African Clawed Frog
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/african_clawed_frog-400×300.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 641px) and (max-width: 920px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/african_clawed_frog-470×370.jpg”);
}
}
@media only screen and (min-width: 921px) {
.jumbotron {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/african_clawed_frog.jpg”);
}
}
A particularly ferocious amphibian!
African Clawed Frog Scientific Classification
- Kingdom
- Animalia
- Phylum
- Chordata
- Class
- Amphibia
- Order
- Anura
- Family
- Pipidae
- Genus
- Xenopus
- Scientific Name
- Xenopus laevis
Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals.
African Clawed Frog Conservation Status
African Clawed Frog Facts
- Prey
- Small Fish, Insects, Spiders
- Name Of Young
- Tadpole
- Group Behavior
-
- Solitary
- Fun Fact
- A particularly ferocious amphibian!
- Estimated Population Size
- Abundant
- Biggest Threat
- Water pollution
- Most Distinctive Feature
- Clawed front toes
- Other Name(s)
- Platanna
- Incubation Period
- 4 – 5 days
- Age Of Independence
- 5 days
- Average Spawn Size
- 2,000
- Habitat
- Warm stagnant water with grassland
- Predators
- Snakes, Birds, Small Mammals
- Diet
- Carnivore
- Lifestyle
-
- Nocturnal
- Common Name
- African Clawed Frog
- Number Of Species
- 1
- Location
- eastern and southern Africa
- Slogan
- A particularly ferocious amphibian!
- Group
- Amphibian
This post may contain affiliate links to our partners like Chewy, Amazon, and others. Purchasing through these helps us further the A-Z Animals mission to educate about the world’s species..

Spiders that fly! Fish that walk! And 1000+ more incredible animals. Discover them all for FREE
.photo-gallery {
–margin: 0px auto 0px;
–padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px;
}
.gallery-link {
background-image: url(“https://a-z-animals.com/media/animals/images/original/african_clawed_frog7.jpg”);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
height: 500px;
justify-content: center;
text-align: center;
align-items: center;
display: flex;
border: 2px solid #000;
}
.gallery-link img {
height: 50%;
}
@media only screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.gallery-link {
height: 300px !important;
}
}
View all of the African Clawed Frog images!
African Clawed Frog Classification and Evolution
The African Clawed Frog is a large species of flat Frog that is primarily found dwelling at the bottom of lakes and rivers. The African Clawed Frog is also known as the Platanna and has a number of very unique features that mean it is specially adapted to its habitat. The African Clawed Frog is thought to have originated in South Africa, and is today found naturally across the African continent. The African Clawed Frog has also been introduced to the Americas and parts of Europe.
African Clawed Frog Anatomy and Appearance
The average adult African Clawed Frog grows to about 12 cm in length, and weighs around 200g. The African Clawed Frog is often a greenish, grey colour although other colours of the African Clawed Frog are not uncommon (such as albino). The colour of the African Clawed Frog’s skin, along with its mottled pattern, gives it more camouflage from hungry predators. They have a line of stitch-marks along either side of their bodies which act as sense organs to detect prey in the surrounding water. Their eyes and nose are located on top of the head enabling them to see and breathe but without being too visible.
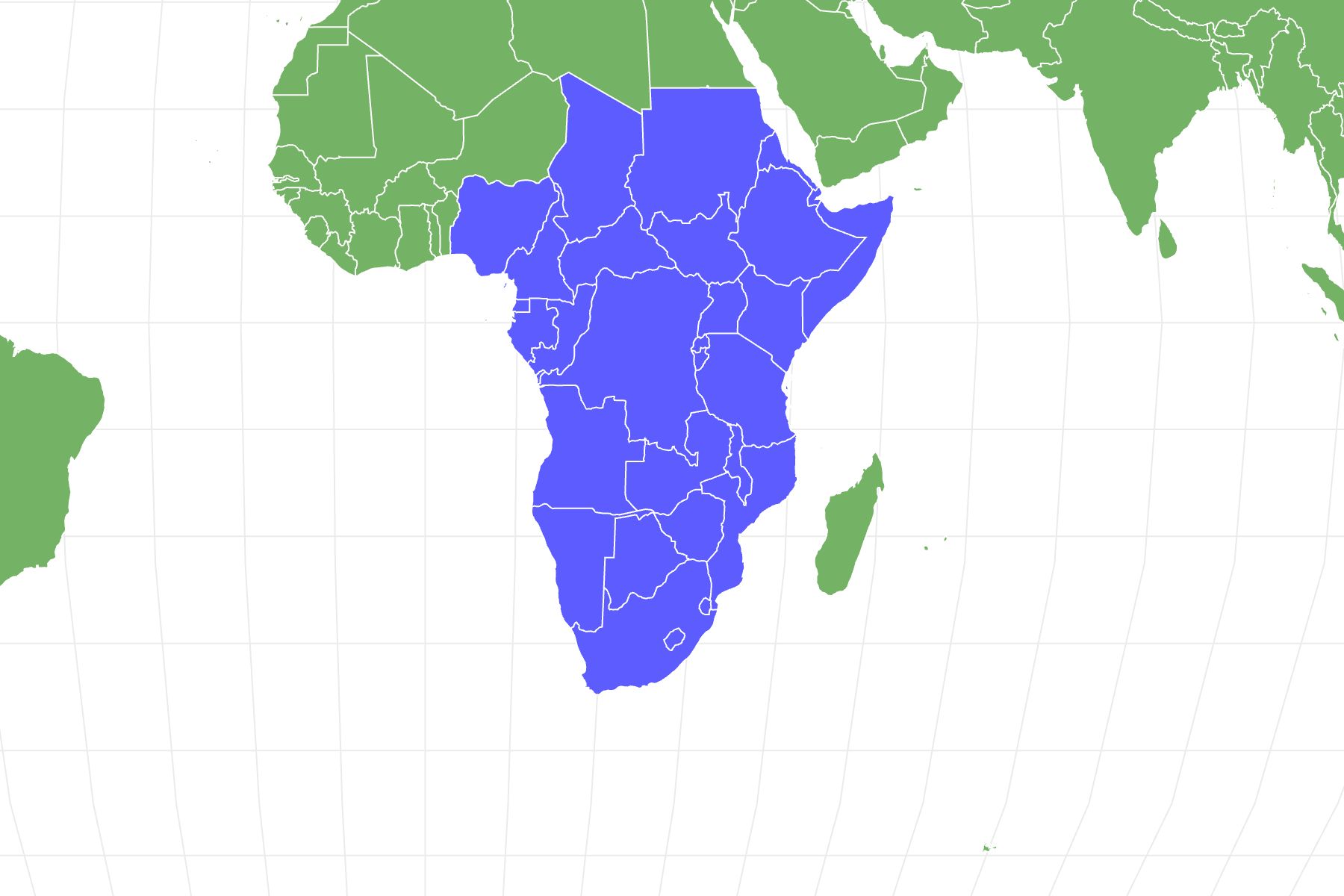
African Clawed Frog Distribution and Habitat
The African Clawed Frog is most commonly found in eastern and southern Africa, along the African Rift Valley where they prefer stagnant waters to fast-flowing streams. African Clawed Frogs are bottom-dwelling animals and will only leave the safety of the water if they are forced to migrate. They inhabit warm shallow creeks and rivers during the summer and move into the flooded forests during the rainy season. Due to introduction by Humans, the African Clawed Frog can now be found in numerous freshwater habitats outside of Africa where they can be a very invasive species.
African Clawed Frog Behaviour and Lifestyle
The African Clawed Frog spends its whole life in water, except for poking its head up to the surface from time to time to breathe. The African Clawed Frog can swim at astonishing speeds sideways, backwards, forwards, up and down, and in all other directions. It is a ferocious predator and once food has been spotted, the African Clawed Frog then catches its prey using its claws, which shovel it into the African Clawed Frog’s mouth. The African Clawed Frog has evolved very successfully as a bottom-dwelling animal, which means that it has greater protection from predators and a better choice of food.
African Clawed Frog Reproduction and Life Cycles
Female African Clawed Frogs are often nearly double the size of the males, and are able to reproduce more than once a year. After mating, the female African Clawed Frog can lay thousands of eggs at a time on an underwater object, which are held together in the water by a jelly-like substance. After hatching, the African Clawed Frog tadpoles begin their life in the water until they grow legs and are able to venture out onto the river banks if need be. The African Clawed Frog is known to have a long lifespan for small aquatic animals, and can live to around 5 to 15 years in the wild. Some adult African Clawed Frogs have been recorded to live to nearly 30 years old in captivity.
African Clawed Frog Diet and Prey
The African Clawed Frog is a carnivorous animal and an apex predator within its underwater environment. The African Clawed Frog’s main food is Water Bugs and small Fish but the African Clawed Frog is also known to eat its own skin whenever it is shed. African Clawed Frogs also hunt other small invertebrates such as Insects, Spiders and Worms, which it scoops into its mouth using its clawed front feet. African Clawed Frogs in captivity have a much less varied diet which primarily consists of Worms.
African Clawed Frog Predators and Threats
Due to its small size, the African Clawed Frog has a number of natural predators within its native environment, that occur both in and out of the water. Small mammals including Rodents, Cats and Dogs, and numerous Birds and Reptiles, all prey on the African Clawed Frog, but herons are their most common threat. By living on the muddy bottoms of lakes and rivers, the African Clawed Frog can remain safely hidden for much of the time, and only its eyes and nose appear above the water-line when it surfaces. Although not as vulnerable as many other amphibians, the African Clawed Frog is also being threatened by water pollution.
African Clawed Frog Interesting Facts and Features
The African Clawed Frog is named for their unique feet, as their hind feet are webbed but their front legs have clawed toes instead, which are used to help shovel food into their mouths. In the 1940s the African Clawed Frog became the world’s first pregnancy test for Humans, which although barbaric, has led to them being found worldwide today. The African Clawed Frog has also been a popular test subject for scientific research for in general. They are known to be highly aggressive animals and particularly ferocious amphibians.
African Clawed Frog Relationship with Humans
Over the years, Humans have managed to find a number of uses for the African Clawed Frog in our day to day lives. The most notable (and probably cruellest) of these practises was the use of the African Clawed Frog females as a type of pregnancy test. The hormone produced by Human babies (passed on through the mother’s urine) known as HCG, induces ovulation in the female African Clawed Frog. Humans also use them in laboratories worldwide for research and teaching. Habitat loss and water pollution caused by people nearby is also having a drastic effect on African Clawed Frog populations.
African Clawed Frog Conservation Status and Life Today
Although the African Clawed Frog has been classified as being at Least Concern from imminent extinction, population numbers have fallen in certain areas due to deteriorating water quality. Elsewhere, African Clawed Frog populations around the world have often become non-native pests to the local plants and wildlife.
View all 127 animals that start with A
African Clawed Frog FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are African Clawed Frogs herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores?
African Clawed Frogs are Carnivores, meaning they eat other animals.
What Kingdom do African Clawed Frogs belong to?
African Clawed Frogs belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
What class do African Clawed Frogs belong to?
African Clawed Frogs belong to the class Amphibia.
What phylum to African Clawed Frogs belong to?
African Clawed Frogs belong to the phylum Chordata.
What family do African Clawed Frogs belong to?
African Clawed Frogs belong to the family Pipidae.
What order do African Clawed Frogs belong to?
African Clawed Frogs belong to the order Anura.
What type of covering do African Clawed Frogs have?
African Clawed Frogs are covered in Permeable Scales.
What genus do African Clawed Frogs belong to?
African Clawed Frogs belong to the genus Xenopus.
Where do African Clawed Frogs live?
African Clawed Frogs live in eastern and southern Africa.
In what type of habitat do African Clawed Frogs live?
African Clawed Frogs live in warm stagnant water with grassland.
What are some predators of African Clawed Frogs?
Predators of African Clawed Frogs include snakes, birds, and small mammals.
What is an interesting fact about African Clawed Frogs?
African Clawed Frogs are a particularly ferocious amphibian!
What is the scientific name for the African Clawed Frog?
The scientific name for the African Clawed Frog is Xenopus laevis.
What is the lifespan of an African Clawed Frog?
African Clawed Frogs can live for 8 to 15 years.
How many species of African Clawed Frog are there?
There is 1 species of African Clawed Frog.
What is the biggest threat to the African Clawed Frog?
The biggest threat to the African Clawed Frog is water pollution.
What is another name for the African Clawed Frog?
The African Clawed Frog is also called the platanna.
How fast is an African Clawed Frog?
An African Clawed Frog can travel at speeds of up to 5 miles per hour.
What do African Dwarf Frogs eat?
African Dwarf frogs can consume nearly anything they come across, and in the wild, they often prefer a mix of live prey and organic matter.
How to say African Clawed Frog in …
Drápatka vodní
Xenopus laevis
Krallenfrosch
African clawed frog
Xenopus laevis
Xenopus laevis
Dél-afrikai karmosbéka
Klauwkikker
Platana szponiasta
Xenopus laevis
Sources
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2011) Animal, The Definitive Visual Guide To The World’s Wildlife
- Tom Jackson, Lorenz Books (2007) The World Encyclopedia Of Animals
- David Burnie, Kingfisher (2011) The Kingfisher Animal Encyclopedia
- Richard Mackay, University of California Press (2009) The Atlas Of Endangered Species
- David Burnie, Dorling Kindersley (2008) Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Animals
- Dorling Kindersley (2006) Dorling Kindersley Encyclopedia Of Animals
- African Clawed Frog Threats, Available here: http://aquaticfrogs.tripod.com/id10.html
- African Clawed Frog Information, Available here: http://nationalzoo.si.edu/Animals/ReptilesAmphibians/Facts/FactSheets/Africanclawedfrog.cfm
- African Clawed Frog Anatomy, Available here: http://www.petstation.com/clfrog.html
- About Clawed Frogs, Available here: http://www.clawedfrogs.com/id1.html
- African Clawed Frogs, Available here: http://allaboutfrogs.org/info/species/clawed.html