of the world. Except for a few species which contain harmful compounds, almost all cuttlefish can be eaten.
What Kingdom do Cuttlefish belong to?
Cuttlefish belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do Cuttlefish belong to?
Cuttlefish belong to the class Cephalopoda.
What phylum to Cuttlefish belong to?
Cuttlefish belong to the phylum Mollusca.
What family do Cuttlefish belong to?
Cuttlefish belong to the family Sepiida.
What order do Cuttlefish belong to?
Cuttlefish belong to the order Decapodiformes.
What type of covering do Cuttlefish have?
Cuttlefish are covered in Smooth skin.
What are some predators of Cuttlefish?
Predators of Cuttlefish include fish, sharks, and cuttlefish.
What are some distinguishing features of Cuttlefish?
Cuttlefish have long bodies and large eyes.
How many babies do Cuttlefish have?
The average number of babies a Cuttlefish has is 200.
What is an interesting fact about Cuttlefish?
Cuttlefish are found throughout the world’s oceans!
What is the scientific name for the Cuttlefish?
The scientific name for the Cuttlefish is Sepiida.
How many species of Cuttlefish are there?
There are 120 species of Cuttlefish.
How do Cuttlefish have babies?
Cuttlefish lay eggs.
What’s the difference between cuttlefish and squid?
Cuttlefish are much smaller than squid, and they also have fans on either side of their head, which squids don’t typically have. Read all about their differences here!
How to say Cuttlefish in …
Sépie (řád)
Tintenfische
Cuttlefish
Sepio
Sources
- Britannica, Available here: https://www.britannica.com/animal/cuttlefish
- Thought Co., Available here: https://www.thoughtco.com/facts-about-cuttlefish-2291937
- PBS (1970) https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/camo/anat-nf.html Jump to top